MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 3 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 3
Which one of the following is an abiotic and renewable resource?
Which of the following methods can be used to separate acetone and water from their mixture?
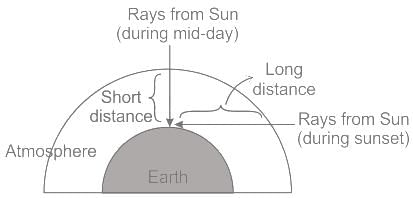
The redness in atmosphere at sunrise and sun-set is due to :
An object of 5 kg is lying at rest. Under the action of a constant force, it gains a speed of 3 m/s. The work done by the force will be _________.
Read the following statements and choose the correct option
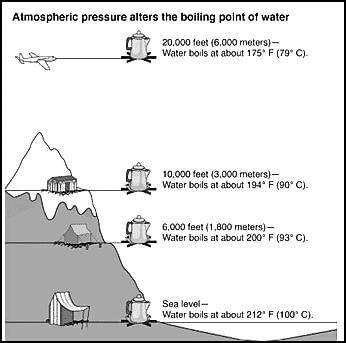
Assertion: Water boils easily at low altitude regions like sea shore.
Reason: Atmospheric pressure is less at lower altitudes.
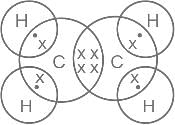
The electronic dot and cross structure of ethene is _______
Consider the following statement about science education:
"Only open ended questions work while teaching science"
Astronomical unit is the average distance between:
Due to excess of fertilizers and sewage a lot of nitrogen is produced in water bodies which causes excessive growth of algae & depletion in oxygen levels, what is the name of this process?
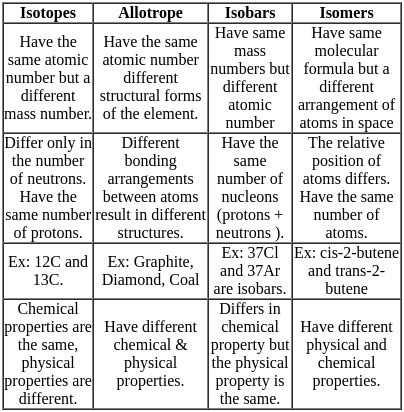
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) S8 is a molecule.
(ii) 03 is compound.
(iii) N3- is an anion.
(iv) Co is an element.
A rotating wheel changes angular speed form 1800 rpm to 3000 rpm in 20 s. What is the angular acceleration assuming it to be uniform?
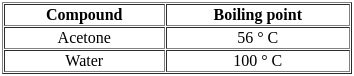
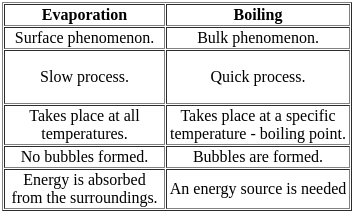
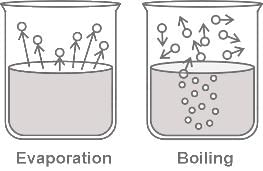
The difference between boiling and evaporation is that
A wooden box of mass 2 kg and dimensions (30 cm × 15 cm × 10 cm) is placed on a table with sides 30 cm and 10 cm touching the tabletop. Which one of the following is the approximate pressure exerted on the table?
One atmospheric pressure is equivalent to
a) 76 cm of Hg
b) 56 cm Hg
c) 60 cm of Hg
d) 70 cm of Hg
Which of these diseases is caused due to an extra 21st chromosome?



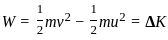
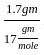 = 0.1 mole
= 0.1 mole