MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 5 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 2 Science Mock Test - 5
Pancreatic juice contains which enzyme that breaks down emulsified fats?
Which of the following is a part of celestial objects?
I. Stars
II. Planets
III. Moon
Which out of the following is not a function of vacuole?
______ validity is an important criterion since it helps the student in ‘learning to learn’ science.
The vitamin which is effective in blood clotting is _________.
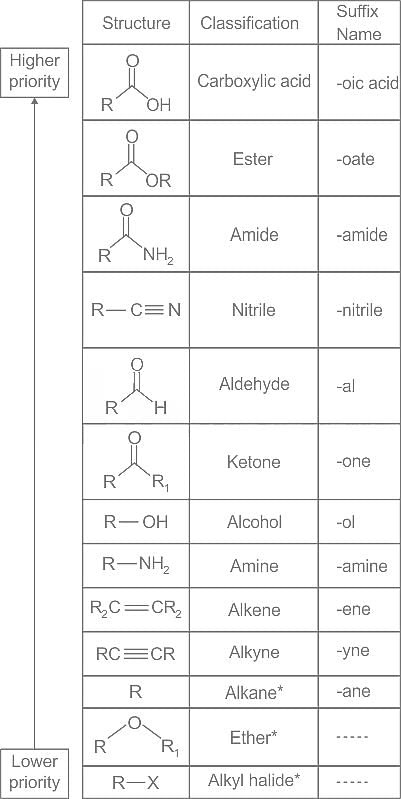
The IUPAC name for
CH3 – CO – CH2 – CH2 – COOH is:
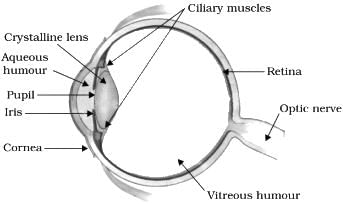
Which of the following is responsible for most of the refraction of light rays entering our eyes?
Match List - I with List - II.
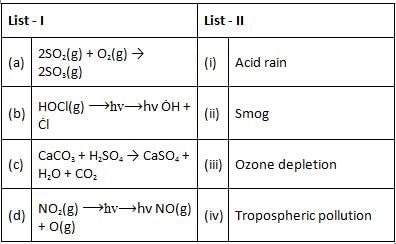
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
The geographical phenomena of hot springs primarily occur due to which among the following?
1. Conduction
2. Convection
3. Radiation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Which of the following is not true regarding lecture method while teaching science?
From the options given below, select the option which DOES NOT contain correct isotopes of the elements.
A. O --> 16O8 , 17O8 , 18O8
B. C --> 13C6 , 14C6 , 15C6
C. S --> 31S16 , 32S16, 33S16, 34S16
D. U --> 233U92 , 235U92 , 238U92
In the context of the human nervous system, which part of the neuron receives the information?
An element “X” has a Z value equal to 17 and mass number equal to 37. What is the number of neutrons present in its nucleus?
Acidic solutions in water conduct electricity because they produce ________.
Which of the following is NOT a postulate of Dalton's Atomic Theory?
An electric iron of 1250 W is used for 3 h per day. The energy consumed in one day by the electric iron is _______ units.
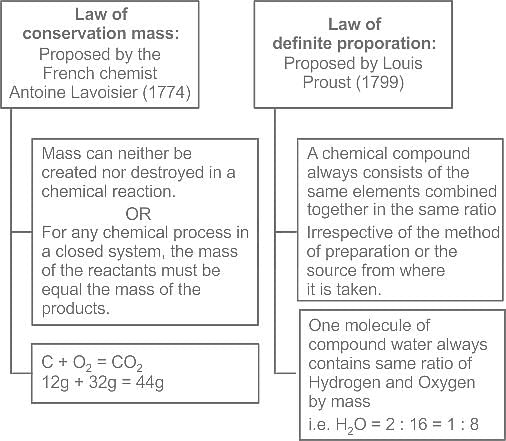
Which of the following reactions is not correct according to the law of conservation of mass.



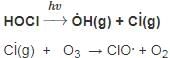
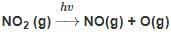
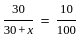
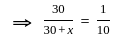
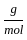
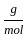
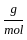 +2 mol x16
+2 mol x16 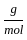 )
)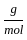 +16
+16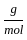 )
)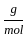
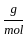
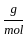
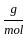 +8 x1
+8 x1 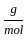 ) +(2 mol x16
) +(2 mol x16 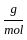 )
)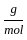 +2 mol x16
+2 mol x16 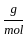 )+(2 mol x1
)+(2 mol x1 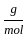 +1 mol x16
+1 mol x16 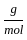 )
)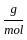
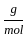
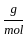 ) +(10 mol x16
) +(10 mol x16 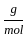 )
)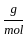 +10 mol x16
+10 mol x16 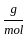 )
)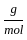
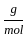
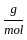
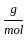 +4 mol x1
+4 mol x1 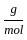 ) +(4 mol x16
) +(4 mol x16 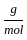 )
)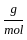 +2 mol x16
+2 mol x16 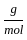 )+2 (2 mol x1
)+2 (2 mol x1 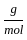 +1 mol x16
+1 mol x16 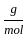 )
)