MPTET Varg 3 Mock Test - 5 - MPTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPTET Varg 3 Mock Test - 5
The personality and intelligence quotient of Mohan are different from Sohan. What are these differences called ?
Limitation(s) of Kohlberg's theory of moral development include(s):
A. underestimating young children's moral reasoning abilities
B. no limitations have been successfully identified
C. basing his theory primarily on interviews of males as subjects
Assertion (A): A teacher should avoid the errors made by students on a given task in teaching-learning process.
Reasoning (R): Considering errors on given task will demotivate students and it is also less meaningful to understand errors on teaching-learning process.
__________ advocates for the educational structure that strikes a balance between delivering knowledge while also taking into account the interests and experiences of the student
In the context of the role of heredity and environment in personality development, which of the following is true?
Sudden appearance of a response after a period of extinction is known as:
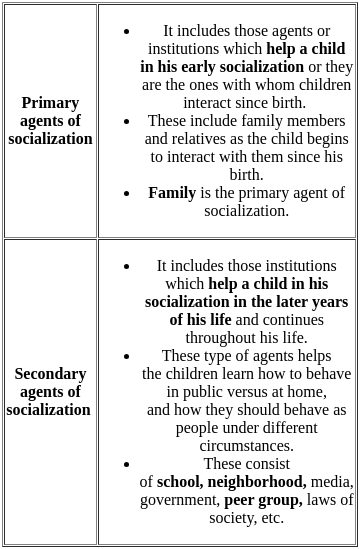
Which of the following is least suitable to mention under the "agents of socialization" in the context of socialization?
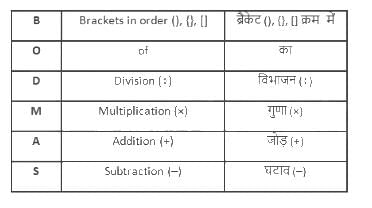
What will be the value of 6.8 × 4.8 ÷ 9.6 × 1.2 - 1.4?
Tall shape of mathematics, mentioned in NCF 2005 refers to
Which one of the following methods is not suitable to teach mathematics?
Evaluation in mathematics is necessary as it helps in:
Which of the following soils is not found in Madhya Pradesh?
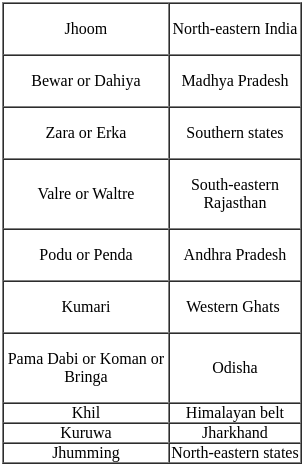
"Slash and burn" agriculture is a type of ____________.
Consequent to the launch of 'Swachh Bharat Abhiyan', India Railways had launched ________ to achieve the vision of Clean India by 2nd Oct 2014.
भाषा कौशलों के दक्षता के साथ शुद्ध प्रयोग में मुख्य भूमिका होती है-
कवि जयदेव का 'वसन्त चित्रण' सुन्दर है, पर मनोहर नहीं, क्योंकि
Dr. Kalam feels that India should be strong in _______.
Indians did not react violently to foreign invasions because _______.
Who has been termed as the father of nuclear material?
What would be the effect of global warming on the world?



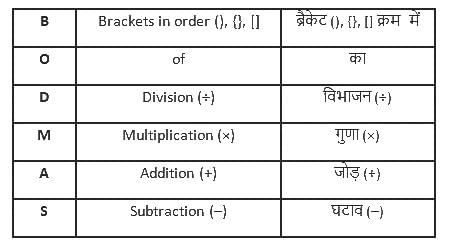
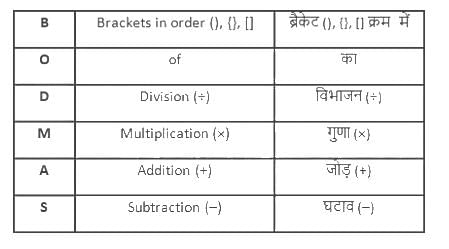
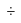 {(–2)
{(–2)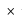 (–8)}]
(–8)}]