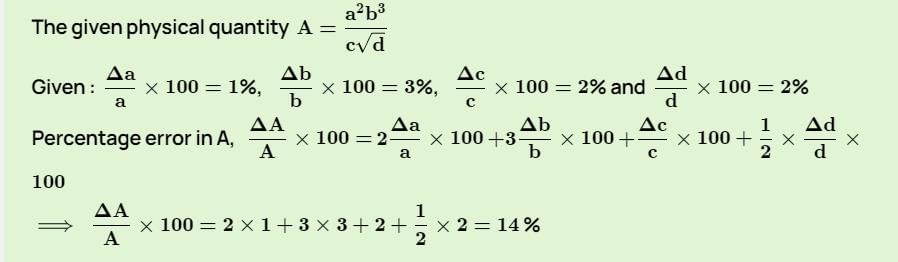DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 10 - DSSSB TGT/PGT/PRT MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test DSSSB PGT Mock Test Series 2025 - DSSSB PGT Physics Mock Test - 10
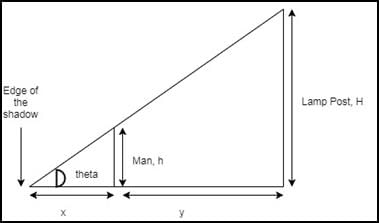
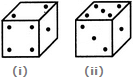
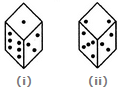
Three different positions X, Y and Z of a dice are shown in the figures given below. Which number lies at the bottom face in position X?
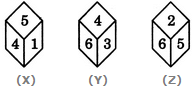

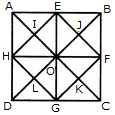
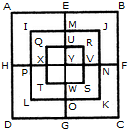
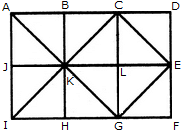
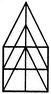
Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.

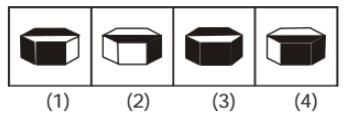
In each of the following questions, you are given a figure (X) followed by four alternative figures (1), (2), (3) and (4) such that figure (X) is embedded in one of them. Trace out the alternative figure which contains fig. (X) as its part.
Question - Find out the alternative figure which contains figure (X) as its part.
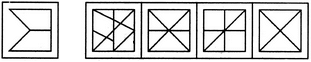 (X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
(X) (1) (2) (3) (4)
In each of the following questions, you are given a figure (X) followed by four alternative figures (1), (2), (3) and (4) such that figure (X) is embedded in one of them. Trace out the alternative figure which contains fig. (X) as its part.

Two positions of a cube are shown below. When the number 4 will be at the bottom, then which number will be at the top?
Statements: All tables are chair. Some plates are table. All glasses are plates.
Conclusions: 1) All glasses are chairs. 2) Some glasses are table 3) All plates are chairs.
Yash starts from a point A and moves 3 m straight then take a right turn and walk 4 m, again take a left turn and walk 5m. Finally he takes a left turn and walk 4m now he is facing north, so in which direction he starts.
Two positions of a dice are shown below: When 2 is at the bottom, what number will be at the top?
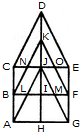
How many triangles and parallelograms are there in the following figure?
If STUDENT is written as RRTBDLS, how will OFFICER be written?
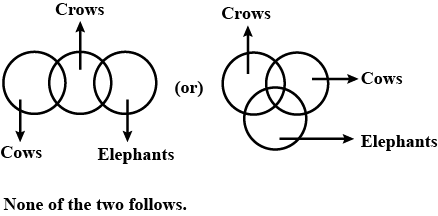
Statements:
Some cows are crows.
Some crows are elephants.
Conclusions:
1. Some cows are elephants.
2. All crows are elephants.
Ram goes 10 m east, then take a right turn and walk 15m and again take a right turn and walk 20m. Calculate the approximate distance of ram from starting point and in which direction he is now from starting point.
If a Paper (Transparent Sheet ) is folded in a manner and a design or pattern is drawn. When unfolded this paper appears as given below in the answer figure. Choose the correct answer figure given below.
Which one of the four boxes given below is created by folding the given key design in the question figure?
Question Figure
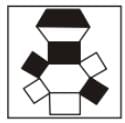
Answer Figure
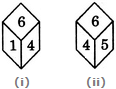
Two positions of a dice are shown below. When number 1 is on the top, what number will be at the bottom?
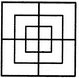
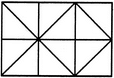
Count the number of squares in the given figure.
If a and b are two physical quantities having different dimensions then which of the following can denote a new physical quantity
Two physical quantities whose dimensions are not same, cannot be :
The number of significant figures in the distance of one light year , 9.4605 × 1015 m is:
The numbers of significant figures in 1.84 x10-27 kg are:
The multiplication of 10.610 with 0.210 upto correct number of significant figure is:
Numbers of significant figures in the volume of a cube of side 6.103 m are:
What is the percentage error in the physical quantity A if it is related to four other physical quantities a, b, c and d as 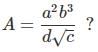 The percentage error in measurement of a, b, c and d are 1%, 3%, 2% and 2% respectively.
The percentage error in measurement of a, b, c and d are 1%, 3%, 2% and 2% respectively.
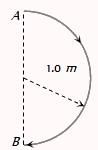
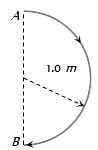
In 1.0 s, a particle goes from point A to point B, moving in a semicircle of radius 1.0 m (see figure). The magnitude of the average velocity is
If a body does not change its direction during the course of its motion, then ______.
A man of height h walks in a straight path towards a lamp post of height H with uniform velocity u. Then the velocity of the edge of the shadow on the ground will be:
Which position – time graph represents the motion of two objects that will never meet?