SSC Havaldar Session I Mock Test - 3 - SSC Havaldar MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - SSC Havaldar Session I Mock Test - 3
A box contains 90 blue balls, 110 red balls, 150 black balls and 50 pink balls. 50% of blue balls and 70% of red balls are taken away. What percentage of the initial number of balls are remaining in the box?
If 1 is added to the denominator of a fraction it becomes 1/2. If 1 is added to the numerator it becomes 1. The product of numerator and denominator of the fraction is
Reena borrowed Rs. 6,450 at 5 percent simple interest repayable in 4 equal installments. What will be the annual installment payable by him?
Sunny can complete a work in 15 days. If Bobby is 60% as efficient as Sunny, in how many days can Bobby complete the work?
A train traveling 60% faster than a car. Both start from point A at the same time and reach point B, 160 km away at the same time. On the way, the train takes 20 minutes for stopping at the stations. What is the speed (in km/hr) of the train?
The HCF of two numbers is 15 and their LCM is 300. If one of the number is 60, the other is :
Excluding stoppages, the average speed of a train is 120 kmph and including stoppages, it is 50 kmph. For how many minutes does the train stop per hour?
While working with 75% of its efficiency a pipe can fill a tank in 80 minutes. In how many minutes can the pipe fill the tank while working with 100% efficiency?
The L.C.M. of three different numbers is 120. Which of the following cannot be their H.C.F.?
The average monthly salary of the workers in a workshop is Rs. 8,500. If the average monthly salary of 7 technicians is Rs. 10,000 and the average monthly salary of the rest is Rs. 7,800, then the total number of workers in the workshop is
Amit can complete a work in 25 days and Punit can complete the same work in 20 days. Punit alone worked at it for 10 days and then left the work. In how many days will Amit alone complete the remaining work?
In a school having roll strength 299, the ratio of boys and girls is 8 : 5. If 25 more girls get admitted into the school, the ratio of boys and girls becomes
The product of two numbers is 1280 and their H.C.F. is 8. The L.C.M. of the number will be ?
A group of girls has an average weight of 34 kg. One girl weighing 58 kg leaves the group and another girl weighing 40 kg joins the group. If the average now becomes 33.4 kg, then how many girls are there in the group?
In a school 30% of the students play football and 50% of students play cricket. If 40% of the students play neither football nor cricket, what percentage of total students play both the games?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions besides.
Six person A, B, C, D, E and F sit around a triangular table. One person sits at each corner of the table facing away from the centre while one person sits at the middle of each edge facing toward the centre.
Three persons sit between C and D, who is not facing the centre. F sits third to the left of C. A is not an immediate neighbour of D. A sits second to the left of E.
Q. What is the position of B with respect to D?
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question:
How is ‘HEALTHY’ written in that code language?
Statement I: In a certain code language, EATING is written as HDRLLE.
Statement II: In a certain code language, REPLACE is written as PHNJDAH.
Directions: Read the given information carefully and answer the questions given beside:
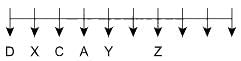
A certain number of people are sitting in a row watching F1 racing. All of them are facing towards the south direction. The distance between any two adjacent persons is the same.
The number of people sitting between A and C is the same as the number of people sitting between X and C. At most 25 people are sitting in a row. X is an immediate neighbour of D, who sits on one of the ends. Two people are sitting between A and Z. The number of people sitting between D and C is the same as the number of people sitting between C and Y. C sits fourth to the right of Z. The number of people sitting to the right of A is the same as the number of people sitting to the left of Z.
Q. Who among the following sits near A?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
In this pyramid number if: 11 22 31 : 12 21 32 :: 9 12 21 : ?
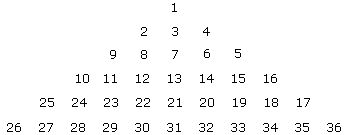
'Horse' is related to 'Hoof' in the same way as 'Eagle' is related to:
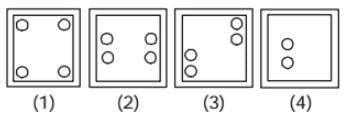
Direction: If a Paper (Transparent Sheet) is folded in a manner and a design or pattern is drawn. When unfolded this paper appears as given below in the answer figure. Choose the correct answer figure given below.
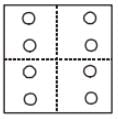
If a paper is folded in a particular manner and punch is made, when, unfolded this paper appears as given below in the question figure. Find out the manner in which the paper is folded and the punch is made from the answer figures given.
Question Figure
Answer figure
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
Race : Fatigue :: Fast : ?
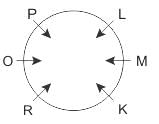
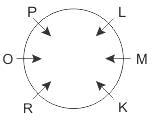
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions besides.
Six people P, L, R, K, O and M sit around the circular table facing the centre. There are two persons between P and K, who is to the right of P. R is adjacent to K and O. M, who is immediate right of K, is second to the left of P.
Q. Who among the following faces L?
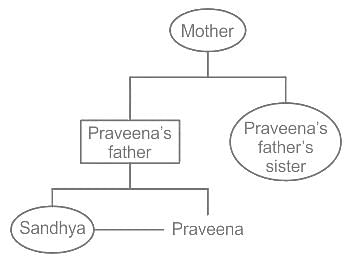
Sandhya is sister of Praveena. How is Praveena’s father’s sister’s mother related to Sandhya?
Directions to Solve
In each word of the following questions consists of pair of words bearing a relationship among these, from amongst the alternatives, pick up the pair that best illustrate a similar relationship.
Question -
Candle : Wick
Directions to Solve
Each of the following questions has a group. Find out which one of the given alternatives will be another member of the group or of that class.
Question -
Lock, Shut, Fasten
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
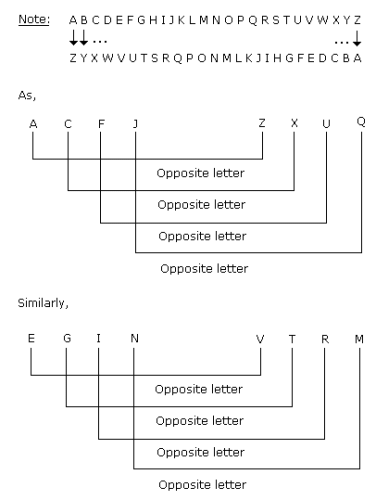
ACFJ : ZXUQ :: EGIN : ?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
16 : 56 :: 32 : ?
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
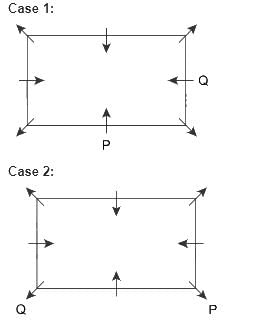
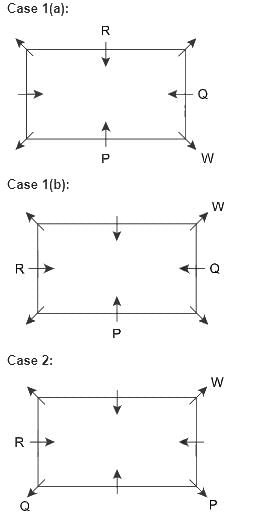
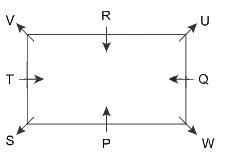
There are 8 persons, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V and W sitting around a rectangular table in such a way that four of them sit at four corners of the table while four sit in the middle of each of four sides. Persons who sit at the corners face outside the centre while those who sit in the middle of the side face inside.
Q sits second to the right of P. R sits third to the left of W. R faces inside. T sits third to the left of U. V sits second to the left of U. R is not an immediate neighbor of P.
Q. Who among the following sits second to the right of the one who sits opposite to R?


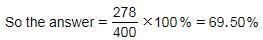
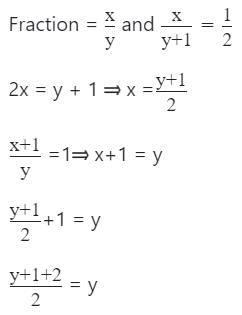

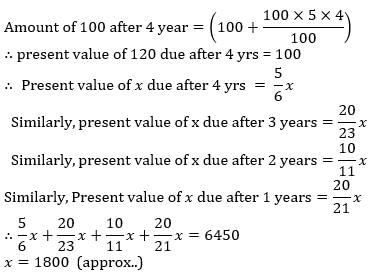
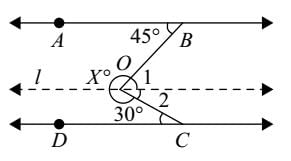
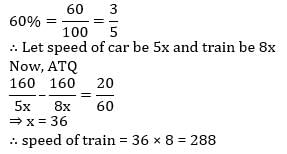
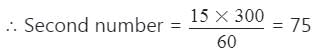
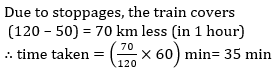
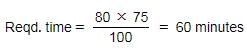
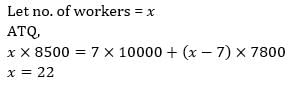
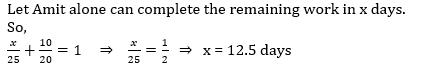
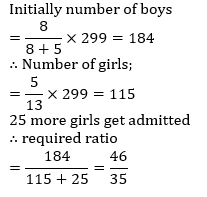
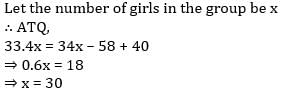
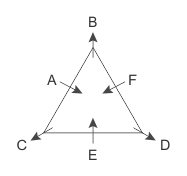
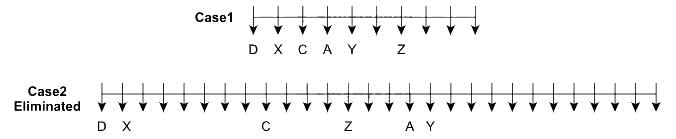 Hence, Case 1 is the final arrangement.
Hence, Case 1 is the final arrangement.