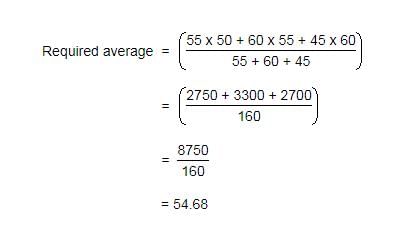Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 3 - UTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Uttarakhand D.El.Ed Mock Test - 3
Which city-state was the last to join the Kingdom of Italy in 1870?
The Great Pyramid of Giza, the oldest and largest of the three pyramids in Giza, is in which country?
What is the primary purpose of the Basic Structure Doctrine in the context of the Indian Constitution?
Which country won the first-ever Women's Hockey World Cup in 1974?
"Ashes" is a term associated with which sport rivalry?
The Jnanpith Award is presented by which organization?
Directions:
In each of the following questions, there are four sentences or parts of sentences that form a paragraph. Identify the sentence(s) or part(s) of sentence(s) that is/are correct in terms of grammar and usage (including spelling, punctuation, and logical consistency). Then, choose the most appropriate option.
A. It's some time since anyone accused GM of making a good move.
B.The company surrendered its title as the worlds top-selling carmaker
C.to Toyota this year, in part because GM underestimated drivers appetite
D.for leaner, greener cars—a desire filled spectacularly by Toyotas Prius.
Directons:
In each of the following questions, a part of the paragraph or sentence has been underlined. From the choices given to you, you are required to choose the one, which would best replace the underlined part.
The LHC is a magnificent engineering project, who's many "gee-whiz" features have been widely reported.
Which organization is the largest research and development body in India?
What is the significance of Purnagiri Temple in Champawat district?
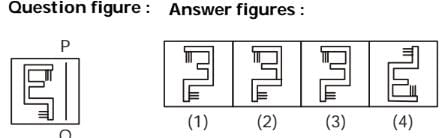
Which answer figure is the exact mirror image of the given question figure when the mirror is held from the right at PQ?
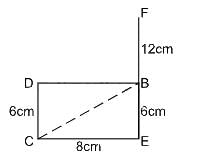
Direction: Study the following information and answer the given questions carefully.
Point B is 12 cm south of point F. Point C is 8 cm west of point E which is 18 cm away in the south direction with respect to F. B is east of D which is 6 cm north of point C.
Q. In which direction is point D with respect to point E?
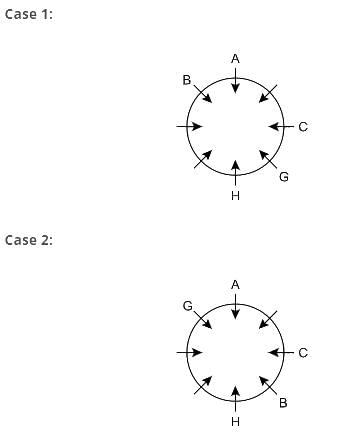
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the given questions besides.
Eight person A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H sit around the circular table facing towards the centre but not necessarily in the same order.
G sits opposite to B. One person sits between A and C, who sits second to the right of H. Both G and B do not sit immediate left of H. D sits second to the left of B. A doesn’t sit beside D. E doesn’t face C.
What is the position of G with respect to C?
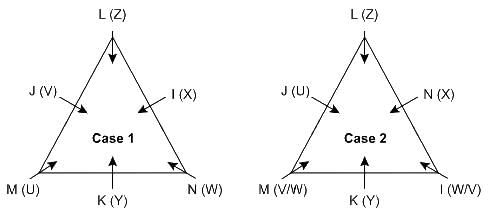
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question:
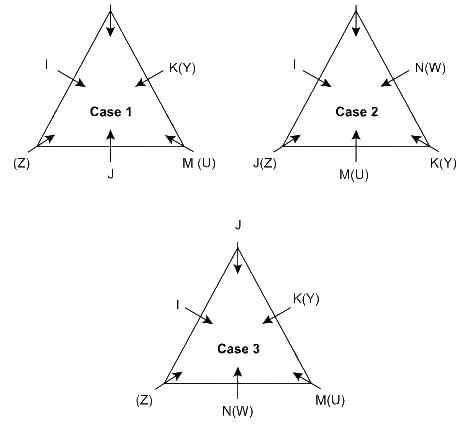
Six persons – I, J, K, L, M, and N have visited different countries – U, V, W, X, Y, and Z and are sitting around a triangular table facing the center, one person on each corner and one person on each side. Who sits 3rd to the left of the one who visited W?
Statement I: K, who visited Y sits 2nd to the right of J. Two persons sits between I and the one who visited U. L visited Z and sits on the corner, just to the right of the one who visited X. M sits immediate left of K. The one who visited W sits at a corner.
Statement II: The one who visited Z, sits just right of I at a corner. Two persons sit between J and N, who visited W. M visited U and sits just left of K who visited Y.
Directions: Each of the following consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question.
What is Rahul's rank in the class?
Statement I: Rahul's rank is 28 less than Monika's rank.
Statement II: Aditi's rank is 42 more than Rahul's rank. Monika's rank is 12 less than Aditi's rank.
Directions: In this type of questions, some particular words are assigned certain substituted names. Then a question is asked that is to be answered in the substituted code language.
If 'orange' is called 'butter', 'butter' is called 'soap', 'soap' is called 'ink', 'ink' is called 'honey' and 'honey' is called 'orange', which of the following is used for washing clothes ?
Direction: Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions
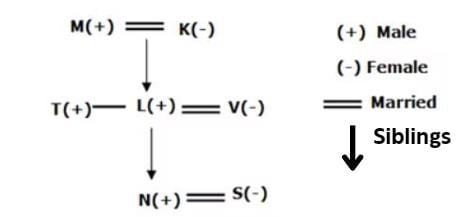
A family consists of seven members and three married couples. T is the paternal uncle of N who is married to S. V is the mother-in-law of S. L has only one kid. S and V are the same genders. K is the paternal grandmother of N. T is the son of M.
Q. How many female members are in a family?
If 1st March is Saturday, then 1st April will be
In the English Alphabet, which letter would be tenth to the right of eighteenth from right?
If the alphabet is written in the reverse order and every alternate letter starting with Y is dropped, which letter will be exactly in the middle of the remaining, letters of the alphabet.
What is the least number that can be added to 7218 make it a perfect square ?
The price of sugar is increased by 25%. If a family wants to keep its expenses on sugar unaltered, then the familiy will have to reduce the consumption of sugar by:
The ratio between two numbers is 7 : 11 and their LCM is 154. The first number is:
If the average marks of three batches of 55, 60 and 45 students respectively is 50, 55, 60, what is the average marks of all the students?
The ratio between the speeds of two trains is 7 : 8. If the second train runs 400 km in 4 hours, What is the the speed of the first train?
At what percentage per annum, will Rs. 10,000 amount to 17,280 in three years? (Compound Interest being reckoned)
A shopkeeper marks the price of an article at ₹ 250. Find the cost price if after allowing a discount of 20% he still gains 25% on the cost price.
A sold a watch to B at a gain of 5% and B sold it to C at a gain of 4%. If C paid Rs. 1,092 for it, the price paid by A is