Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (History) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Kerala SET Mock Test Series 2025 - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 1 (History)
The passage suggests that the term "Swaraj" within the Congress.
Consider the following statements about the scripts used in the Ashokan inscriptions :
1. Kharosthi script was written from left to right.
2. Brahmi script was written from right to left.
3. Greeks changed their horizontal writing direction from right-to-left to left-to-right for better efficiency.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Which among the following is not a book of Alexander Cunningham?
Assertion(A): The humanists of the Renaissance period believed that classical antiquity constituted a reservoir of excellence-literacy, intellectual, artistic and moral.
Reason(R): The vernacular translation of scriptures during the Renaissance hastened the process of secularisation of society.
In the context of the above statements which of the following is correct?
With reference to the Mauryan Art, consider the following statements.
Assertion(A):- The tradition of constructing pillars is very old and it may be observed that erection of pillars was prevalent in the Achamenian empire as well.
Reason(R):- The Mauryan pillars are very similar to the Achamenian pillars.
Below given are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R):
Assertion (A) : The Congress Boycotted the Simon Commission.
Reason (R) : The Commission did not have a single Indian member.
Codes:
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A):- In sharp contrast to Egypt and Mesopotamia, we do not find evidences of temple at the Harappan sites.
Reason(R):- However, indications of the priestly class being one of the ruling classes is quite evident.
How many Prime Ministers of India have been awarded Bharat Ratna till date?
consider the following statement about Junagarh Inscription :
1. The earliest specimen of the Kavya style was found in the Junagarh Inscription.
2. This inscription was made under the rule of Rudradaman 1.
3. This inscription was written in the Prakrit language.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
The most popular title of Ashoka is Devnamapriya Priyadarshi. In how many inscriptions, Ashoka's name 'Ashoka' is found?
Consider the following statements:
Assertion(A):- In sharp contrast to Egypt and Mesopotamia, the Harappan culture was poor in the artistic works made of stone.
Reason(R):- We do not come across any massive work of art in stone.
Lucknow pact was signed between Indian National Congress and _____________ in 1916?
With reference to the significance of the Revolt of 1857, consider the following statements:
1. It exposed the shortcomings in the Company's administration.
2. It brought India under politico-administrative unification.
3. It brought out in the open the grievances of people.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
Who was the first President of the All India Trade Union Congress established in 1920?
Match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
List I
I. Jawaharlal Nehru
II. Sardar Patel
III. J.B. Kripalani
IV. Dr. Rajendra Prasad
List II
a. States Committee
b. Provincial Constitution Committee
c. Steering Committee
d. Fundamental Rights Sub-Committee
Codes:
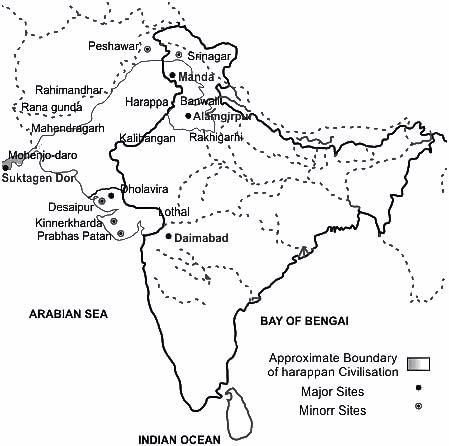
Sites of Indus Valley Civilization are given below:
A: Alamgirpur
B: Daimabad
C: Manda
D: Sutkangandor
Arrange them in (North→South→East→West) points.
Which of the following categories of land are mentioned in the Chola inscriptions?
1. Pallichchhandam
2. Shalabhoga
3. Vetti
4. Kadamai
5. Vellanvagai
Which of the following acts abolished the dyarchy in provinces?
Consider the following statements about the Pashupati Seal of the Harappan civilization:
i. It was found at Mohen-Jo-Daro.
ii. A human figure in Yogic posture is depicted on the seal.
iii. Marshall coined it, Proto Shiva.
iv. A pictographic inscription of six symbols is inscribed on the seal.
Choose the right answer:
Who was the founder of Prarthna Samaj?
Match List I with List II, and select the correct answer by using the codes given below the lists:
Author
I. Minaj-us-Siraj
II. Barani
III. Zia Nakshabi
IV. Alberuni
Work
a) Tutu Nama
b) Kitab-ul-Hind
c) Tarikh-i-Firoz Shahi
d) Tabaqat-i- Nasari
Codes:
In which year, collector in each District of Bengal was made responsible for settling the revenue and collecting it?