Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (Geography) - KTET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Kerala SET Mock Test Series 2025 - Kerala SET Paper 2 Mock Test - 5 (Geography)
As per the Census-2011, which of the following states recorded the lowest population?
Consider the following statement of computation of composite index and state which of these are true- i. The index has indicators like development vulnerabilities, exclusions etc.
ii. They compare country performances.
iii. They are not easy to interpret.
iv. It summarizes multi-dimensional realities.
When was the first modern paper mill of the country set up?
Any industry located in a rural area which produces any goods, renders any service with or without the use of power is known as ________
Consider the following statements about insolation and choose the correct option.
(A) Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth
(B) The amount and the intensity of the insolation vary during a day, in a second and in a year
(C) The amount of insolation increases from the equator towards the poles
In …………. Layer, the sun’s rays are is ionized
Which port was developed as a satellite port of Mumbai Port?
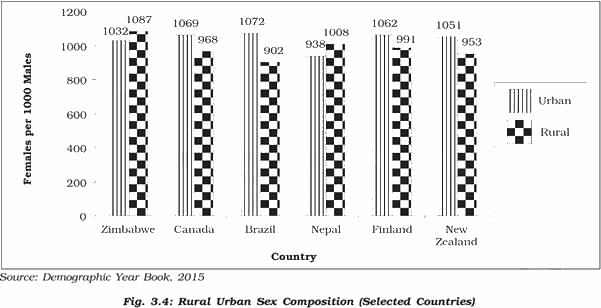
Consider the following statements with reference to most of the western countries:
1. Males outnumber females in rural areas.
2. Females outnumber the males in urban areas.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
Assertion- Richard Hartshorne attempts to capture difference between systematic geography and regional geography.
Reasoning- Regional geography is study of any two-dimensional area of interest.
Select the correct answer from options given below :
The winds that blow from the sea contain …………….. moisture
Which of the following is/are cold current/s ?
A. Peru Current
B. El Nino
C. California Current
D. Norwegian Current
Select correct answer from the codes given below :
According to the Radioactive Theory of Mountain Building, which of the following is not a factor that contributes to the formation of mountains?
The oldest rocks tend to be found __________.
a) Potholes and Plunge pools are found in the upper course of the river.
b) During the formation of meanders, the river does the erosional work on the convex bank and the depositional work on the concave bank.
c) A large number of tributaries joining the main river also lead to the formation of Deltas.
d) Braided stream is that which gets divided into several networks due to excess deposits on the river plain.
Which of the following statements are correct?