UPSSSC JE Civil Mock Test - 3 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPSSSC JE Civil Mock Test - 3
The compressive strength of a good Portland cement and standard sand mortar after 3 days of curing should not be less than
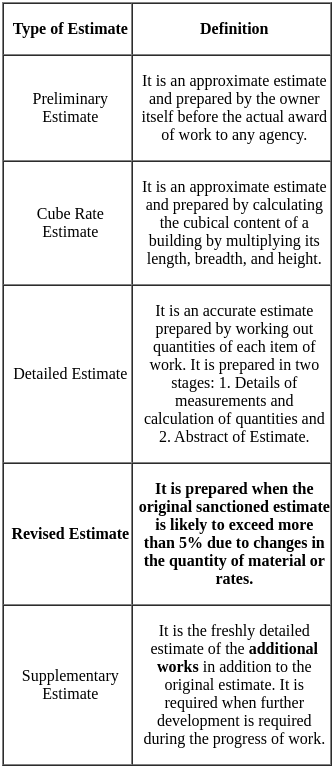
Which of the following statements is/are correct with respect to methods of valuation?
(i) In Rental method of valuation, the net income by way of rent is found out by deducting all outgoings from the gross rent.
(ii) In Development method of valuation, the building should be divided into four parts i.e. Walls, roofs, floor and doors, windows.
(i) In Rental method of valuation, the net income by way of rent is found out by deducting all outgoings from the gross rent.
(ii) In Development method of valuation, the building should be divided into four parts i.e. Walls, roofs, floor and doors, windows.
In a steel beam, when the width to thickness ratio of the compression flange is sufficiently large, local buckling of compression flange may occur even before extreme fibre yields. Such sections are generally known as
Under which of the following conditions does lateral torsional buckling need not be considered?
(i) The bending is about the minor axis of the section
(ii) The ratio between the moment of inertia about the major and minor axis is not high
(iii) The non-dimensional slenderness ratio is less than 0.4 in the case of major axis bending
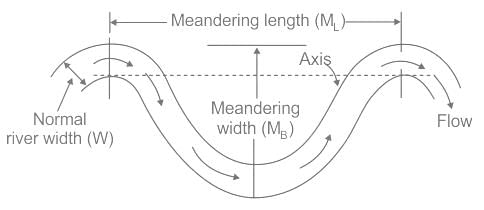
For a meandering alluvial river of width W in flood plain, the meander length is about:
A solid circular shaft carries a torque of 50 Nm. If the allowable shear stress of the material is 140 MPa, assuming factor of safety 2, the minimum diameter required for the shaft is
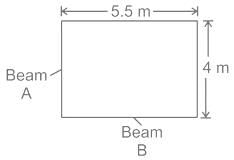
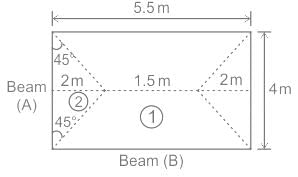
Determine the slab area of which load is acting on supporting beams A and B
Consider the following statements regarding torsion reinforcement:
1. It shall be provided at any corner where the slab is simply supported and both edges meetings at that corner.
2. It shall consist of top bottom reinforcement, each with layers of bars placed parallel to the sides of the slab and extending from the edges a minimum distance of one-fifth of the shorter span.
3. Torsion reinforcement equal to three quarters of the area required for maximum mid-span moment by edges over only one of which the slab.
Which of the above statements are correct?
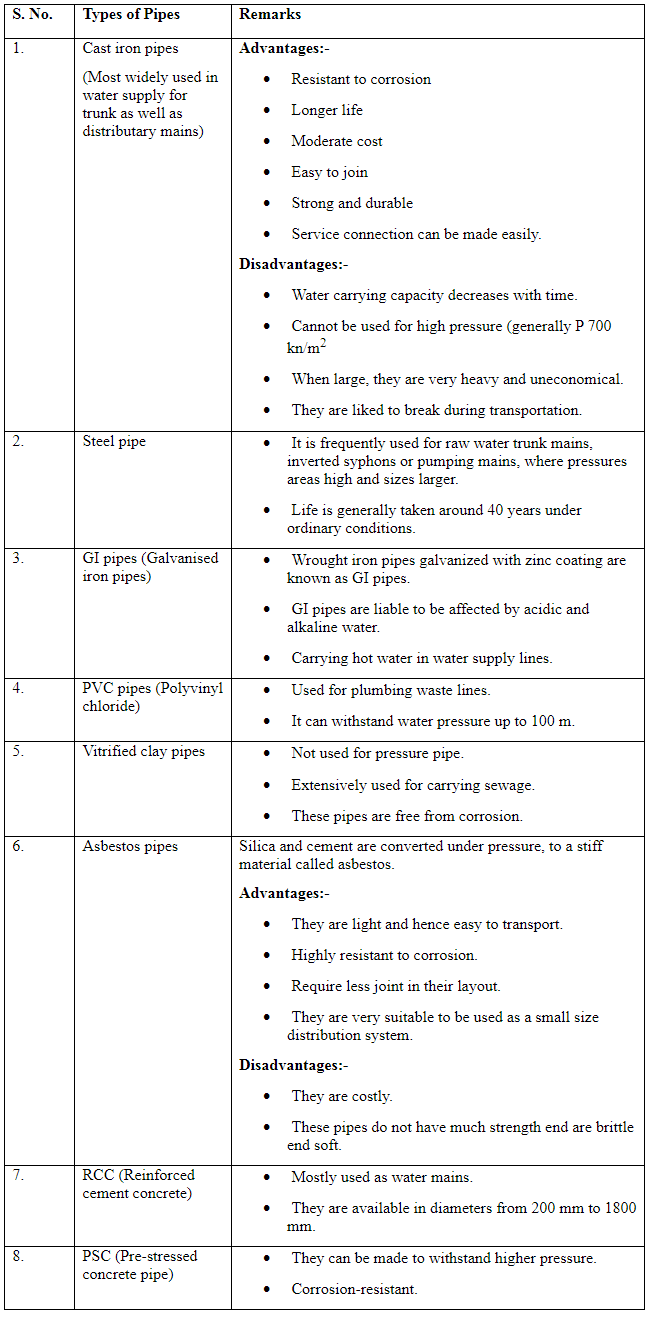
Consider the following statements in respect of cast iron pipes employed for water supply:
1. Easy to make joints
2. Strong and durable
3. Corrosion resistant
4. Long life
Which of the above statements are correct?
From the following statements, select the most appropriate statement:
Westergaard's analysis for stress computation within soil mass assumes.
For a given type of compaction, higher the compactive effort:
Which one of the documents is not attached to the contract agreement or bond which should be endorsed and sealed?
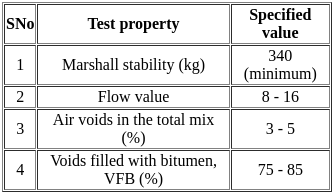
Consider the following criteria for the Marshall mix design for bituminous concrete
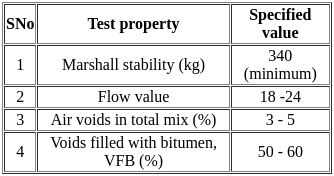
Which of the design criteria is/are true?
The bond between steel and concrete is mainly due to
1. Mechanical resistance
2. Pure adhesive resistance
3. Frictional resistance
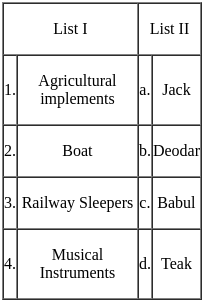
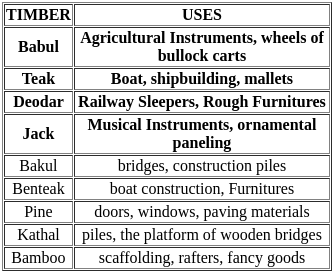
Match List-I of various uses with their corresponding suitable timber in List-II
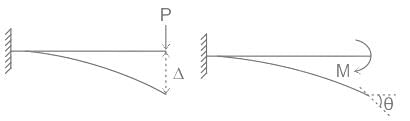
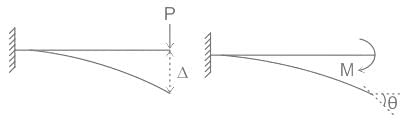
For a linearly elastic structure, Which of the following principles states that where external forces only cause deformation, the complementary energy is equal to the deformation energy?
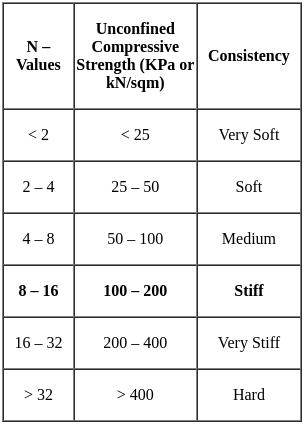
A clay having an unconfined compressive strength of 160 kN/sq.m would be classified as:
Consider the following statements :
- The maximum possible over consolidation ratio of normally consolidated soil is unity.
- The compressibility of a field deposit is slightly greater than that shown by a laboratory sample.
- In Terzaghi’s theory of one-dimensional consolidation, only hydrodynamic lag is considered whereas plastic lag is ignored.
Which of these statements are correct?
The following statements (S1 and S2) pertain to the effect of factors affecting the workability of concrete.
S1 : High ratio of volume of coarse aggregate to fine aggregate results in higher workability of the concrete mix (keeping all other parameters of mix constant).
S2 : As the placing time of concrete increases, the workability of the mix decreases.
A reinforced cement concrete beam section has a size of 300 mm width and 400 mm effective depth, the grade of concrete used is M20 and grade of steel is Fe 415. If the ultimate bending moment of 150 kN-m acts at the section, the beam has to be designed as
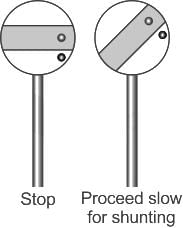
What does the inclined red band at 45° indicates in a shunting signal?
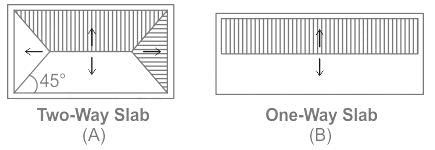
The analysis of slab spanning in one direction is done by assuming it to be a beam of


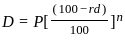

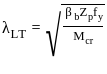
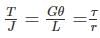
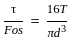
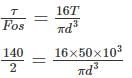
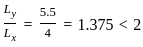
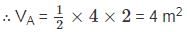
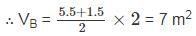
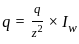
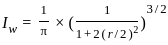
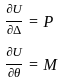
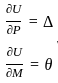
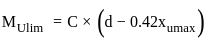
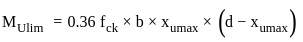
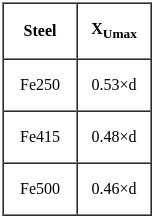
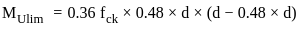
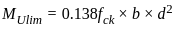 kN-m
kN-m