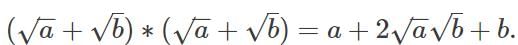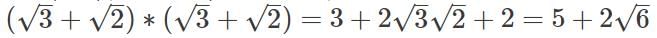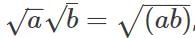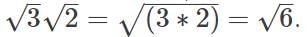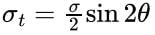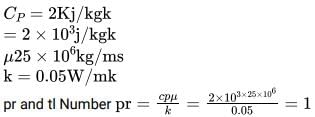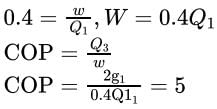HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 5 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - HPCL Mechanical Engineer Mock Test - 5
Direction: In these Questions, Out of the four alternatives choose the one which can be substituted for the given words/sentence.
Something no longer in use.
Direction: In the following question, the sentences have been given in Active/ Passive Voice. From the given alternatives, choose the one that best expresses the given sentence in Passive/ Active Voice.
We have warned you.
To represent 9 x which of following fraction form is appropriate.
Find the remainder when 6799 is divided by 7
If the ratio of the width to the length of a rectangle is 2 : 3 and the area of the rectangle is 54 cm2, what is the difference between its width and length?
Six friends have an average height of 172 cm. A boy with height 152 cm leaves the group. What is the new average height of the group?
In a school 30% of the students play football and 50% of students play cricket. If 40% of the students play neither football nor cricket, what percentage of total students play both the games?
Diya can complete a work in 80 days. In how many days can she complete it with 80% of her efficiency?
In the adjoining figure, AB || CD, t is the traversal, EG and FG are the bisectors of ∠BEF and ∠DFE respectively, then ∠EGF is equal to:

The population of a village is 1200. 58.33% of the total population are males. 50% of males and 60% of females of the village are literate. What is the total illiterate population of the village?
The average weight of A, B, C and D is 64 kg. If the average weight of A and B is 50 kg and that of B, C and D is 70 kg, what is the weight of B?
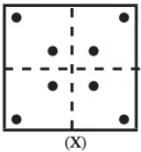
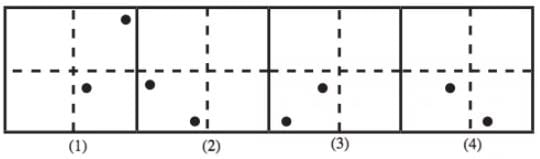
If a Paper (Transparent Sheet ) is folded in a manner and a design or pattern is drawn. When unfolded this paper appears as given below in the answer figure. Choose the correct answer figure given below.
Find out from the four alternatives as how the pattern would appear when the transparent sheet is folded at the dotted line.
Question Figure
Answer Figure
The ratio of Young’s Modulus of elasticity to the bulk modulus of elasticity for Poisson’s ratio 0.2 is
The angle between the line of stroke (line of motion of the follower) and the normal to the pitch curve at any point is referred to as
If a prismatic bar be subjected to an axial tensile stress σ, then shear stress-induced on a plane inclined at θ with the axis will be
The flow of water in a whirlpool of the river, is an example of
A 220 V series motor takes a current 35 amp and runs at 500 rpm. Armature resistance =0.25W and series field resistance = 0.3W. If iron and friction losses amount to 600W. Whatis the armature torque
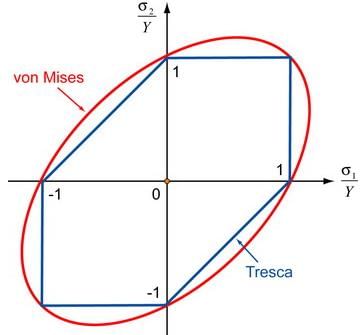
Which one of the following graph represents Von-Mises yield criterion
A fluid flowing over a flat plate has the following properties Dynamic Viscosity = 25×106 kg/ms Specific heat = 2.0 kJ /kg K, Thermal Conductivity = 0.05 W/mk
Find the Pr and tl Number
The equivalent spring constant for a bar of length L, cross-sectional area A and modulus of elasticity E is subjected to an axial force P is
In the figure shown, E is the heat engine with an efficiency of 0.4, and R is the refrigerator. Given that Q2 + Q4 = 3Q1, the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator is
Which of the following statement is correct?
Which of the following property of air does not increase with the rise in temperature?
When a cast iron specimen is subjected to a tensile test, then percentage reduction in the area will be equal to



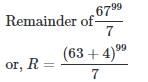
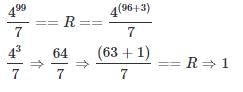
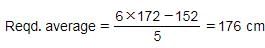
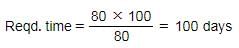
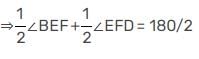
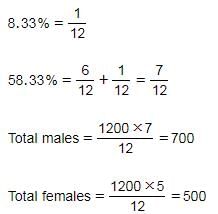
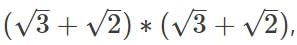 we get __________
we get __________