RSMSSB JE Electrical Mock Test - 4 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - RSMSSB JE Electrical Mock Test - 4
Who among the following was the founder of Niranjani sect?
In order to control the speed of a 3-phase slip ring induction motor through injected voltage in its rotor circuit, this voltage and the rotor voltage should essentially be
A series RLC circuit has a resonance frequency of 1 KHz and a quality factor Q = 100. If each of R, L, C doubled from its original value. The new quality factor Q of the circuit is
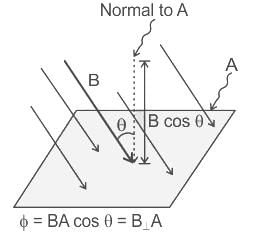
The magnetic flux through a 150 turns coil increases at the rate of 0.08 wb/s. What is the induced EMF between the ends of the coil?
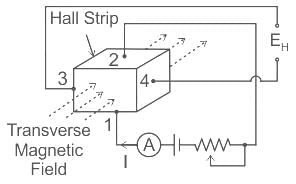
Which of the following transductions is done by the Hall effect device as a transducer?
The number of roots of s3 + 5s2 + 7s + 3 = 0 in the left half of the s-plane is
A transformer can have regulation closer to zero on __________.
A damper winding is used in a synchronous motor for-
What are the materials which exhibit electric polarization even in the absence of an applied electrical field?
Rajasthan is endowed with a solar radiation intensity of around_______Kwh/sq-m/day.
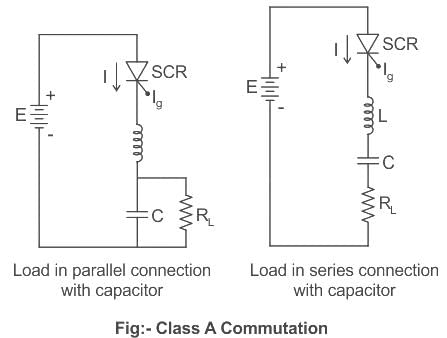
UJT is used for which of the following applications?
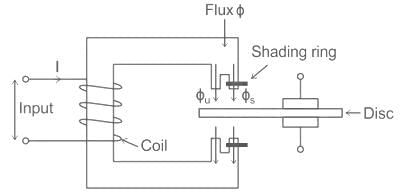
Torque produced in shaded pole structure induction type relay is:
Two synchronous generators G1 and G2 rated 200 MW and 400 MW respectively are operated in parallel to supply a total load of 300 MW. If the governors in both the machines are set to a droop of 4%, what would be the individual power supplied by each generator?



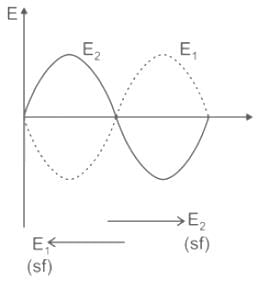
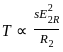
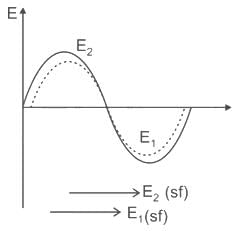
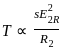
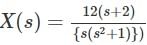 will be
will be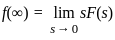
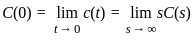
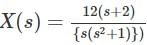
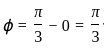
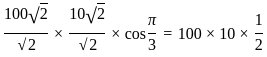
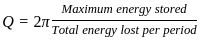
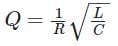
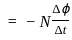
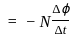
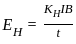

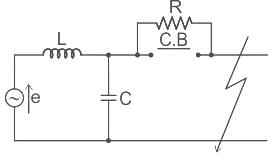
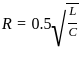
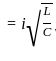
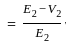
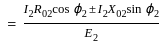
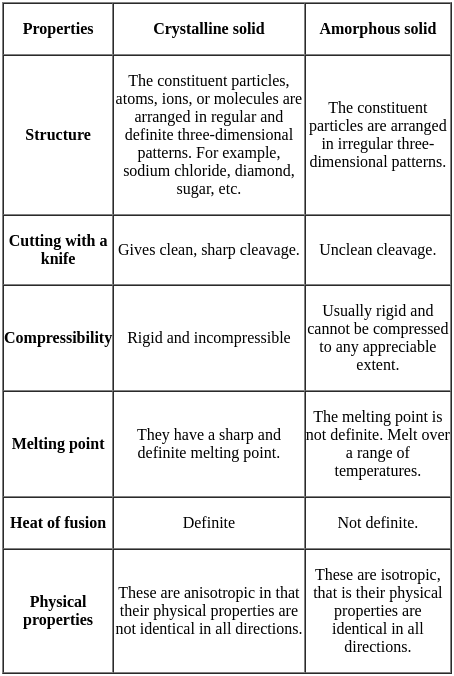
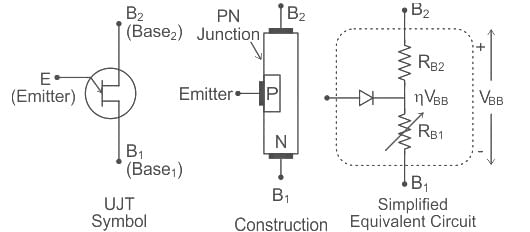
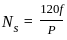
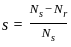
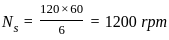
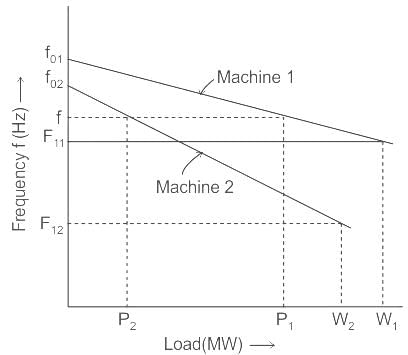
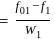
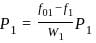
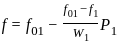 .... (1)
.... (1)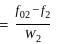
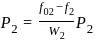
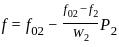 .... (2)
.... (2)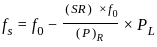
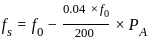 .............(2)
.............(2)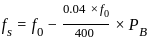 .............(3)
.............(3)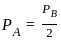 ..................(4)
..................(4)










