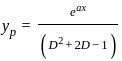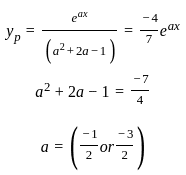TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 3 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 3
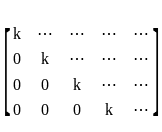
Find for what value of k, the set of equations
2x - 3y + 6z - 5t = 3
y - 4z + t = 1
4x - 5y + 8z - 9t = k
has an infinite number of solutions for ‘k’ equal to
2x - 3y + 6z - 5t = 3
y - 4z + t = 1
4x - 5y + 8z - 9t = k
has an infinite number of solutions for ‘k’ equal to
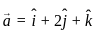 is
is
For stability and economic reasons we operate the transmission line with power angle in the range
Choose the correct statement about the kinetic friction and static friction.
For the reaction 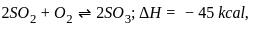 which one of the following statement is correct?
which one of the following statement is correct?
Which of the following is/are the indicating instruments?
Given the systems (i) y(n) = n x(n) and (ii) y(n) = ex(n)
A tuned amplifier has center frequency of 3 MHz and required bandwidth for speech is 5 kHz. The Q factor of amplifier will be ______.
The inverse z-transform of a given function
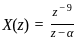 is αn-ku(n - k).
is αn-ku(n - k).
Then, the value of k is _____.
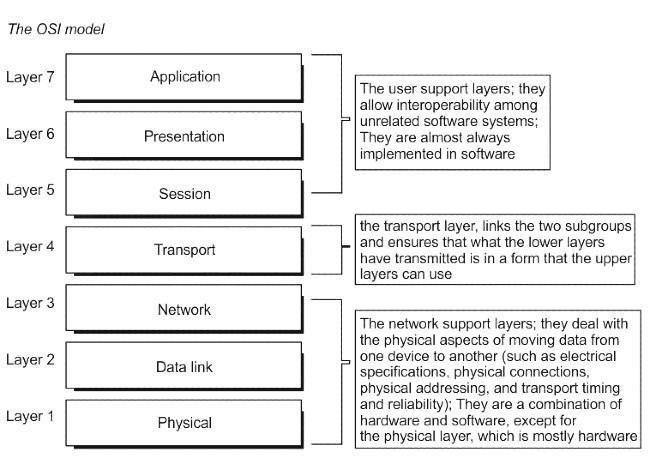
Which of the following is/are true about different layers of the OSI model?
I. Segmentation of datagram is performed at Network layer
II. Data compression is done at transport layer
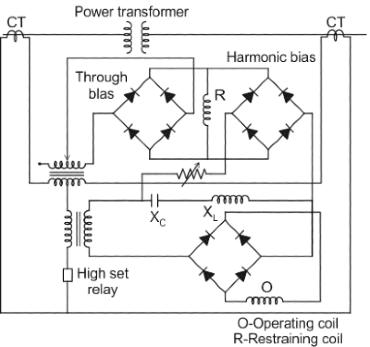
Harmonic restraint feature is imparted to transformer differential relays to prevent its maloperation due to.
A relay has a rating of 5 A, 2.2 sec IDMT and a relay setting of 125% TMS = 0.6. It is connected to a supply circuit through a C.T. 400/5 ratio. The fault current is 4000 A. The operating current of the relay is
Every network adaptor has a unique identity in the form of a _______.
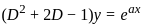 is
is 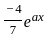 , then the value of 'a' is
, then the value of 'a' is
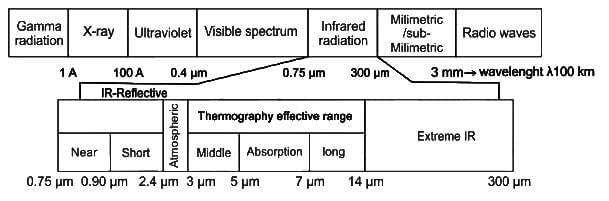
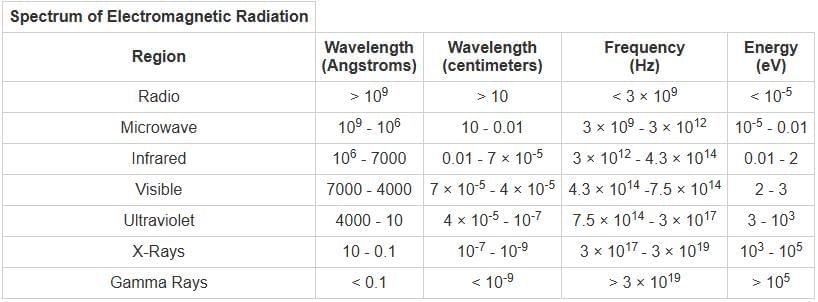
The regions of electromagnetic spectrum given in terms of wave length for Microwave, Visible and Mid. IR spectroscopy are given respectively by


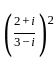 is
is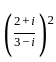
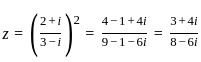
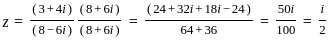
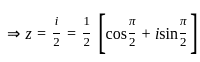
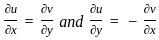 i.e. ux = vy and uy = -vx
i.e. ux = vy and uy = -vx

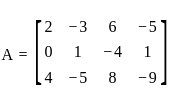
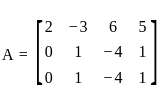
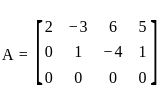

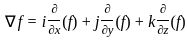

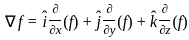
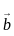 ) = î + 2ĵ + k̂
) = î + 2ĵ + k̂ 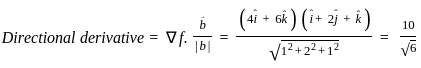
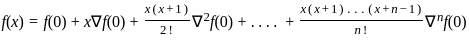 represents
represents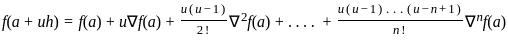
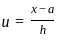
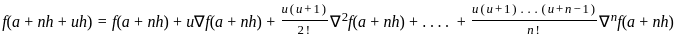
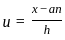
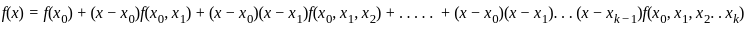
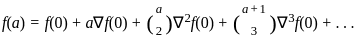
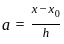 and
and 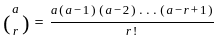
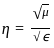
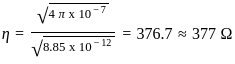

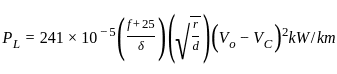
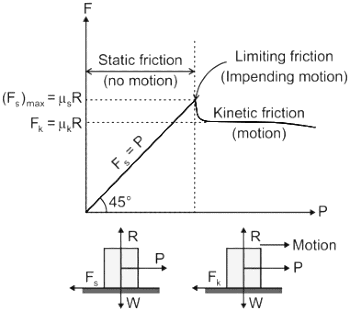
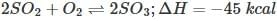 , the most favourable conditions of temperature and pressure for greater yield of SO2 are high pressure and low temperature.
, the most favourable conditions of temperature and pressure for greater yield of SO2 are high pressure and low temperature.
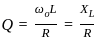
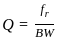
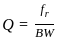
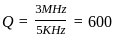
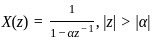
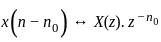
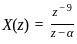
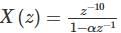
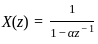 , its IZT = α
, its IZT = α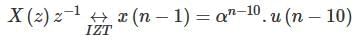
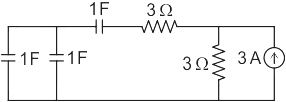
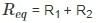
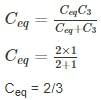

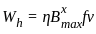
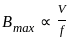
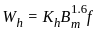
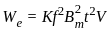
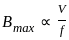
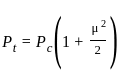
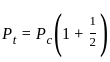
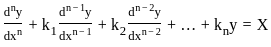
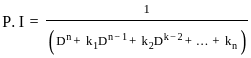 X
X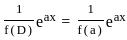 provided f(a) ≠ 0
provided f(a) ≠ 0