TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 4 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - TANGEDCO AE EE Full Test - 4
Let z(t) = x(t) * y(t), where “ * ” denotes convolution. Let c be a positive real-valued constant. Choose the correct expression for z(ct).
The value of 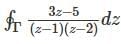 along a closed path Γ is equal to (4 π i), where z = x + iy and i=√-1. The correct path Γ is
along a closed path Γ is equal to (4 π i), where z = x + iy and i=√-1. The correct path Γ is
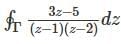 along a closed path Γ is equal to (4 π i), where z = x + iy and i=√-1. The correct path Γ is
along a closed path Γ is equal to (4 π i), where z = x + iy and i=√-1. The correct path Γ isThe function f(x) = 3 + |x - 2| at the point (2, 3) is
An alternator having an induced emf of 1.6 pu is connected to an infinite bus of 1.0 pu. If the bus bar has reactance of 0.6 pu and alternator has reactance of 0.2 pu, what is the maximum power that can be transferred?
A radio station broadcasts at a frequency of 108 M. If the broadcast is an electromagnetic wave, then what is its wavelength?
Determine the output of following C code segment:
int add (int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
main()
{
int c;
c = add (10, 20);
printf("c = %d", c);
}
Given,
Gas: H2, CH4, CO2, SO2.
Critical temperature/K: 33, 190, 304, 630.
On the basis of data given above, predict which of the following gases shows the least adsorption on a definite amount of charcoal?In C programming, which of the following loop use explicitly breaks out of the loop by executing the break; statement?
A network has a pole at s = -1 and a zero at s = -2. If this network is excited by sinusoidal input, the output
Calculate the regulation of the transformer in which ohmic loss is 1% of the output and reactance drop is 5% of the voltage, when the power factor is 0.8 leading
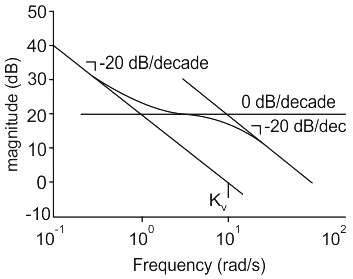
For a type 1 system, the low frequency asymptote of its Bode plot will have a slope of
Determine the inverse z-transform of: 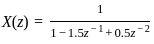 Where ROC: |Z| > 1
Where ROC: |Z| > 1
At a particular instant, the R- phase voltage of a balanced 3-phase system is +30 V, and the Y - phase voltage is -90V. The voltage of B - phase at that instant is
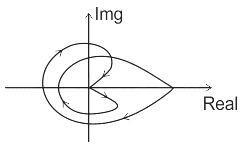
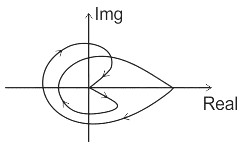
The Nyquist plot for a control system is shown below, the type of the system is
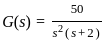 . The steady state error for unit acceleration input is
. The steady state error for unit acceleration input is
A single phase full bridge converter supplies a load drawing current (constant and ripple free) If the triggering angle is 30°, the input power factor will be
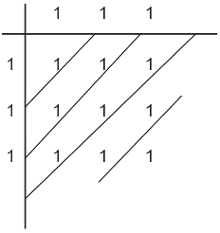
What is the convolution of the sequences of x1(n) = x2(n) = {1, 1, 1}?
A carrier voltage is simultaneously modulated by two sine waves causing modulating indexes of 0.4 and 0.3. The overall modulation index is
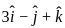 and perpendicular to the vector
and perpendicular to the vector 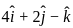 is
is
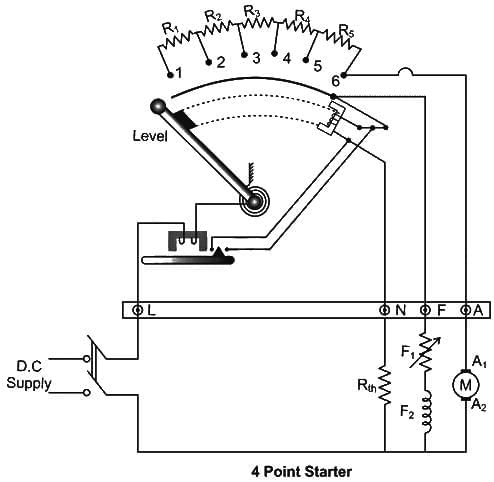
The purpose of including an external resistance at the time of starting a DC motor is to


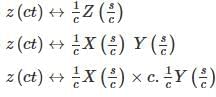
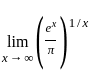
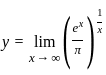
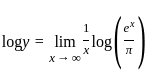
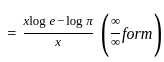
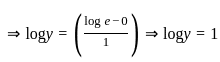

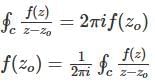

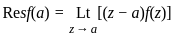
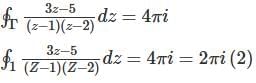
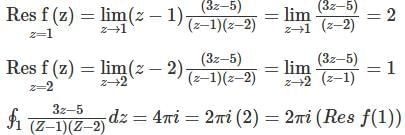
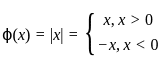
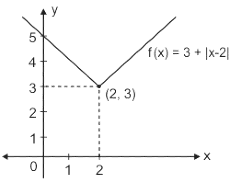
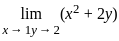 is equal to
is equal to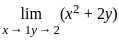
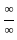
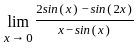
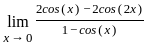
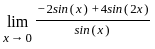
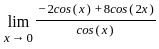
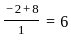
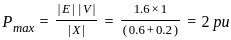
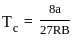
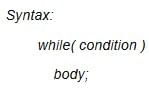
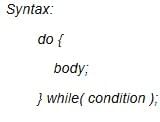

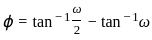
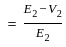
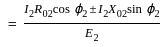
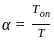
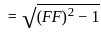
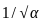
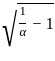
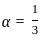
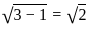 ≈ 1.5
≈ 1.5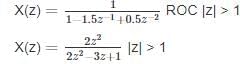
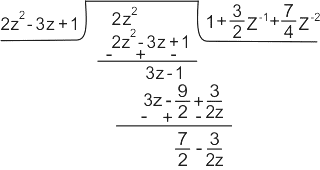
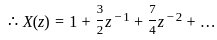 …1)
…1)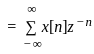
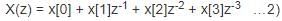
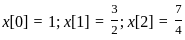
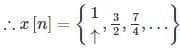
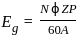
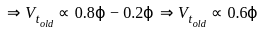
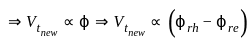
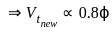
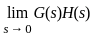
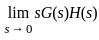
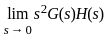
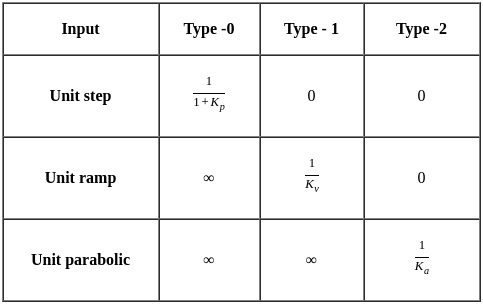
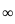 steady-state error for parabolic-input.
steady-state error for parabolic-input.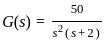
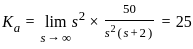
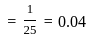
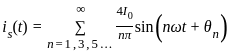
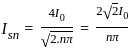
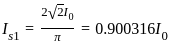
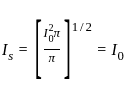
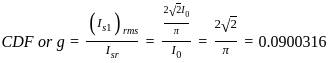


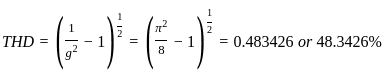
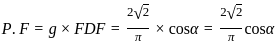
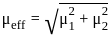
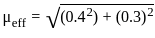
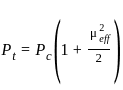
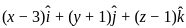
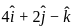 their dot product becomes zero
their dot product becomes zero