Test: Biodiversity & Conservation - 1 - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Biodiversity & Conservation - 1
What is the protection and conservation of species outside their natural habitat called?
If all the members of a host species die then all its unique parasites also die off, representing:
When we will move away from the equator towards poles, we will find:
In a wetland the primary factor controlling the environment and the associated plant and animal life will be:
If we say, India has about 50,000 type of rice and 1000 types of varieties of mango what level of diversity it indicates:
Alexander Von Humbolt described for the first time
What are the species called whose number of individuals is greatly reduced to a critical level?
How many hotspots of biodiversity in the world have been identified till date?
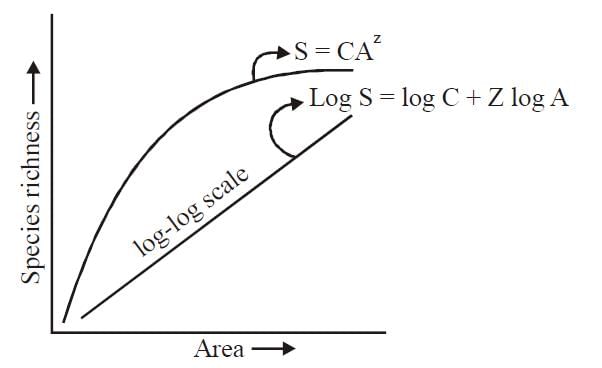
When we compare the relationship between species richness and area for wide variety of taxa, the graph appears to be a :
How many species of plants contribute to the traditional medicines used by native peoples around the world?
To preserve seeds that rapidly lose viability, can’t survive dessication and plants which are propagated vegetatively, method employed is :
Introducing exotic species into new areas will:
i) increase competition for food & space.
ii) introduce diseases
iii) improve habitat
iv) lead to extinction of native species
How many species in the world are facing threat of extinction?
What percent of the total oxygen in the Earth’s atmosphere is released by the Amazon forest?
The great German naturalist and geographer Alexander von Humboldt observed that within a region species richness increased with increasing explored area, but only up to a limit. In fact, relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa (angiosperm plants, birds, bats, freshwater fishes) turns out to be a rectangular hyperbola. Now find out correct equations shown in the graph:
The organisms that has been completely eliminated or died out from earth are called?
Loss of biodiversity may lead to all except:
Which of the following are also called lungs of our planet?
Which one of the following have the highest number of species in nature?
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
i. India accounts for 8.1% of global species diversity despite covering only 2.4% of the world's land area.
ii. Approximately 45,000 plant species have been documented in India, along with twice as many animal species.
iii. According to global estimates, only 22% of all living species have been identified so far.
iv. It is estimated that there are less than 100,000 undiscovered plant species in India.
Which of the following statements regarding the diversity of plants and animals in tropical regions is/are correct?
i. Species diversity is generally higher in tropical regions compared to temperate and polar areas due to longer evolutionary timeframes.
ii. Tropical environments, being less seasonal and more constant, promote niche specialization which contributes to greater species diversity.
iii. The greater availability of solar energy in tropical regions leads to higher productivity, which indirectly supports greater biodiversity.
iv. Polar regions have been less affected by glaciation events than tropical regions, resulting in higher species diversity in the poles.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct regarding alien species invasions and co-extinctions?
i. The introduction of the Nile perch in Lake Victoria caused the decline of indigenous cichlid fish species.
ii. Invasive weed species such as Lantana and water hyacinth do not pose a significant threat to native species.
iii. Co-extinctions occur when a species extinction leads to the extinction of its associated mutualistic partners.
iv. The African catfish Clarias gariepinus has been legally introduced into rivers for aquaculture purposes.
Assertion (A): Conserving biodiversity is essential because it provides numerous direct economic benefits to humans.
Reason (R):
The majority of medicinal products currently available are derived from a small fraction of plant species.
What was the main focus of the Convention on Biological Diversity held in 1992?
|
65 videos|390 docs|202 tests
|