Test: Microbes as Biofertilizers (NCERT) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Microbes as Biofertilizers (NCERT)
Farmers have reported over 50% higher yields of rice by using which of the following biofertilisers?
Unicellular symbiotic organisms that improve the yield of legumes by
Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil. Which of the following can be used as biofertilisers?
The reason that the chemical/synthetic fertilisers should be replaced by biofertilisers is that the former:
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding mycorrhiza?
Which of the following statements regarding biofertilizers and their symbiotic associations is incorrect?
A nitrogen fixing microbe associated with the fern Azolla in rice fields is:
Which of the following is non-symbiotic biofertilizer?
Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched?
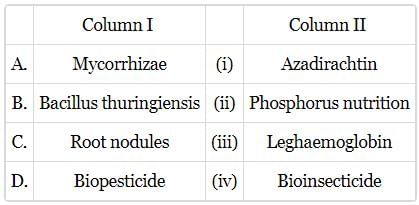
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Nitrogen fixation in root nodules of alnus is brought about by
Which one of the following can be used as biofertiliser in cotton field?
|
78 videos|277 docs|174 tests
|




















