Test: Post-Fertilization (Structures & Events) - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Post-Fertilization (Structures & Events)
Milk of tender coconut represents (i) and the surrounding white coconut meal represents (ii).

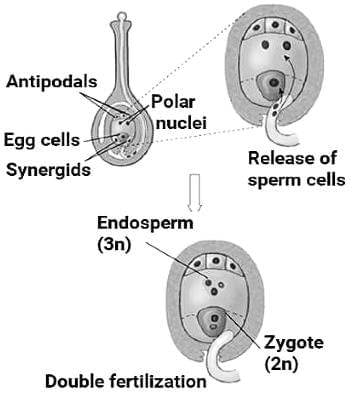
Assertion : In the most common type of endosperm development, the PEN undergoes successive nuclear division to give rise to free nuclei.
Reason : Embryo develops at the chalazal end of the embryo sac where zygote is situated.
Reason : Embryo develops at the chalazal end of the embryo sac where zygote is situated.
The endosperm cells in angiosperms are:
Endosperm is consumed by a developing embryo in the seed of ______.
Identify the wrong statement regarding post fertilization development.
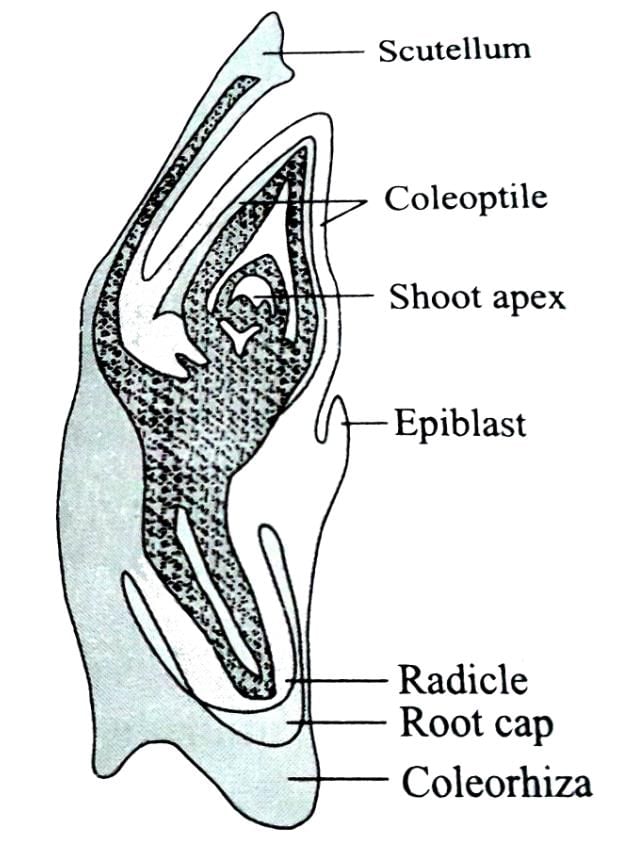
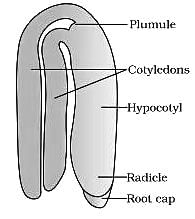
Coleorhiza and coleoptile are the protective sheaths coverging_______and__________respectively.
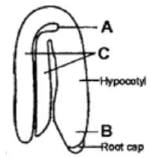
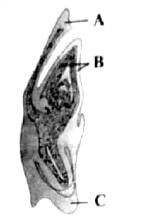
Identify the parts labelled A, B and C in the given figure and select the correct option.
In the most common type of endosperm development:
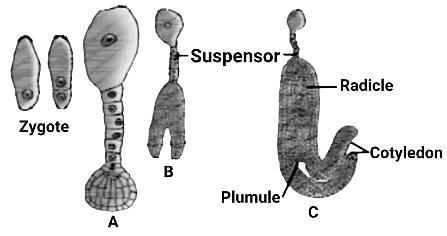
The diagram shows stages in embryo development in a dicot where A, B, and C respectively are:
The cells of endosperm have 24 chromosomes. What will be the number of chromosomes in the gametes?
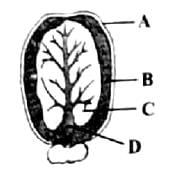
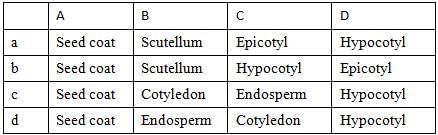
Identify the parts labelled as A, B, C and D in the given figure and select the correct option from the codes given below
Persistent nucellus is called as______________and is found in __________.
Endosperm development precedes ____ development.
In the given diagram, X represents

Go through the given diagram of a typical dicot embryo. In which of the following all the 3 parts labelled as A, B, C with their respective functions are correctly identified