Test: Principles of Inheritance and Variation- 1 - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Biology Class 12 - Test: Principles of Inheritance and Variation- 1
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation of a dihybrid cross is
A pure tall and a pure dwarf plant were crossed and produced offspring. Offspring were self crossed.Then find out the ratio between true breeding tall to true breeding dwarf ?
What is the expected outcome of a cross between a homozygous dominant tall pea plant (TT) and a homozygous recessive dwarf pea plant (tt)?
What determines the differences between the progeny and parents?
The gene which controls many characters is called
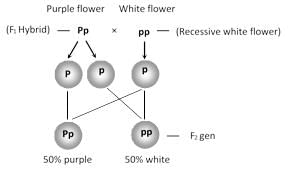
Heterozygous purple flower is crossed with recessive white flower. The progeny has the ratio:
Mating of an organism to a double recessive in order to determine whether it is homozygous or heterozygous for a character under consideration is called
Which of the following is not a Mendelian disorder?
In human ABO group system ________ different alleles allow the possibility of _______ different types of genotypes in the population.
Column-I
(a) Multiple alleles
(b) Polygenes
(c) Pleiotropy
Column-II
(i) Phenylketonuria in humans
(ii) Blood groups in humans
(iii) Skin color in humans
|
65 videos|390 docs|202 tests
|