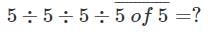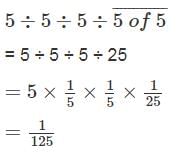FSSAI TO / AD (Technical) Mock Test - 6 - Agriculture Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test FSSAI TO / AD (Technical) / CFSO Mock Test Series 2025 - FSSAI TO / AD (Technical) Mock Test - 6
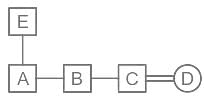
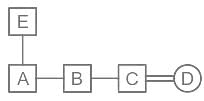
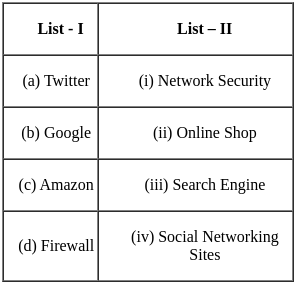
Match the following and select the correct code:

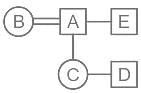
A is father of C and D is son of B. E is brother of A. If C is sister of D, then how is B related to E?
The HCF of two numbers is 15 and their LCM is 225. If one of the number is 75, then the other number is ?
With the round robin CPU scheduling in a time-shared system, ______.
10, 7, 4, …, is an AP, what will be the 30th term of this series?
A is the brother of B. B is the brother of C. C is the husband of D. E is the father of A. D is related to E.
The HCF and LCM of two numbers are 12 and 924 respectively. Then the number of such pairs is
FSSAI designed which of the following Book for kitchens in Indian homes so that the food prepared is safe, hygienic, and nutritious?
Consider the following statements:
A. The location of the food industry should be away from environmentally polluted areas.
B. The location of the food industry should be nearest to the populous area.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
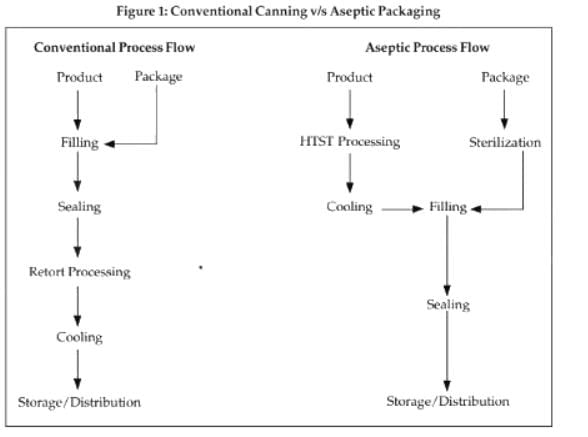
Advantages of aseptic processing includes___
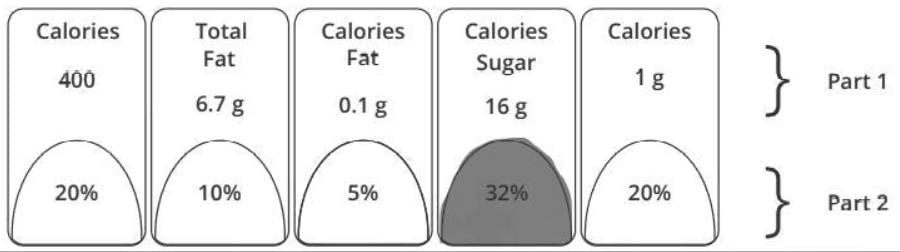
For discouraging the consumption of processed food, FSSAI has introduced__________ on food packaging.
Starch is a____________, which is a large molecule formed when small molecules of the same kind chain together.
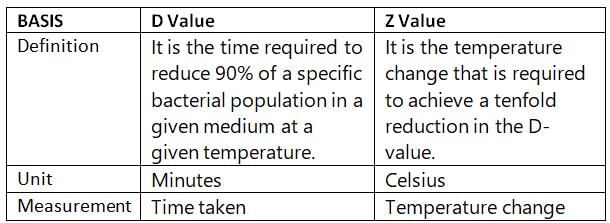
Time (in min) at specified temperature required to destroy 90% of the cells at the respective microbial population is called as:
When a deviation from critical limits happens what should be done?
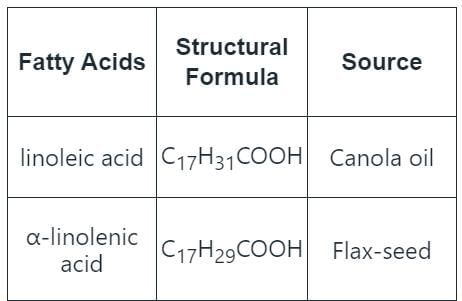
Two unsaturated fatty acids are also called as "essential fatty acids" because:
Flour which has been stored for a long time gives higher values of _______________