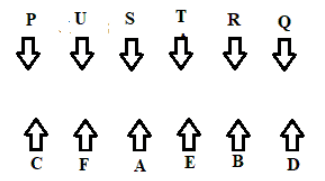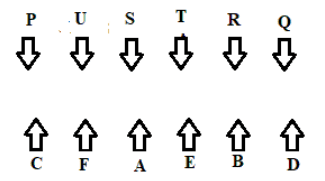PFRDA Assistant Manager Phase 1 Mock Test - 3 (Paper 1) - Insurance Exams MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test PFRDA Assistant Manager Mock Test Series 2025 - PFRDA Assistant Manager Phase 1 Mock Test - 3 (Paper 1)
Direction: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
India’s e-commerce sector, poised to grow four times to $150 billion by 2022, is still a work in progress when it comes to safeguarding customer interest. Consumers are still compelled to take wild chances in online transactions. There is little they can do if their calls go wrong. Returns and reimbursements are risky and cumbersome. There are no authentic ways to figure out if product reviews, ratings or even discounts are genuine. So, it is heartening to see the government coming up with a set of guidelines to protect interests of consumers. The guidelines released last week by the Consumer Affairs Ministry in this regard emphasise that an e-commerce entity shall not influence the price of the goods or services, adopt any unfair or deceptive methods to influence transactional decisions of consumers or falsely represent themselves as consumers and post reviews about goods and services. The guidelines on returns and refunds favour consumers. The message seems simple: If online companies want to dupe consumers to earn extra bucks, they’re in trouble.
Clearly, the Ministry’s thinking seems to be in line with the way the Centre’s approach to regulating the fast-growing e-commerce sector. It is, however, worth considering whether the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (then DIPP) will strike the right balance between regulating consumer interests and encouraging innovation and investment, without discriminating against a particular class of investors. Now marketplace entities won’t be able to buy more than 25 per cent from a single vendor, give discounts on products or sell the goods of the companies in which there is equity participation by the marketplace entity. The changes had irked foreign e-tailers who felt the rules would _____ (A) _____ their business models and could cost them time and money. But anecdotal evidence does not entirely seem to bear that out.
The DPIIT is also framing an e-commerce policy and, like the Consumer Affairs Ministry, has put up the draft for comments. The draft talks about the country retaining ownership and control of data generated within the country, rigorous monitoring of cross-border imports, placing the responsibility of consumer protection on the intermediary and addressing the issue of piracy. That said, the element of indecision over data localisation requirements is still a worry. Attempts made by both the DPIIT and the MeitY in the e-commerce policy and the data protection policy, respectively, to make a case for storage of personal data locally (along with the RBI in the case of payment systems) have predictably resulted in a lot of protests from the EU and US entities. While the Centre is certainly on a sound wicket here, it should take a call soon — without succumbing to the recent tendency to over-regulate business.
Q. Which among the following is correct regarding the opinion of the government on the storage of data, as stated in the passage?
Direction: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
India’s e-commerce sector, poised to grow four times to $150 billion by 2022, is still a work in progress when it comes to safeguarding customer interest. Consumers are still compelled to take wild chances in online transactions. There is little they can do if their calls go wrong. Returns and reimbursements are risky and cumbersome. There are no authentic ways to figure out if product reviews, ratings or even discounts are genuine. So, it is heartening to see the government coming up with a set of guidelines to protect interests of consumers. The guidelines released last week by the Consumer Affairs Ministry in this regard emphasise that an e-commerce entity shall not influence the price of the goods or services, adopt any unfair or deceptive methods to influence transactional decisions of consumers or falsely represent themselves as consumers and post reviews about goods and services. The guidelines on returns and refunds favour consumers. The message seems simple: If online companies want to dupe consumers to earn extra bucks, they’re in trouble.
Clearly, the Ministry’s thinking seems to be in line with the way the Centre’s approach to regulating the fast-growing e-commerce sector. It is, however, worth considering whether the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (then DIPP) will strike the right balance between regulating consumer interests and encouraging innovation and investment, without discriminating against a particular class of investors. Now marketplace entities won’t be able to buy more than 25 per cent from a single vendor, give discounts on products or sell the goods of the companies in which there is equity participation by the marketplace entity. The changes had irked foreign e-tailers who felt the rules would _____ (A) _____ their business models and could cost them time and money. But anecdotal evidence does not entirely seem to bear that out.
The DPIIT is also framing an e-commerce policy and, like the Consumer Affairs Ministry, has put up the draft for comments. The draft talks about the country retaining ownership and control of data generated within the country, rigorous monitoring of cross-border imports, placing the responsibility of consumer protection on the intermediary and addressing the issue of piracy. That said, the element of indecision over data localisation requirements is still a worry. Attempts made by both the DPIIT and the MeitY in the e-commerce policy and the data protection policy, respectively, to make a case for storage of personal data locally (along with the RBI in the case of payment systems) have predictably resulted in a lot of protests from the EU and US entities. While the Centre is certainly on a sound wicket here, it should take a call soon — without succumbing to the recent tendency to over-regulate business.
Q. Which among the following is/are the problem(s) faced by the e-commerce customers in India these days, as stated in the passage?
I. They do not get the money back easily in case they have to return the products delivered to them.
II. They have no credible information regarding the products and the feedback regarding them available to them.
III. They have to pay extra to ship the products directly to their homes as they do not need to come out for shopping.
I. They do not get the money back easily in case they have to return the products delivered to them.
II. They have no credible information regarding the products and the feedback regarding them available to them.
III. They have to pay extra to ship the products directly to their homes as they do not need to come out for shopping.
Directions: In the question given below there are two statements, each statement consists of two blanks. You have to choose the option which provides the correct set of words that fits both the blanks in both the statements appropriately and in the same order making them meaningful and grammatically correct.
I. India is a ________ after destination for medical tourism, but in the area of early screening and intervention it is still ________ behind, and early developmental screening is more the exception than the rule.
II. The minister interacted with the local residents and ________ their feedback on the developmental policies as he wanted to know why the district, which was a knowledge hub earlier, was presently ________ in crucial indicators of development.
Direction: In each of the questions given below, a paragraph is given which has some blanks and those blanks have to be filled with the same word out of five words given below it. You have to choose that same word as your answer and fill up the blanks with that appropriate word.
It is very important to ____________ to rules and regulations in life if you want to achieve something. If you are a person who hates discipline and cannot ____________ to any stupid set of norms, you should definitely opt for startup stints. There you will not have to ____________ anything fixed and you can only focus on your performance.
Direction: In the questions given below a sentence is given with two blanks in each. Corresponding to each question two columns are given with three words in each column. Which combination of words from the two columns will perfectly fit into the blanks to make the sentence contextually correct and meaningful?
Taking a cue from these complaints, the National Human Rights Commission had ____________ a draft of patients’ rights charter with the Ministry and it was ____________ at the 11th meeting of the National Council of Clinical Establishments.
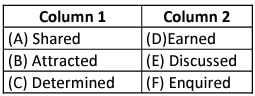
Directions: In the question given below, a sentence has been broken down into four fragments labelled (A), (B), (C) and (D) and arranged, not necessarily in the correct order. You have to find the correct order of arrangement from the options given below.
She and her husband bought a helicopter (A) / staffed with uniformed servants (B) / in order to commute between their opulent Connecticut (C) / manor and an apartment on Central Park West. (D)
Directions: In each of the questions below, a sentence is given with one word highlighted in underline. From the given options, identify the sentence which expresses a meaning opposite to the given sentence, with the highlighted word replaced by a word of the opposite meaning.
A more robust approach in addressing the widening CAD would be to institute wideranging measures to boost exports.
Either Nemmu or Mennu / are in the wrong; / both can / certainly never be.
Supposing if / it rains / what shall / we do?
Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on it.
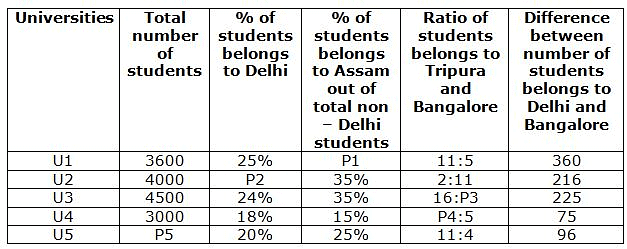
The following given table gives partial information about the number of students studying in five different universities – U1, U2, U3, U4 and U5 belongs to four different states – Delhi, Assam, Tripura and Bangalore. Detailsof % of students belongs to Delhi out of total number of students in a particular university, % of students belongs to Assam out of total non – Delhi students, ratio of number of students belongs to Tripura and Bangalore and difference between number of students belong to Delhi and Bangalore are given below. Number of students who belongs to Delhi is more than the number of students belongs to Bangalore for universities U1, U3 and U5 and for rest universities this statement is not true.
A mixture of milk and water of 88 litres in the ratio of P4:P3 respectively. Find the amount of milk?
(e )None of these
Read the following information carefully and answer the questions based on it.
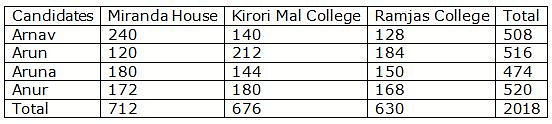
In a Delhi University election for President, there were four candidates – Arnav, Arun, Aruna and Anur. Three colleges participated in the election – Miranda House, Kirodimal and Ramjas. Candidates who got the highest number of votes in all three colleges together are considered as a winner and he/she will be the president of Delhi University.
Miranda House: Ratio of votes received by Arun and Arnav was 1:2 while that of Arun and Anur was 30:43. Aruna received 25(25/89) % of total votes which was 8 more than that of Anur.
Kirodimal: Ratio of number of votes received by Anur in Miranda house and Kirodimal was 43:45. Aruna received (20/7) % more votes than Arnav and (1700/53) % less than that of Arun. Total votes received in Kirodimalwere 36 less than that of Miranda House.
Ramjas: Votes received by Arun is 22.66% more than that of Aruna and Anur received 6.66% less votes than what he received in Kirodimal. Arnav received (1280/63) % of total votes of RamjasCollege. Votes received byArnavis 40 lessthan that of what Anur received in Ramjascollege.Sum of votes received by Arun and Arunais 334.
Number of votes received by Arun and Anur together in Ramjas college is how much % of total number of votes received by Arun and Aruna together?
The price of petrol increases by 12.5%. By how much percentage must a person reduce his consumption so that his expenditure on it does not increase?
Directions: Study the given passage carefully and answer the following question.
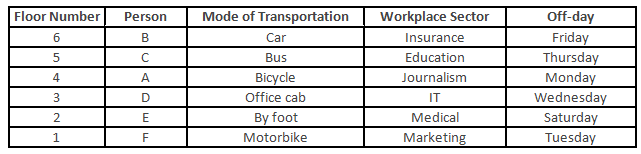
In a six-storey building, there are six friends A, B, C, D, E and F working in different sectors, i.e. Marketing, Insurance, IT, Education, Medical and Journalism. They live on different floors numbered 1 to 6. They go their offices by six different modes of transportation - bus, office cab, motorbike, car and bicycle, by foot, in no particular order. Each person has one day off between Monday and Saturday. B drives a car, works in the Insurance sector, and lives on the topmost floor of the building. E and A live on even-numbered floors and have a day off on Saturday and Monday, respectively. The person working in the Marketing sector lives on the lowermost floor and has his a day off on Tuesday. The person working in the Education sector lives on the floor which is next to the floor on which B lives and has a day off on Thursday. The one who is working in the Journalism sector rides a bicycle and has a day off on Monday. F drives a motorbike and has only one neighbour. One of the persons living on even-numbered floors has a day off on Friday. There is only one floor between the floors of C and D. C's floor is above D's. D goes to office by the office cab. E, who is not a neighbour of C, goes to office by foot and has a day off on Saturday. The person working in the Medical sector lives on an even-numbered floor.
On which floor does the person working in the Medical sector live?
Directions: Study the information carefully and answer the question that follows:
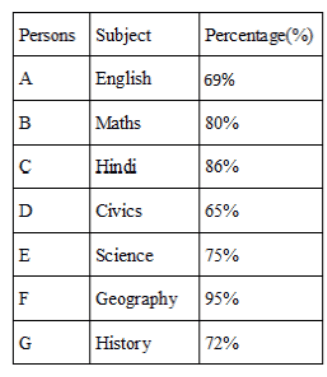
Seven persons - A, B, C, D, E, F and G like different subjects i.e., Mathematics, Hindi, English, Science, History, Geography and Civics. They all have cleared the exams with different percentages i.e., 65%, 69%, 72%, 75%, 80%, 86% and 95%, but not necessarily in the same order.
Person who likes Civics has secured less than 70%. The one who likes Hindi has secured more than 79%. A likes English. E likes Science. F has not secured less than 88%. Person who likes Geography has not secured less than 90%. B and C have secured more than 78%. The person who likes English secured less than 70%. One who likes History has secured less than 75%. Only one person has secured more than the person who likes Hindi. B does not like Hindi. D has secured less than A.
Which of the following options is correct?
Directions: Read the following passage carefully and answer the question below.
Six boys P, Q, R, S, T, U and six girls A, B, C, D, E and F are sitting on two parallel benches. All the boys are sitting on one bench facing south and all the girls are sitting on the other bench facing north, but not necessarily in the same order. They are sitting in such a manner, so that each girl is facing one boy and vice versa. S is sitting third to the right of Q. The girl who is facing Q is sitting second to the right of E. Either S or Q is sitting at the extreme ends of their row. Neither B, nor F is sitting at the extreme ends of their row and there are two girls sitting between them. R and T are immediate neighbours. The immediate neighbour of B faces the boy who is sitting third to the left of P. C is sitting second to the left of A and T is not facing the immediate neighbour of D.
Who among the following girls faces S?
Directions: Read the following passage carefully and answer the question below.
Six boys P, Q, R, S, T, U and six girls A, B, C, D, E and F are sitting on two parallel benches. All the boys are sitting on one bench facing south and all the girls are sitting on the other bench facing north, but not necessarily in the same order. They are sitting in such a manner, so that each girl is facing one boy and vice versa. S is sitting third to the right of Q. The girl who is facing Q is sitting second to the right of E. Either S or Q is sitting at the extreme ends of their row. Neither B, nor F is sitting at the extreme ends of their row and there are two girls sitting between them. R and T are immediate neighbours. The immediate neighbour of B faces the boy who is sitting third to the left of P. C is sitting second to the left of A and T is not facing the immediate neighbour of D.
Which one of the following is correct regarding T?
Directions: In the question, a statement is followed by two courses of action that are numbered I and II. A course of action is a step or administrative decision to be taken for improvement, follow-up or further action in regard to the problem, policy, etc. On the basis of the information given in the statement, you have to assume everything in the statement to be true and then decide which of the suggested courses of action should logically be taken.
Statement: The employees` union of the Municipal Corporation has decided to go on a strike for indefinite period in protest against the management`s refusal to grant bonus.
Courses of action:
I. The government should immediately pay ex-gratia grant to the Municipal Corporation to grant bonus to its employees.
II. The striking employees should be persuaded to defer the strike notice.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions:
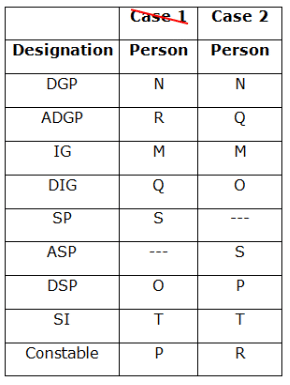
Eight persons viz. M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are working in the police department with different designations such as Director-General of police (D.G.P), Additional Director General of Police (A.D.G.P), Inspector General (I.G), Deputy Inspector General (D.I.G), Superintendent of Police (S.P), Assistant Superintendent of Police (A.S.P), Deputy Superintendent of Police (D.S.P), Sub Inspector (S.I) and Constable, with one vacant position. Their positions are given in descending order of seniority, such that D.G.P is the highest position and Constable is the lowest position. The consecutive alphabetical name of the person doesn’t hold a consecutive designation.
Q is five designations senior to P. M hold the third-highest position whereas T hold the second junior-most position and the A.S.P designation is not vacant. The number of persons junior to T is one more than the number of persons senior to N, who is the senior-most person. The immediate persons above and below the vacant position are S and O.The number of designations between M and N is one less than the number of persons between S and R.
Eight persons viz. M, N, O, P, Q, R, S and T are working in the police department with different designations such as Director-General of police (D.G.P), Additional Director General of Police (A.D.G.P), Inspector General (I.G), Deputy Inspector General (D.I.G), Superintendent of Police (S.P), Assistant Superintendent of Police (A.S.P), Deputy Superintendent of Police (D.S.P), Sub Inspector (S.I) and Constable, with one vacant position. Their positions are given in descending order of seniority, such that D.G.P is the highest position and Constable is the lowest position. The consecutive alphabetical name of the person doesn’t hold a consecutive designation.
Q is five designations senior to P. M hold the third-highest position whereas T hold the second junior-most position and the A.S.P designation is not vacant. The number of persons junior to T is one more than the number of persons senior to N, who is the senior-most person. The immediate persons above and below the vacant position are S and O.The number of designations between M and N is one less than the number of persons between S and R.
Which of the following is the designation of the person immediately junior to S?
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions:
3248 2397 5724 7415 3276
How many numbers is/are there in the number series between the third digit of the second number from the left end and second digit of the third number from the right end?
Directions: In the question below are given four statements, followed by three conclusions numbered I, II and Ill. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow(s) from the given statements, disregarding the commonly known facts.
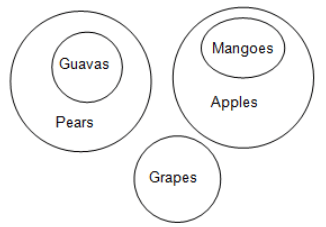
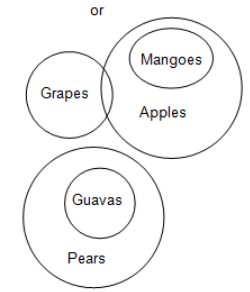
Statements:
All mangoes are apples.
No guavas are apples.
All guavas are pears.
No guavas are grapes.
Conclusions:
I. Some grapes are apples is a possibility.
II. Some pears are guavas.
III. Some guavas are mangoes is a possibility.
Study the following information carefully and answer the below questions:
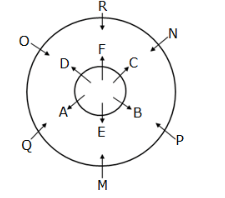
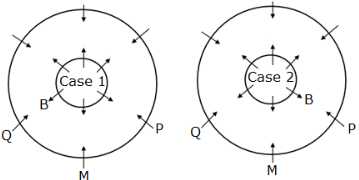
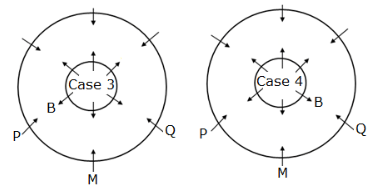
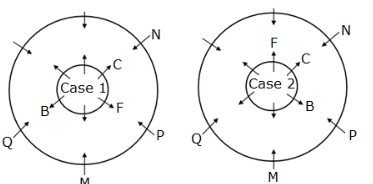
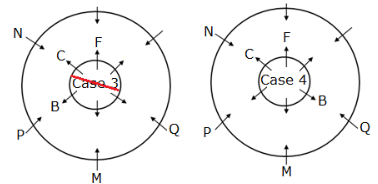
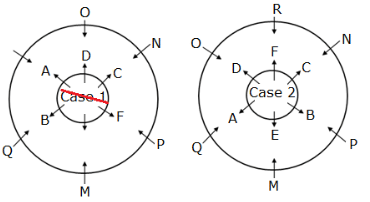
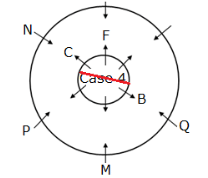
Twelve members are seated on the concentric circular tables, six in each viz. A, B, C, D, E and F are seated in the inner circle and faces outwards whereas M, N, O, P, Q and R are seated in the outer circle and faces inwards, but not necessarily in the same order. The person in the inner circle exactly faces the person seated in the outer circle.
M faces the immediate neighbour of B. Both P and Q are sitting adjacent to M. Both F and C are immediate neighbours where C faces N who sits adjacent to P.B sits second to the right of F.D faces O and sits to the immediate right of A, who doesn’t face R.
How many persons sit between Q and R, when counted from the left of Q?
Read both the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
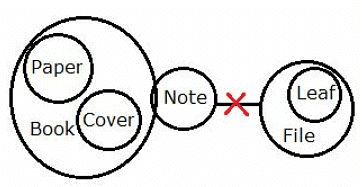
Statements:
All Papers are Book.
Some Books are Note.
Only Books are Cover.
No File is Note.
All Leafs are File.
Conclusion:
I. Some Paper can be Cover.
II. Some Books can never be File.
Consider the following pairs:
1. Justice Yashwant Varma Case - Discovery of cash and opaque proceedings highlight judicial accountability issues.
2. In-House Procedure - Formal inquiry procedure with legal standards for judicial misconduct.
3. First Caste-Based Census since 1931 - Scheduled for 2027 Census.
4. Digital Census Challenges - Addressed solely by improving digital literacy among enumerators.
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
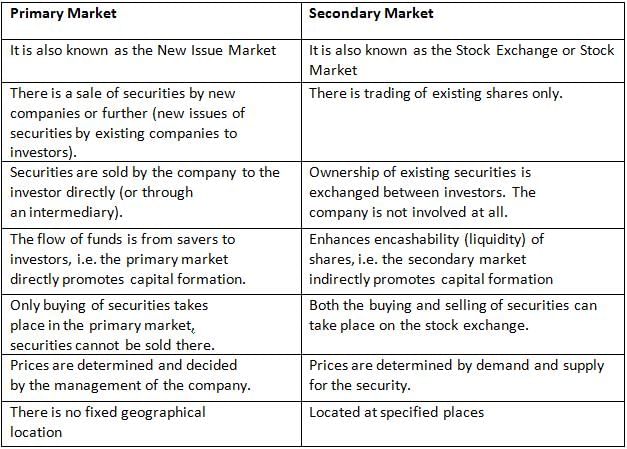
In which of the markets securities cannot be sold?
What is the authorized capital of Regional Rural Banks?
Consider the following statements
- Priority sector lending target of Urban Cooperative Banks(UCBs) is at par with the target applicable to commercial banks.
- There are penal provisions for UCBs for non-attainment of targets to priority sector and weaker sections.
- There are incentives for UCBs if they achieve priority sector lending targets.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?