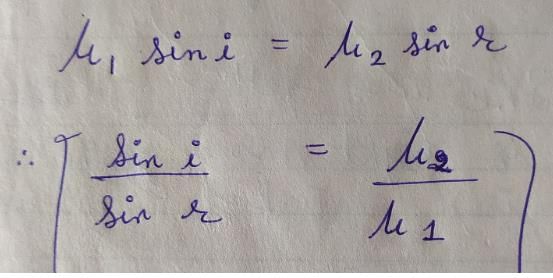Test: Ray Optics - 1 - Class 10 MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test Science Class 10 - Test: Ray Optics - 1
An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between its image and the pole is
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distance of the object from the mirror equals the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be
The magnification m of an image formed by a spherical mirror is negative. It means, the image is
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The object-distance u is
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will
If an incident ray passes through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror, the reflected ray will
A ray of light travelling in air falls obliquely on the surface of a calm pond. It will
A ray of light goes from a medium of refractive index μ1 to a medium of refractive index μ2. Theangle of incidence is i and the angle of refraction is r. Then, sin i/sin r is equal to
A thin lens and a spherical mirror have a focal length of + 15 cm each.
A convex lens forms a virtual image when an object is placed at a distance of 18 cm from it. The focal length must be
The radius of curvature of the curved surface of a plano-convex lens is 20 cm. If the refractive index of the material of the lens be 1.5, then focal length of lens will be:
In order to obtain a magnification of, -0.6 (minus 0.6) with a concave mirror, the object must be placed:
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
Two big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he finds that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B remains the same:
|
83 videos|438 docs|74 tests
|