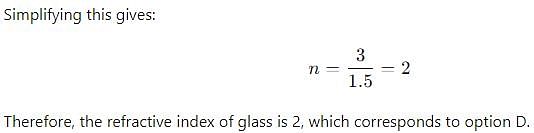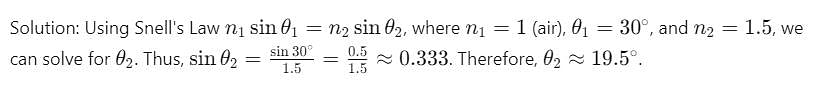UPSC Exam > UPSC Tests > General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi > Test: Refraction through Glass - UPSC MCQ
Test: Refraction through Glass - UPSC MCQ
Test Description
10 Questions MCQ Test General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi - Test: Refraction through Glass
Test: Refraction through Glass for UPSC 2024 is part of General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi preparation. The Test: Refraction through Glass questions and answers have been
prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus.The Test: Refraction through Glass MCQs are made for UPSC 2024 Exam. Find important
definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Refraction through Glass below.
Solutions of Test: Refraction through Glass questions in English are available as part of our General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi for UPSC & Test: Refraction through Glass solutions in
Hindi for General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi course. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock
test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: Refraction through Glass | 10 questions in 10 minutes | Mock test for UPSC preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study General Science(Prelims) by IRS Divey Sethi for UPSC Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 1
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 2
What will happen when a ray enters from glass to air medium ?
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 2
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 3
The speed of light in glass is 1.5 x 108m/s. Then refractive index of glass is
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 3
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 4
Light travels faster in substance X as compared to substance Y, then refractive index is greater for
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 4
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 5
During refraction through a rectangular glass slab, what can be said about the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction at the refracting surfaces?
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 5
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 6
Light enters from air to glass having a refractive index of 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in a vacuum is 3×108 m/s.
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 6
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 7
A light ray is incident at an angle of 30 degrees on a medium with a refractive index of 1.5. What is the angle of refraction if the light is moving from air to the medium?
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 8
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 9
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 9
Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 10
Which of the following statements about the refractive index of water is true?
Detailed Solution for Test: Refraction through Glass - Question 10
|
39 videos|110 docs|262 tests
|
Information about Test: Refraction through Glass Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: Refraction through Glass solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: Refraction through Glass, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
|
39 videos|110 docs|262 tests
|
Download as PDF