MPSC MCS (Mizoram) Prelims Paper-II Mock Test- 9 - MPSC MCS (Mizoram) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - MPSC MCS (Mizoram) Prelims Paper-II Mock Test- 9
Directions (Q. 1-8) Read the following two passages and answer the items that follow each passage. Your answers to these items should be based on these passages only.
Passage 1
"Rent-seeking" is what economists call a special type of money-making: the sort made possible by political connections. This can range from outright graft to a lack of competition, poor regulation and the transfer of public assets to firms at bargain prices. Well-placed people have made their fortunes this way ever since rulers had enough power to issue profitable licences, permits and contracts to their cronies. In America, this system reached its apogee in the late 19th century, and a long and partially successful struggle against robber barons ensued. Antitrust rules broke monopolies such as John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil. The flow of bribes to senators shrank.
In the emerging world, the past quarter-century has been great for rent-seekers. Soaring property prices have enriched developers who rely on approvals for projects. The commodities boom has inflated the value of oilfields and mines, which are invariably intertwined with the state. Some privatisations have let tycoon's milk monopolies or get assets cheaply. The links between politics and wealth are plainly visible in China, where a third of billionaires are party members.
Capitalism based on rent-seeking is not just unfair, but also bad for long-term growth. As our briefing on India explains, resources are misallocated: crummy roads are often the work of crony firms. Competition is repressed: Mexicans pay too much for their phones. Dynamic new firms are stifled by better-connected incumbents. And if linked to the financing of politics, rent-heavy capitalism sets a tone at the top that can let petty graft flourish. When ministers are on the take, why shouldn't underpaid junior officials be?
Q. Which of the following statements are valid with reference to the above passage?
1. Rent seeking was a fortune maker for the ruler's cronies
2. Only politicians can make money by seeking rent.
Passage 1
"Rent-seeking" is what economists call a special type of money-making: the sort made possible by political connections. This can range from outright graft to a lack of competition, poor regulation and the transfer of public assets to firms at bargain prices. Well-placed people have made their fortunes this way ever since rulers had enough power to issue profitable licences, permits and contracts to their cronies. In America, this system reached its apogee in the late 19th century, and a long and partially successful struggle against robber barons ensued. Antitrust rules broke monopolies such as John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil. The flow of bribes to senators shrank.
In the emerging world, the past quarter-century has been great for rent-seekers. Soaring property prices have enriched developers who rely on approvals for projects. The commodities boom has inflated the value of oilfields and mines, which are invariably intertwined with the state. Some privatisations have let tycoon's milk monopolies or get assets cheaply. The links between politics and wealth are plainly visible in China, where a third of billionaires are party members.
Capitalism based on rent-seeking is not just unfair, but also bad for long-term growth. As our briefing on India explains, resources are misallocated: crummy roads are often the work of crony firms. Competition is repressed: Mexicans pay too much for their phones. Dynamic new firms are stifled by better-connected incumbents. And if linked to the financing of politics, rent-heavy capitalism sets a tone at the top that can let petty graft flourish. When ministers are on the take, why shouldn't underpaid junior officials be?
Q. According to the passage, which of the following statement(s) are NOT correct?
1. The rent seeking system ended the struggle against robber barons in America
2. China exemplifies the close relationship between politics and wealth
Passage 1
"Rent-seeking" is what economists call a special type of money-making: the sort made possible by political connections. This can range from outright graft to a lack of competition, poor regulation and the transfer of public assets to firms at bargain prices. Well-placed people have made their fortunes this way ever since rulers had enough power to issue profitable licences, permits and contracts to their cronies. In America, this system reached its apogee in the late 19th century, and a long and partially successful struggle against robber barons ensued. Antitrust rules broke monopolies such as John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil. The flow of bribes to senators shrank.
In the emerging world, the past quarter-century has been great for rent-seekers. Soaring property prices have enriched developers who rely on approvals for projects. The commodities boom has inflated the value of oilfields and mines, which are invariably intertwined with the state. Some privatisations have let tycoon's milk monopolies or get assets cheaply. The links between politics and wealth are plainly visible in China, where a third of billionaires are party members.
Capitalism based on rent-seeking is not just unfair, but also bad for long-term growth. As our briefing on India explains, resources are misallocated: crummy roads are often the work of crony firms. Competition is repressed: Mexicans pay too much for their phones. Dynamic new firms are stifled by better-connected incumbents. And if linked to the financing of politics, rent-heavy capitalism sets a tone at the top that can let petty graft flourish. When ministers are on the take, why shouldn't underpaid junior officials be?
Q. The reason petty corruption in politics flourished is :
Passage 1
"Rent-seeking" is what economists call a special type of money-making: the sort made possible by political connections. This can range from outright graft to a lack of competition, poor regulation and the transfer of public assets to firms at bargain prices. Well-placed people have made their fortunes this way ever since rulers had enough power to issue profitable licences, permits and contracts to their cronies. In America, this system reached its apogee in the late 19th century, and a long and partially successful struggle against robber barons ensued. Antitrust rules broke monopolies such as John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil. The flow of bribes to senators shrank.
In the emerging world, the past quarter-century has been great for rent-seekers. Soaring property prices have enriched developers who rely on approvals for projects. The commodities boom has inflated the value of oilfields and mines, which are invariably intertwined with the state. Some privatisations have let tycoon's milk monopolies or get assets cheaply. The links between politics and wealth are plainly visible in China, where a third of billionaires are party members.
Capitalism based on rent-seeking is not just unfair, but also bad for long-term growth. As our briefing on India explains, resources are misallocated: crummy roads are often the work of crony firms. Competition is repressed: Mexicans pay too much for their phones. Dynamic new firms are stifled by better-connected incumbents. And if linked to the financing of politics, rent-heavy capitalism sets a tone at the top that can let petty graft flourish. When ministers are on the take, why shouldn't underpaid junior officials be?
Q. Which of the following is caused by rent heavy Capitalism?
1. Competition is repressed
2. Inflation occurs
3. Bribery flourishes
4. Long term growth suffer
Passage 2
Newton's surprising success at developing the laws of motion, as well as the development and refinement of other physical laws, led to the idea of scientific determinism. The first expression of this principle was in the beginning of the nineteenth century by Laplace, a French scientist. Laplace argued that if one knew the position and velocity of all the particles in the universe at a given time, the laws of physics would be able to predict the future state of the universe.
Scientific determinism held sway over a great many scientists until the early twentieth century, when the quantum mechanics revolution occurred. Quantum mechanics introduced the world to the idea of the uncertainty principle, which stated that it was impossible to accurately measure both the position and the velocity of a particle at one time. Because Laplace's omniscience could never occur, even in theory, the principle of scientific determinism was thrown into doubt. However, quantum mechanics does allow for a reduced form of scientific determinism. Even though physicists are unable to know precisely where a particle is and what its velocity is, they can determine certain probabilities about its position and velocity. These probabilities are called wave functions. By use of a formula known as the Schrodinger equation, a scientist with the wave function of a particle at a given time can calculate the particle's future wave function. These calculations can give the particle's position or velocity, but not both. Thus, the physicist is in possession of exactly half of the information needed to satisfy Laplace's view of determinism. Unfortunately, under modern physics theories, that is far as any researcher can go in predicting the future.
Q. The passage suggests that if scientific determinism were TRUE:
Passage 2
Newton's surprising success at developing the laws of motion, as well as the development and refinement of other physical laws, led to the idea of scientific determinism. The first expression of this principle was in the beginning of the nineteenth century by Laplace, a French scientist. Laplace argued that if one knew the position and velocity of all the particles in the universe at a given time, the laws of physics would be able to predict the future state of the universe.
Scientific determinism held sway over a great many scientists until the early twentieth century, when the quantum mechanics revolution occurred. Quantum mechanics introduced the world to the idea of the uncertainty principle, which stated that it was impossible to accurately measure both the position and the velocity of a particle at one time. Because Laplace's omniscience could never occur, even in theory, the principle of scientific determinism was thrown into doubt. However, quantum mechanics does allow for a reduced form of scientific determinism. Even though physicists are unable to know precisely where a particle is and what its velocity is, they can determine certain probabilities about its position and velocity. These probabilities are called wave functions. By use of a formula known as the Schrodinger equation, a scientist with the wave function of a particle at a given time can calculate the particle's future wave function. These calculations can give the particle's position or velocity, but not both. Thus, the physicist is in possession of exactly half of the information needed to satisfy Laplace's view of determinism. Unfortunately, under modern physics theories, that is far as any researcher can go in predicting the future
Q. According to the passage, wave functions:
Passage 2
Newton's surprising success at developing the laws of motion, as well as the development and refinement of other physical laws, led to the idea of scientific determinism. The first expression of this principle was in the beginning of the nineteenth century by Laplace, a French scientist. Laplace argued that if one knew the position and velocity of all the particles in the universe at a given time, the laws of physics would be able to predict the future state ofthe universe.
Scientific determinism held sway over a great many scientists until the early twentieth century, when the quantum mechanics revolution occurred. Quantum mechanics introduced the world to the idea of the uncertainty principle, which stated that it was impossible to accurately measure both the position and the velocity of a particle at one time. Because Laplace's omniscience could never occur, even in theory, the principle of scientific determinism was thrown into doubt. However, quantum mechanics does allow for a reduced form of scientific determinism. Even though physicists are unable to know precisely where a particle is and what its velocity is, they can determine certain probabilities about its position and velocity. These probabilities are called wave functions. By use of a formula known as the Schrodinger equation, a scientist with the wave function of a particle at a given time can calculate the particle's future wave function. These calculations can give the particle's position or velocity, but not both. Thus, the physicist is in possession of exactly half ofthe information needed to satisfy Laplace's view ofdeterminism. Unfortunately, under modern physics theories, that is far as any researcher can go in predicting the future.
Q. Which of the following best describes the organization of the passage?
Passage 2
Newton's surprising success at developing the laws of motion, as well as the development and refinement of other physical laws, led to the idea of scientific determinism. The first expression of this principle was in the beginning of the nineteenth century by Laplace, a French scientist. Laplace argued that if one knew the position and velocity of all the particles in the universe at a given time, the laws of physics would be able to predict the future state of the universe.
Scientific determinism held sway over a great many scientists until the early twentieth century, when the quantum mechanics revolution occurred. Quantum mechanics introduced the world to the idea of the uncertainty principle, which stated that it was impossible to accurately measure both the position and the velocity of a particle at one time. Because Laplace's omniscience could never occur, even in theory, the principle of scientific determinism was thrown into doubt. However, quantum mechanics does allow for a reduced form of scientific determinism. Even though physicists are unable to know precisely where a particle is and what its velocity is, they can determine certain probabilities about its position and velocity. These probabilities are called wave functions. By use of a formula known as the Schrodinger equation, a scientist with the wave function of a particle at a given time can calculate the particle's future wave function. These calculations can give the particle's position or velocity, but not both. Thus, the physicist is in possession of exactly half of the information needed to satisfy Laplace's view of determinism. Unfortunately, under modern physics theories, that is far as any researcher can go in predicting the future
Q. Which of the following, if true, would most strengthen the author's conclusion in the passage's final sentence?
Directions for the following 4 (four) questions:
Following table shows tea production data of India for various years. Study the following graph and answer the questions.
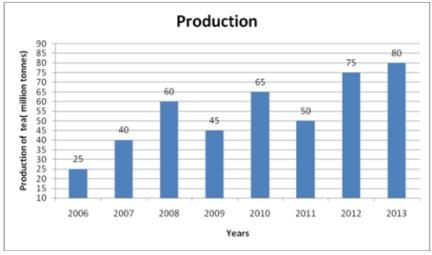
Q. Which year has maximum increment in percentage value compared to previous year?
Following table shows tea production data of India for various years. Study the following graph and answer the questions.
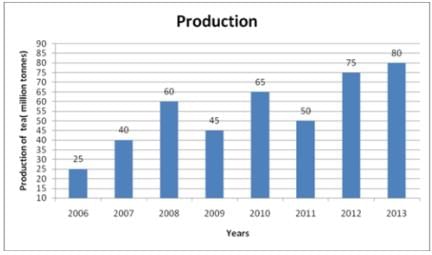
Q. What is percentage increase in production for 2013 when compared with 2008?
Following table shows tea production data of India for various years. Study the following graph and answer the questions.
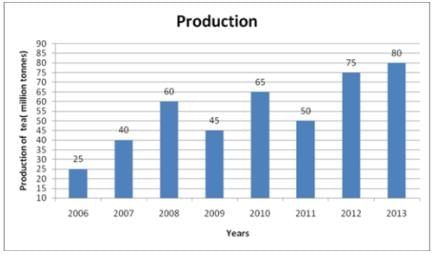
Q. Out of eight years, in how many years production was lesser than simple average of all eight years?
Following table shows tea production data of India for various years. Study the following graph and answer the questions.

Q. What is difference between simple average of first four years and last four years?
The number of solutions of (x2 + 1)2 + 2(x2 + 1) - 3 = 0 is equal to
If f(x) = x - 4, then what is value of f(f(3)) = ?
Which of the following has maximum value?
P and Q are two real numbers.
How many solutions do the equation 1/x + 1/(x + 1) = 1/3 have?
Let f(x) = 2x + 4. Which of the following statements is true?
The lines y = 2x and 2y = -x are
Write following sentence in mathematical form "The price is no less than 100 rupees and is at most 145"
Directions for following 4(four) questions:
Following chart indicates internal division of electricity usage for two years. Study the graph carefully and answer questions given below.
Q. If consumption in one sector is increased it will be marked 2 and decreased then by -1. If it remained unchanged then it will marked as 0. What is total of all 6 sectors?
Following chart indicates internal division of electricity usage for two years. Study the graph carefully and answer questions given below.
Q. Total electricity consumption in 2012 is 1.5 times of the total electricity consumption in 2011, then what is percentage increase in the electricity consumption of the agricultural sector?
Following chart indicates internal division of electricity usage for two years. Study the graph carefully and answer questions given below.
Q. What is maximum number of sectors one should add to cross 50% consumption for 2012 year?
Following chart indicates internal division of electricity usage for two years. Study the graph carefully and answer questions given below.
Q. The agricultural consumption of electricity doubled for given years. By how much percentage has the total electricity consumption grown up?
Directions for the following 9 (nine) items:
Read the following four passages and answer the items that follow each passage. Your answers to these items should be based on these passages only.
Passage 1
The Slavic languages are a group of closely related languages that have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and certain parts of Asia. The Slavic languages are broadly divided into three main branches, including East Slavic, West Slavic, and South Slavic, each of which is further divided into subgroups. The standard, or literary, components of each of the Slavic languages are distinct. However, the spoken dialects of each language are often closely related, and there exist what scholars call transitional dialects that bridge the gaps between the three Slavic languages. The common ancestor of the three Slavic languages is believed to be the Proto-Baltic-Slavic language, a dialect spoken approximately 3,000 B.C. in what today is Lithuania. The fact that the three branches of Slavic languages share approximately 280 words is usually given as proof for such a parent, ancestor language.
Q. What would be an appropriate title for this short passage?
Passage 1
The Slavic languages are a group of closely related languages that have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and certain parts of Asia. The Slavic languages are broadly divided into three main branches, including East Slavic, West Slavic, and South Slavic, each of which is further divided into subgroups. The standard, or literary, components of each of the Slavic languages are distinct. However, the spoken dialects of each language are often closely related, and there exist what scholars call transitional dialects that bridge the gaps between the three Slavic languages. The common ancestor of the three Slavic languages is believed to be the Proto-Baltic-Slavic language, a dialect spoken approximately 3,000 B.C. in what today is Lithuania. The fact that the three branches of Slavic languages share approximately 280 words is usually given as proof for such a parent, ancestor language.
Q. According to the author, which of the following is TRUE?
Passage 2
The St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre was a series of Catholic mob violence episodes against members of the French Protestant Reformed Church. On August 24, 1572, Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, the leader of the Protestant Reformed Church, was murdered, and this set of a crime wave that continued for well over one month and spread throughout the French countryside. In all, it is estimated that 50,000 people were killed. The events which transpired in France in August and September of 1572 were the result of many factors, including the Glorious Reformation which had its roots in Germany and because of growing strife within the Catholic Church. However, historians disagree whether the massacre was premeditated, and in fact many now agree that Rome had only a secondary role in the planning and execution of the massacre. However, proponents of the idea that Rome was directly responsible for the massacre refer to the fact that Pope Gregory XIII commissioned the production of a special commemorative medal to honor the massacre of the Protestants.
Q. Which of the following statements would the author most likely disagree with?
Passage 2
The St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre was a series of Catholic mob violence episodes against members of the French Protestant Reformed Church. On August 24, 1572, Admiral Gaspard de Coligny, the leader of the Protestant Reformed Church, was murdered, and this set of a crime wave that continued for well over one month and spread throughout the French countryside. In all, it is estimated that 50,000 people were killed. The events which transpired in France in August and September of 1572 were the result of many factors, including the Glorious Reformation which had its roots in Germany and because of growing strife within the Catholic Church. However, historians disagree whether the massacre was premeditated, and in fact many now agree that Rome had only a secondary role in the planning and execution of the massacre. However, proponents of the idea that Rome was directly responsible for the massacre refer to the fact that Pope Gregory XIII commissioned the production of a special commemorative medal to honor the massacre of the Protestants.
Q. Which of the following best describes the development of the passage?
Passage-3
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31, NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light- years away from Earth. The Andromeda Galaxy is in the constellation Andromeda, and it is the nearest spiral galaxy to our own, the Milky Way. Both the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy are members of the Local Group, which also includes the Griangulum Galaxy, among others. Until recently, it was believed that the Andromeda Galaxy had the greatest mass of the three Galaxies in the Local Group, but recent findings suggest that the Milky Way has the most dark matter out of the three, and this fact may suggest that in fact the Milky Way is the most massive. Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter. In terms of the actual number of stars, however, the Andromeda Galaxy contains approximately 1 trillion stars, which is much more than are contained in the Milky Way.
The Andromeda Galaxy is visible to the naked eye in a moderately dark sky, and it appears quite small without a telescope because only the central part is bright enough to be visible. However, the angular diameter of the Andromeda Galaxy is seven times that of the full moon, and so if all of the stars of the Andromeda Galaxy were easily visibly to the naked eye, the galaxy would be the dominant object in the sky.
Q. According to the passage, which of the following is TRUE?
Passage-3
The Andromeda Galaxy, also known as Messier 31, NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light- years away from Earth. The Andromeda Galaxy is in the constellation Andromeda, and it is the nearest spiral galaxy to our own, the Milky Way. Both the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy are members of the Local Group, which also includes the Griangulum Galaxy, among others. Until recently, it was believed that the Andromeda Galaxy had the greatest mass of the three Galaxies in the Local Group, but recent findings suggest that the Milky Way has the most dark matter out of the three, and this fact may suggest that in fact the Milky Way is the most massive. Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter. In terms of the actual number of stars, however, the Andromeda Galaxy contains approximately 1 trillion stars, which is much more than are contained in the Milky Way.
The Andromeda Galaxy is visible to the naked eye in a moderately dark sky, and it appears quite small without a telescope because only the central part is bright enough to be visible. However, the angular diameter of the Andromeda Galaxy is seven times that of the full moon, and so if all of the stars of the Andromeda Galaxy were easily visibly to the naked eye, the galaxy would be the dominant object in the sky.
Q. In the passage, the author writes, "Scientists are still uncertain, and more research is needed to settle the matter," referring to the fact that scientists are uncertain about the relative masses of the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy. If the author wanted to include more details about this, which of the following should also be included in the passage?














