UPSC CAPF Paper 1 Mock Test - 8 (General & Mental Ability) - CDS MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - UPSC CAPF Paper 1 Mock Test - 8 (General & Mental Ability)
What do Core Interests and Temporary Interests represent in the context of national interests?
In which year the first meeting of Constituent Assembly took place?
Which party always won elections in Mexico since its independence in 1930 until 2000?
Which of the following materials CANNOT be recycled?
What type of radiation is trapped on the earth’s surface by the green house effect ?
Porosity of a soil sample is the ratio of:
The coefficient of price elasticity of demand is always
Workers in the______________ sector do not produce goods.
The reward for labor is known as:
What does monotonicity of preferences imply?
Who was sworn in as Pakistan's 14th President?
A student heats 25g of reactant ‘A’ with 50g of reactant ‘B’. He obtains 50g of product ‘C’ and recovers 25 g of unreacted ‘B’. Which of the following law is confirmed in the following reaction?
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the object is at:
In Newlands law of octaves elements are arranged in order of
When light rays from stars enter into earth’s atmosphere, it travels from
Which of the following constitute a food chain ?
The angle of elevation of a ladder leaning against a wall is 60º and the foot of the ladder is 4.6 m away from the wall. The length of the ladder is:
Arrange the following famous Ancient Indian astronomers and mathematicians in the chronological order:
I. Aryabhatta
II. Varahamihira
III. Brahmagupta
IV. Bhaskara
What was the name of the Sultan who ascended the throne of Delhi after the death of Balban?
The fortress of Vijayanagar was located on the bank of the river
There were some immediate factors that led to the birth of the Indian National Congress in 1885. Which of the following was not one such factor?
Who said: “The British rule was a bleeding drain from India”?
A sample of milk diluted with water has density 1036kgm−3. if pure milk has a density 1080kgm−3 what is the percentage of water by volume in milk ?
Time rate of flow of electric charge measures electric _________.
Which of the following statements can help a chemistry student to predict chemical properties of an element?
(I) Position of element in the periodic table
(II) Atomic number of the element
(III) Number of shells in the atom
(IV) Number of electrons in the outermost shell.
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
MO : 13 11 :: HJ : ?
Directions to Solve
In each of the following questions find out the alternative which will replace the question mark.
Question -
8 : 28 :: 27 : ?



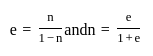

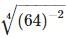 is
is 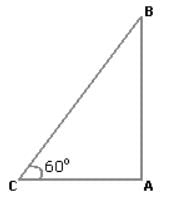
 ACB = 60º and AC = 4.6 m.
ACB = 60º and AC = 4.6 m.

















