JEE Main Part Test - 2 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test Mock Tests for JEE Main and Advanced 2026 - JEE Main Part Test - 2
In aqueous solution the ionization constants for carbonic acid are K1 = 4.2 x 10-7 and K2 = 4.8 x 10-11 Selection the correct statement for a saturated 0.034 M solution of the carbonic acid.
[AIEEE-2010]
A particle is projected upward from the surface of earth (radius = R) with a speed equal to the orbital speed of a satellite near the earth’s surface. The height to which it would rise is
A spherical hole is made in a solid sphere of radius R. The mass of the original sphere was M.The gravitational field at the centre of the hole due to the remaining mass is
A spray gun is shown in the figure where a piston pushes air out of a nozzle. A thin tube of uniform cross section is connected to the nozzle. The other end of the tube is in a small liquid container.
As the piston pushes air through the nozzle, the liquid from the container rises into the nozzle and is sprayed out. For the spray gun shown, the radii of the piston and the nozzle are 20 mm and 1 mm respectively. The upper end of the container is open to the atmosphere.

Q. If the piston is pushed at a speed of 5 mms–1, the air comes out of the nozzle with a speed of
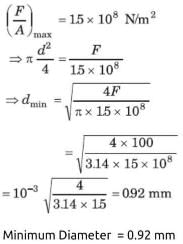
If the elastic limit of copper is 1.5 × 108 N/ m2, determine the minimum diameter a copper wire can have under a load of 10.0 kg if its elastic limit is not to be exceeded.
A circular steel wire 2.00 m long must stretch no more than 0.25 cm when a tensile force of 400 N is applied to each end of the wire. What minimum diameter is required for the wire? Young's modulus for steel: E = 20 × 1010 Pa .
Water is flowing continuously from a tap having an internal diameter 8 × 10-3m. The water velocity as it leaves the tap is 0.4 ms-1. The diameter of the water stream at a distance 2 × 10-1 m below the tap is close to
[AIEEE 2011]
There are two identical small holes on the opposite sides of a tank containing a liquid. The tank is open at the top. The difference in height between the two holes is h. As the liquid comes out of the two holes, the tank will experience a net horizontal force proportional to
Two soap bubbles with radii come in contact. Their common surface has a radius of curvature r. Then
The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab, consisting of two materials having coefficients of thermal conductivity K and 2K and thickness x and 4x, respectively, are T2 and T1 (T2 >T1) . The rate of heat transfer through the slab, in a steady state is 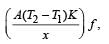 with f equal to
with f equal to 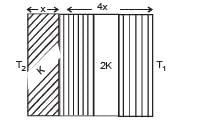
The complex [Fe(H2O)5NO]2+ is formed in the ring-test for nitrate ion when freshly prepared FeSO4 solution is added to aqueous solution of
followed by the addition of conc. H2SO4. NO exists as NO+ (nitrosyl).
Q. Magnetic moment of Fe in the ring is
The pKa of a weak acid, HA, is 4.80. The pKb of a weak base, BOH, is 4.78. The pH of an aqueous solution of the corresponding salt, BA, will be -
[AIEEE-2008]
How many litres of water must be added to litre of an aqueous solution of HCl with a pH of 1 to create an aqueous solution with pH of 2?
[AIEEE-2013]
For the following electrochemical cell reaction at 298 K:
Zn(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) ⇌ Cu(s) + Zn²⁺(aq),
Given that the standard cell potential (E° cell) is +1.10 V.
A 0.10 M solution of a weak acid, HX, is 0.059% ionized. Evaluate Ka for the acid.
AgCI(s)is sparingly soluble salt,
AgCl (s)  Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
There is
Which one of the following is the approximate pH of 0.01 M solution of NaOH at 298 k?
In the expansion of (1+x)60, the sum of coefficients of odd powers of x is
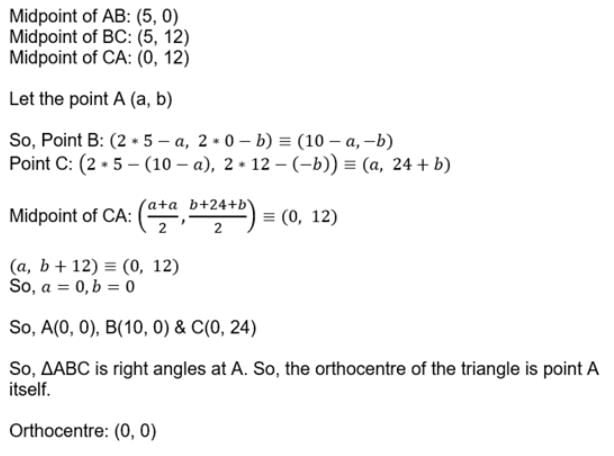
The mid points of the sides of a triangle are (5, 0), (5, 12) and (0, 12), then orthocentre of this triangle is
Area of a triangle whose vertices are (a cos q, b sinq), (–a sin q, b cos q) and (–a cos q, –b sin q) is
If A(cosa, sina), B(sina, – cosa), C(1, 2) are the vertices of a ΔABC, then as a varies, the locus of its centroid is
Two perpendicular tangents to the circle x2+y2 = r2 meet at P. The locus of P is
The locus of a variable point whose distance from the point (2, 0) is 2/3 times its distance from the line x = 9/2 is
The locus of a point such that two tangents drawn from it to the parabola y2 = 4ax are such that the slope of one is double the other is
Two vertices of a triangle are (3,−2) and (−2, 3) and its orthocentre is (−6, 1). The coordinates of its third vertex are-
|
517 docs|120 tests
|


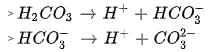
 cannot be 0.034 M as there is no complete dissociation.
cannot be 0.034 M as there is no complete dissociation. 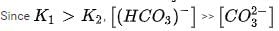
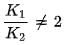 . So The concentration of H+ is not double that of
. So The concentration of H+ is not double that of 
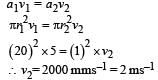
 E = 20 × 1010 Pa .
E = 20 × 1010 Pa .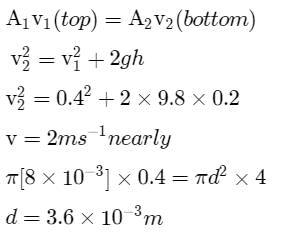
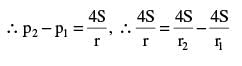
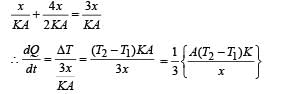
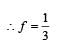
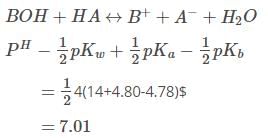
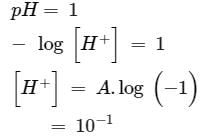
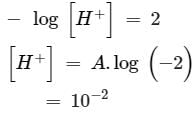
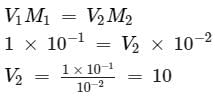
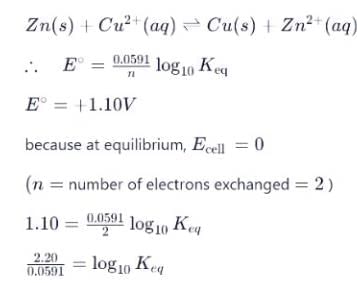
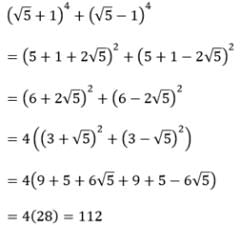
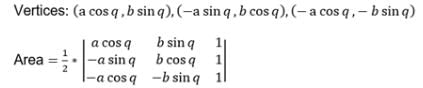
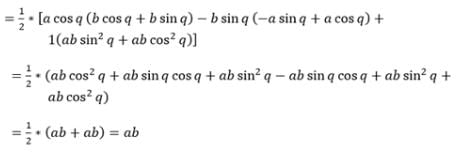

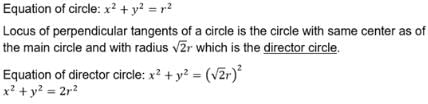

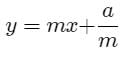
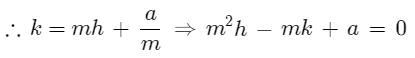

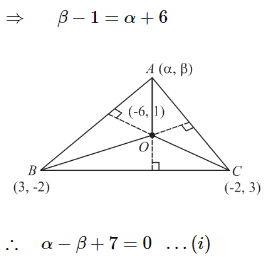
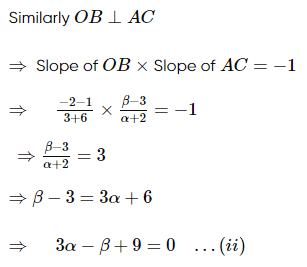
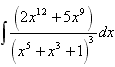 is equal to
is equal to