Test: Stereochemistry Level - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Stereochemistry Level - 2
Ring flipping of the compound in the following conformation leads to:
Draw the structure of (2R, 3S) – 2, 3 – dichloropentane:
The most stable confirmation of following compound is:
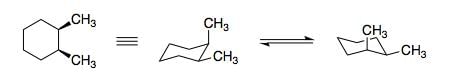
Structure of 1, 2-dimethylcyclohexane is show below. Which of the following is an enantiomer to the given conformer:
Which is the most stable conformation of 1-chloro-4-methylcyclohexane:
Which of the following is a structure representation is R-Lactic acid:
The favored conformation (gauche, anti) for the molecule 1, 2-dichloro ethane; and 1,2-ethanediol will be respectively:
Which of the following term best describes the pair of compound shown below:
The major product is formed in the following reaction is:
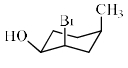
The configurations at the three chiral centres in the bicyclodecano l given below, are:
The S enantiomer of ibuprofen is responsible for its pain – relieving properties. Which one of the following structures shown in (S) – ibuprofen:
The major product formed in the following reaction is:
Draw the structure of (1 R, 2 S, 3 S)-1, 2-dibromo-3-ethyl cyclo hexane:
The absolute configurations of the chiral centers in X and Y are:
Stereoisomers which are not mirror image isomers are:
The configuration of the following position of (I) and (II) is:
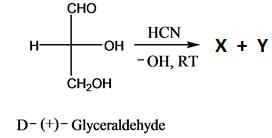
Which is the correct structure of D-Glyceraldehyde:
Which of the following structure represents meso compounds:
Which of the following statements is true for the compound (R)-2-butanol:
Among the structures given below, the most stable conformation for the following compound is:
Which of the following term correctly describes the structural relationship between cis-1,3 dimethyl cyclopentane and trans-1,3-dimethyl cyclopentane:
The gauche conformation (θ = 60o) of n-butane possess:
The absolute configuration of the two stereogenic (Chiral) centers in the following molecule is:
The gauche interaction values for Me/Me, Me/Br and Br/Br are 3.3, 0.8 and 3.0 kJ/mol, respectively. Among the following, the most stable conformation of 2,3-dibromobutane is:
The most stable conformations of 1,2-difluoroethane and dl-2, 3-butanediol are: