Test: IR Spectroscopy - Chemistry MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Test: IR Spectroscopy
Which compound having molecular formula C5H10 shows absorption at 1380 cm-1?
What is the effect of ring strain in lactone (cyclic ester) or a lactam (cyclic amide)?
What is the relation between wave number of IR absorption and the reduced mass?
Which of the following molecules will not show infrared spectrum?
Why Monomeric saturated aliphatic carboxylic acids show carbonyl stretching frequency near 1760 cm-1, while saturated aliphatic ketones near 1720 cm-1?
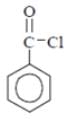
Why in the IR spectrum of Benzoyl chloride, a weak band near 1750 cm-1 is formed?
Why ketenes absorb in IR at a very high frequency (2150 cm-1)?
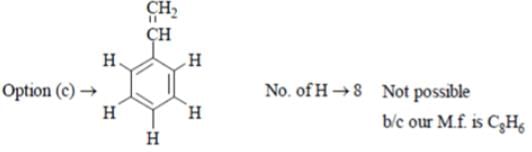
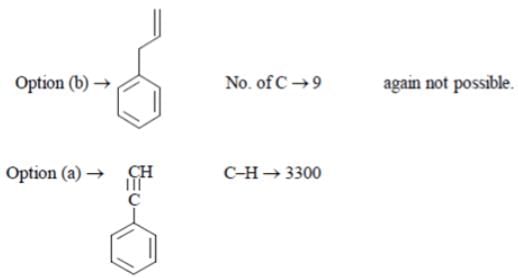
A compound C8 H6 decolorizes Br2 in CCl4 and gives a white precipitate with Tollen’s reagent. It has sharp band at 3300 cm-l and weak bands at 3085, 2110 cm-l. What is this compound?
What is the number of vibrational degrees of freedom in C6H5CH3?
The phosphorescence spectrum of the excited species is due to which transition?



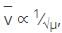 , frequency is directly proportional to wave number. So, wave number is inversely proportional to reduced mass as shown in the above relation.
, frequency is directly proportional to wave number. So, wave number is inversely proportional to reduced mass as shown in the above relation.