Test: Balancing of Single & Multi Cylinder Engines & Linear Vibration Analysis of Mechanical Systems - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Balancing of Single & Multi Cylinder Engines & Linear Vibration Analysis of Mechanical Systems - 2
Consider the following statements for a 4-cylinder inline engine whose cranks are arranged at regular intervals of 90°:
1. There are 8 possible firing orders for the engine.
2. Primary force will remain unbalanced for some firing orders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
2. Primary force will remain unbalanced for some firing orders.
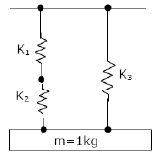
A mass of 1 kg is suspended by means of 3 springs as shown in figure. The spring constants K1, K2 and K3 are respectively 1 kN/m, 3kN/m and 2 kN/m. The natural frequency of the system is approximately
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
The primary disturbing force due to inertia of reciprocating parts of mass m at radius r moving with an angular velocity ω is given by
If the length of the cantilever beam is halved, then natural frequency of the mass M at the end of this cantilever beam of negligible mass is increased by a factor of
If the ratio of the length of connecting rod to the crank radius increases, then
The assembly shown in the figure is composed of two mass less rods of length ‘l’ with two particles, each of mass m. The natural frequency of this assembly for small oscillations is
Assertion (A): For a radial engine containing four or more cylinders, the secondary forces are in complete balance,
Reason (R): The secondary direct and reverse cranks form a balanced system in the radial engines.
There are four samples P, Q, Rand S, with natural frequencies 64, 96, 128 and 256 Hz, respectively. They are mounted on test setups for conducting vibration experiments. If a loud pure note of frequency 144 Hz is produced by some instrument, which of the samples will show the most perceptible induced vibration?
A single cylinder, four-stroke I.C. engine rotating at 900 rpm has a crank length of 50 mm and a connecting rod length of 200 mm. if the effective reciprocating mass of the engine is 1.2 kg, what is the approximate magnitude of the maximum ‘shaking force’ created by the engine?
In a spring-mass system, the mass is 0.1 kg and the stiffness of the spring is 1 kN/m. By introducing a damper, the frequency of oscillation is found to be 90% of the original value. What is the damping coefficient of the damper?
When the primary direct crank of a reciprocating engine is positioned at 30° clockwise, the secondary reverse crank for balancing will be at
A machine of 250 kg mass is supported on springs of total stiffness 100 kN/m. Machine has an unbalanced rotating force of 350 N at speed of 3600 rpm. Assuming a damping factor of 0.15, the value of transmissibility ratio is
In a multi-cylinder in-line internal combustion engine, even number of cylinders is chosen so that
A mass M, of 20 kg is attached to the free end of a steel cantilever beam of length 1000 mm having a cross-section of 25 x 25 mm. Assume the mass of the cantilever to be negligible and Esteel = 200 GPa. If the lateral vibration of this system is critically damped using a viscous damper, then damping constant of the damper is
Which of the following pair(s) is/are correctly matched?
I. Four bar chain……………………….Oscillating - Oscillating converter
II. Inertia governor……………………... Rate of change of engine speed
III. Hammer blow ………………………Reciprocating unbalance.
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
A mass m attached to a spring is subjected to a harmonic force as shown in figure. The amplitude of the forced motion is observed to be 50 mm. The value of m (in kg) is
Assertion (A): d' Alembert's principle is known as the principle of dynamic equilibrium.
Reason(R): d' Alembert's principle converts a dynamic problem into a static Problem.
A vibratory system consists of a mass 12.5 kg, a spring of stiffness 1000 N/m, and a dashpot with damping coefficient of 15 Ns/m.
The value of logarithmic decrement is:
In the figure given above, when is the absolute velocity of end B of the coupler equal to the absolute velocity of the end A of the coupler?
The value of critical damping of the system is
In case of reciprocating engines the primary forces
A vehicle suspension system consists of a spring and a damper. The stiffness of the spring is 3.6 kN/m and the damping constant of the damper is 400 Ns/m. If the mass is 50 kg, then the damping factor ξξ and damped natural frequency (fd), respectively, are
Consider the following statements:
An in-line four-cylinder four-stroke engine is completely balanced for
1. primary forces
2. secondary forces
3. primary couples
4. secondary couples
Of these statements:
A reciprocating engine, running at 80 rad/s, is supported on springs. The static deflection of the spring is 1 mm. Take g = 10 rn/s2. When the engine runs, what will be the frequency of vibrations of the system?
What causes a variation in the tractive effort of an engine?
If air resistance is neglected, while it is executing small oscillations the acceleration of the bob of a simple pendulum at the mid-point of its swing will be
The method of direct and reverse cranks is used in engines for
The static deflection of a shaft under a flywheel is 4 mm. Take g = 10m/s2. What is the critical speed in rad/s?
What causes a variation in the tractive effort of an engine?
A rod of uniform diameter is suspended from one of its ends in vertical plane. The mass of the rod is 'm' and length ' ℓ ', the natural frequency of this rod in Hz for small amplitude is
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|

















