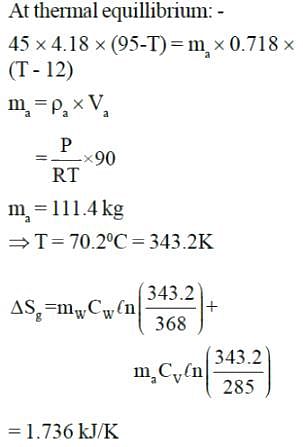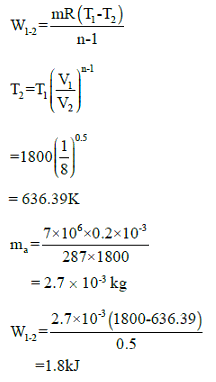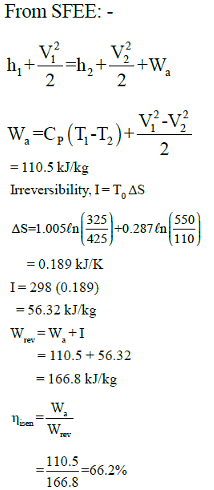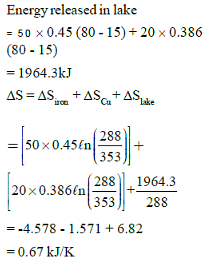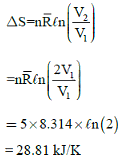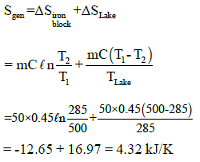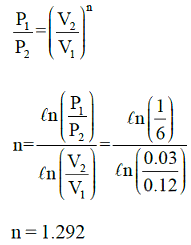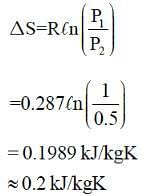Test: Basic Thermodynamics - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Basic Thermodynamics
Air undergoes a polytropic process in an adiabatic nozzle with n = 1.2. Inlet state of air is 800 kPa, 1230C with a velocity of 32 m/s and exit state is 300 kPa. Find out the velocity of air at nozzle exit.
A 5m X 8m X 0.3m size concrete slab ( ρ = 2200 kg/m3, CP = 0.88 kJ/kg-K) is used as thermal storage mass in solar heated house. If slab cools overnight from 230C to 180C in 180C house, what will be the net entropy change associated with process?
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Water at 950C having mass of 45 kg is filled in a container and is placed in well-insulated room. Heat transfer takes place between water and air in room till thermal equilibrium is established. Entropy generation will be: - Vair = 90m3, Tair = 120C, P = 101.3kPa, CW = 4.18 kJ/kg-K, CP = 1.005 kJ/K
The reading of the pressure gauge fitted on a vessel is 25 bar. The atmospheric pressure is 1.03 bar and the value of 'g' is 9.81 m/s2. The absolute pressure in the vessel is
Consider air in a cylinder volume of 0.2 L at 7 MPa, 1800K. It now expands in a reversible polytropic process with exponent, n = 1.5, through a volume ratio of 8:1. Calculate the work for the process.
Common data for 6, 7 & 8:
In adiabatic turbine, air enters at 550 kPa, 425K and leaves at 110kPa, 325K. The inlet and exit velocities of air are 150m/s and 50m/s respectively
T0 = 250C, CP = 1.005 kJ/kg-K, R = 0.287 kJ/kg-K
Q. Actual work will be:-
Common data for 6, 7 & 8:
In adiabatic turbine, air enters at 550 kPa, 425K and leaves at 110kPa, 325K. The inlet and exit velocities of air are 150m/s and 50m/s respectively
T0 = 250C, CP = 1.005 kJ/kg-K, R = 0.287 kJ/kg-K
Q. Reversible work will be:-
Common data for 6, 7 & 8:
In adiabatic turbine, air enters at 550 kPa, 425K and leaves at 110kPa, 325K. The inlet and exit velocities of air are 150m/s and 50m/s respectively
T0 = 250C, CP = 1.005 kJ/kg-K, R = 0.287 kJ/kg-K
Q. Isentropic efficiency is: -
What is the effect on internal energy during adiabatic expansion process in a closed system?
An insulated tank contains 120L of water at 250C ( ρ = 997 kg/m3, CP = 4.18 kJ/kg0C). A 50kg copper block (CP = 0.386 kJ/kg0C) initially at 800C is dropped into water. Total entropy change for this process will be:-
Two blocks of iron and copper, both initially at 800C, are dropped into a large lake at 150C. The mass of the iron and copper blocks are 50kg and 20 kg respectively. After a while, the system is in thermal equilibrium due to heat transfer between blocks and lake water.
Total entropy change for this process is:-
Ciron = 0.45 kJ/kg0C, Ccopper = 0.386 kJ/kg0C
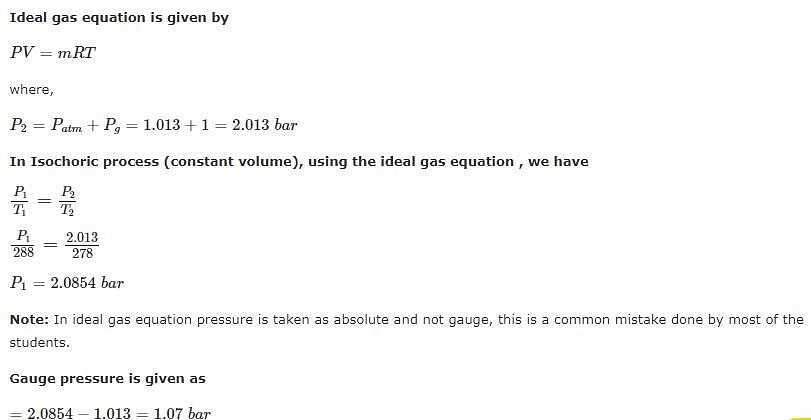
A football was inflated to a gauge pressure of 1 bar when the ambient temperature was 15°C. When the game started next day, the air temperature at the stadium was 5°C. Assume that the volume of the football remains constant at 2500 cm3. Gauge pressure of air to which the ball must have been originally inflated so that it would equal 1 bar gauge at the stadium is _____.
A rigid insulated tank has two equal parts by partition. First part initially contains 5k mol of an ideal gas at
500 kPa, 400C and other part is evacuated. If partition is removed, then the gas fills the entire tank, what will be the total entropy change during this process.
In an isobaric process, 1kg of air at 400K is mixed with 1kg of air at 500K. If pressure is 100 kPa and Q = 0, the entropy generation in process will be:-
Which of the following statements are true for a polytropic process.
[n < γ]
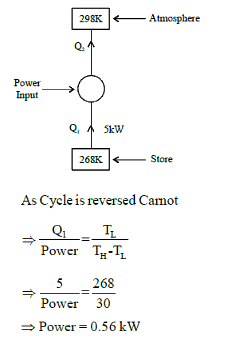
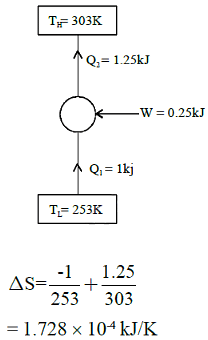
A refrigeration plant for food storage operates as a reversed carnot heat engine cycle. The store is to be maintained at -50C and the heat transfer from the store to the cycle is at the rate of 5 kW. If heat is transferred from the cycle to the atmosphere at a temperature of 250C, the power required to drive the plant is ____kW
(Important - Enter only the numerical value in the answer)
A 50-Kg block of iron casting at 500K is thrown into a large lake that is at a temperature of 285K. The iron block eventually reaches thermal equilibrium with the lake water. Assuming an average specific heat of 0.45 kJ/Kg-K for the iron, the entropy generation during the process is:
A cylinder contains 0.12m3 of air at 1 bar and 900C. It is compressed to 0.03m3, the final pressure being 6 bar. The index of the compression will be
Air at 100 KPa and 280 K is compressed steadily to 600 KPa and 400 K. The mass flow rate of air is 0.02 Kg/s and a heat loss of 16 kJ/Kg occurs during the process. The power input to compressor will be_____kW
Common data for 20 & 21:
An insulated nozzle is there in which helium gas enters with velocity of 10 m/s, operating at steady state at 1300K, 4 bar. At the exit, temperature & pressure of the helium are 900K and 1.45bar, respectively. The environment is at T0 = 200C and P0 = 1 atm.
Take CP = 5.1926 kJ/kg-K, R = 2.0769 kJ/kg-K, γ = 1.667
Q. Exit velocity of nozzle is: -
Common data for 20 & 21:
An insulated nozzle is there in which helium gas enters with velocity of 10 m/s, operating at steady state at 1300K, 4 bar. At the exit, temperature & pressure of the helium are 900K and 1.45bar, respectively. The environment is at T0 = 200C and P0 = 1 atm.
Take CP = 5.1926 kJ/kg-K, R = 2.0769 kJ/kg-K, γ = 1.667
Q. Rate of exergy destruction (in kJ/kg) is:-
Specific entropy generation when air at 1MPa, 300K is throttled to 0.5 MPa is: -
A refrigerator transfers 1kJ of heat from a cold region at -200C to hot region at 300C. If COP of refrigerator is 4, total entropy change of region’s will be:-
Air enters heat exchanger at 95 kPa and 200C with rate of 1.6 m3/s. The combustion gases (CP = 1.1 kJ/kg-0C) enters at 1800C with rate of 2.2 kg/s and leave at 950C. Rate of entropy generation is
Exit velocity of nozzle is 400m/s. If efficiency of nozzle is 0.88, what will be ideal exit velocity?
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|