Test: Modes of Heat Transfer - 1 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Modes of Heat Transfer - 1
For a given heat flow and for the same thickness, the temperature drop across the material will be maximum for
A copper block and air mass having similar dimensions are subjected to symmetrical heat transfer from once face of each block. The other face of the block will be reaching to the same temperature at a rate
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Consider the following statements:
The Fourier heat conduction equation Q =  presumes
presumes
1. Steady-state conditions
2. Constant value of thermal conductivity.
3. Uniform temperatures at the wall surfaces
4. One-dimensional heat flow. Of these statements:
The Fourier heat conduction equation Q =
1. Steady-state conditions
2. Constant value of thermal conductivity.
3. Uniform temperatures at the wall surfaces
4. One-dimensional heat flow. Of these statements:
Steady two-dimensional heat conduction takes place in the body shown in the figure below. The normal temperature gradients over surfaces P and Q can be considered to be uniform. The temperature gradient at surface Q is equal to 10 k/m. Surfaces P and Q are maintained at constant temperatures as shown in the figure, while the remaining part
of the boundary is insulated. The body has a constant thermal conductivity of 0.1 W/m.K. The values of and
at surface P are:
A plane wall is 25 cm thick with an area of 1 m2, and has a thermal conductivity of 0.5 W/mK. If a temperature difference of 60°C is imposed across it, what is the heat flow?
Which one of the following expresses the thermal diffusivity of a substance in terms of thermal conductivity (k), mass density (ρ) andspecific heat (c)?
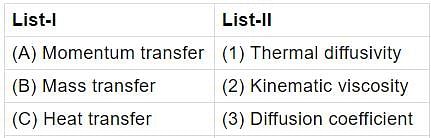
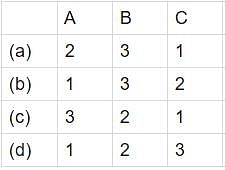
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Temperature profiles for four cases are shown in the following figures and are labelled A, B, C and D.
Match the above figures with
1. High conductivity fluid
2. Low conductivity fluid
3. Insulating body
4. Guard heater
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Assertion (A): Thermal diffusivity is a dimension less quantity.
Reason (R): In M-L-T-Q system the dimensions of thermal diffusivityare [L2T-1]
Assertion (A): Thermal diffusivity is a dimensionless quantity.
Reason (R): In M-L-T-Q system the dimensions of thermal diffusivityare [L2T-1]
Assertion (A): Hydrogen cooling is used for high capacity electrical generators.
Reason (R): Hydrogen is light and has high thermal conductivity ascompared to air
Assertion (A): Cork is a good insulator.
Reason (R): Good insulators are highly porous.
An oil cooler in a high performance engine has an outside surface area 0.12 m2 and a surface temperature of 65 degree Celsius. At any intermediate time air moves over the surface of the cooler at a temperature of 30 degree Celsius and gives rise to a surface coefficient equal to 45.4 W/ m 2 K. Find out the heat transfer rate?
A wall of thickness 0.6 m has width has a normal area 1.5 m2 and is made up of material of thermal conductivity 0.4 W/mK. The temperatures on the two sides are 800°C. What is the thermal resistance of the wall?
A composite wall of a furnace has 2 layers of equal thickness having thermal conductivities in the ratio of 3 : 2. What is the ratio of the temperature drop across the two layers?
One dimensional unsteady state heat transfer equation for a sphere with heat generation at the rate of 'q' can be written as
For the three-dimensional object shown in thefigure below, five faces are insulated. Thesixth face (PQRS), which is not insulated,interacts thermally with the ambient, with aconvective heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/m2.K. The ambient temperature is 30°C. Heatis uniformly generated inside the object at therate of 100 W/m3. Assuming the face PQRS tobe at uniform temperature, its steady statetemperature is:
In a composite slab, the temperatureat the interface (Tinter) between twomaterials is equal to the average ofthe temperatures at the two ends.Assuming steady one-dimensionalheat conduction, which of thefollowing statements is true aboutthe respective thermalconductivities?
Heat flows through acomposite slab, as shownbelow. The depth of the slabis 1 m. The k values are inW/mK. the overall thermalresistance in K/W is:
A stainless steel tube (ks = 19 W/mK) of 2 cm ID and 5 cm OD is insulated with 3 cm thick asbestos (ka = 0.2 W/mK). If the temperature difference between the innermost and outermost surfaces is 600°C, the heat transfer rate per unit length is:
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|


















