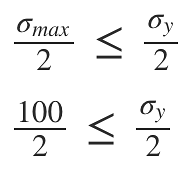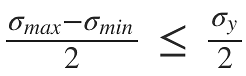Test: Principal Stress & Strain - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test GATE Mechanical (ME) Mock Test Series 2025 - Test: Principal Stress & Strain - 2
When two mutually perpendicular principal stresses are unequal but like, the maximum shear stress is represented by
Assertion (A): A plane state of stress does not necessarily result into a plane state of strain as well.
Reason (R): Normal stresses acting along X and Y directions will also result into normal strain along the Z-direction.
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
Principal strains at a point are 100 x 10-6 and -200 x 10-6 . What is the maximum shear strain at the point?
The number of strain readings (using strain gauges) needed on a plane surface to determine the principal strains and their directions is:
Assertion (A): Mohr's construction is possible for stresses, strains and area moment of inertia.
Reason (R): Mohr's circle represents the transformation of second-order tensor.
On a plane, resultant stress is inclined at an angle of 45o to the plane. If the normal stress is 100 N /mm2, the shear stress on the plane is:
The complementary shear stresses of intensity τ are induced at a point in the material, as shown in the figure. Which one of the following is the correct set of orientations of principal planes with respect to AB?
A body is subjected to a pure tensile stress of 100 units. What is the maximum shear produced in the body at some oblique plane due to the above?
A material element subjected to a plane state of stress such that the maximum shear stress is equal to the maximum tensile stress, would correspond to
A solid circular shaft of diameter 100 mm is subjected to an axial stress of 50 MPa. It is further subjected to a torque of 10 kNm. The maximum principal stress experienced on the shaft is closest to
The maximum principle stress for the stress state shown in the figure is
In a Mohr's circle, the radius of the circle is taken as:
Where, σx and σy are normal stresses along x and y directions respectively and τxy is the shear stress.
The Mohr's circle of plane stress for a point in a body is shown. The design is to be done on the basis of the maximum shear stress theory for yielding. Then, yielding will just begin if the designer chooses a ductile material whose yield strength is:
Determine the directions of maximum and minimum principal stresses at the point “P” from the Mohr's circle
Which one of the following Mohr‟s circles represents the state of pure shear?
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.
Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
When a component is subjected to axial stress the normal stress σn is maximum, if cos θ is _______ . (σn=σxCos2θ)
1. maximum
2. minimum
3. always one
4. always zero
An elastic material of Young‟s modulus E and Poisson‟s ratio ν is subjected to a compressive stress of σ1 in the longitudinal direction. Suitable lateral compressive stress σ 2 are also applied along the other two each of the lateral directions to half of the magnitude that would be under σ1 acting alone. The magnitude of σ2 is
If the principal stresses and maximum shearing stresses are of equal numerical value at a point in a stressed body, the state of stress can be termed as
A piece of material is subjected, to two perpendicular tensile stresses of 70 MPa and 10 MPa. The magnitude of the resultant stress on a plane in which the maximum shear stress occurs is
Principal stresses at a point in plane stressed element are σx = σy = 500 kg/cm2 . Normal stress on the plane inclined at 45o to x-axis will be:
At a point in two-dimensional stress system σx = 100 N/mm2, σy = τxy = 40 N/mm2. What is the radius of the Mohr circle for stress drawn with a scale of: 1 cm = 10 N/mm2?
Assertion (A): Mohr's circle of stress can be related to Mohr's circle of strain by some constant of proportionality
Reason (R): The relationship is a function of yield stress of the material.
The principal strains at a point in a body, under biaxial state of stress, are 1000 ×10–6 and –600 × 10–6. What is the maximum shear strain at that point?
Which of the following stresses can be determined using Mohr's circle method?
Normal stresses of equal magnitude p, but of opposite signs, act at a point of a strained material in perpendicular direction. What is the magnitude of the resultant normal stress on a plane inclined at 45° to the applied stresses?
A point in two-dimensional stress state, is subjected to biaxial stress as shown in the above figure. The shear stress acting on the plane AB is
What are the normal and shear stresses on the 45o planes shown?
If a body is subjected to stresses in xy plane with stresses of 60N/mm² and 80N/mm² acting along x and y axes respectively. Also the shear stress acting is 20N/mm²Find the maximum amount of shear stress to which the body is subjected.
State of stress in a plane element is shown in figure I. Which one of the following figures -II is the correct sketch of Mohr's circle of the state of stress?
|
29 docs|220 tests
|
|
29 docs|220 tests
|