Test: Simplex Method & Transportation Model - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Simplex Method & Transportation Model - 2
Consider the following statements regarding linear programming:
1. Dual of a dual is the primal.
2. When two minimum ratios of the right-hand side to the coefficient in the key column are equal, degeneracy may take place.
3. When an artificial variable leaves the basis, its column can be deleted from the subsequent Simplex tables.
Select the correct answer from the codes given below:
2. When two minimum ratios of the right-hand side to the coefficient in the key column are equal, degeneracy may take place.
3. When an artificial variable leaves the basis, its column can be deleted from the subsequent Simplex tables.
Which one of the following conditions should be satisfied for the application of optimality test on an initial solution of transportation model?
A simplex table for a linear programming problem is given below:
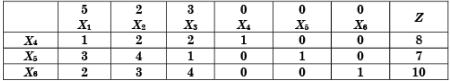
Which one of the following correctly indicates the combination of entering and leaving variables?
Consider the following statements on transportation problem:
1. In Vogel's approximation method, priority allotment is made in the cell with lowest cost in the column or row with least penalty
2. The North-West corner method ensures faster optimal solution
3. If the total demand is higher than the supply, transportation problem cannot be solved
4. A feasible solution may not be an optimal solution.
Which of these statements are correct?
In the solution of a linear programming problem by Simplex method, if during iteration, all ratios of right-hand side bi to the coefficients of entering variable a are found to be negative, it implies that the problem has
In a connected network of 'n' arcs (roads) joining 'm' vertices (towns), a selection of roads is taken up for resurfacing based on a minimum spanning tree of network as being the least cost solution. This spanning tree will contain
While solving a linear programming problem by simplex method, if all ratios of the right-hand side (bi) to the coefficient, in the key row (aij) become negative, then the problem has which of the following types of solution?
Assertion (A): In the solution of transportation problem, for application of optimality test, the number of allocations required is m + n – 1 and these should be in independent positions.
Reason (R): If the number of allocations is not m + n – 1, values of all oddments, i.e., ui and vj cannot be found.
A linear programming problem with mixed constraints (some constraints of ≤ type and some of ≥ type) can be solved by which of the following methods?
In a transportation problem North-West corner rule would yield
Consider the following statements:
1. A linear programming problem with three variables and two constraints can he solved by graphical method.
2. For solutions of a linear programming problem with mixed constraints. Big-M-method can be employed.
3. In the solution process of a linear programming problem using Big-M-method, when an artificial variable leaves the basis, the column of the artificial variable can be removed from all subsequent tables.
Which one these statements are correct?
Assertion (A): Vogel's approximation method yields the best initial basic feasible solution of a transportation problem.
Reason (R): Vogel's method gives allocations to the lowest cost elements of the whole matrix.
When solving the problem by Big-M method, if the objective functions row (evaluation row) shows optimality but one or more artificial variables are still in the basis, what type of solution does it show?
In a transportation problem, the materials are transported from 3 plants to 5 warehouses. The basis feasible solution must contain exactly, which one of the following allocated cells?
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
When there are 'm' rows and 'n' columns in a transportation problem, degeneracy is said to occur when the number of allocations is:
A solution is not a basic feasible solution in a transportation problem if after allocations.
In order for a transportation matrix which has six rows and four columns not to degenerate, what is the number of occupied cells in the matrix?
Match List-I (O.R. Techniques) with List-II (Application) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
Assertion (A): Transportation problem can be solved by VAM heuristic much faster as compared to the solution through linear programming method.
Reason (R): VAM heuristic gives an approximate solution. It is checked for optimality test. If it is optimal, the algorithm stops there. If it is not an optimal solution, then improved solutions are found out through very little iteration till optimality is reached.
Assertion (A): In distribution problem, unit cost of production as well as transportation cost is considered.
Reason (R): The Vogel approximation method can reduce the number of iterations required to move from the initial assignment to the optimal solution.
In a 6 × 6 transportation problem, degeneracy would arise, if the number of filled slots were:
The solution in a transportation model (of dimension m × n) is said to be degenerate if it has
Consider the following statements:
In a transportation problem, North-West corner method would yield
1. An optimum solution
2. An initial feasible solution
3. Vogel's app roximat e solution
Of these statements:
Consider the location of a warehouse to distribute books for the cities of Bombay, Bangalore and Calcutta. The estimated volume of distribution to Bombay, Bangalore and Calcutta are 55,000, 20,000 and 25,000 units respectively. Using some appropriate origin, the (x, y) co-ordinates of Bombay, Bangalore and Calcutta can be approximated as (10, 20), (20, 10) and (30, 30) respectively. The (x, y) co-ordinates or the optimal location would be:














