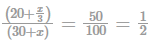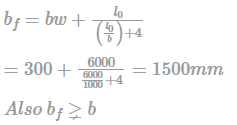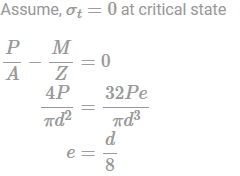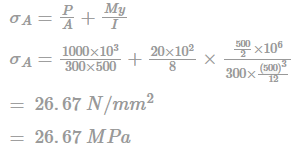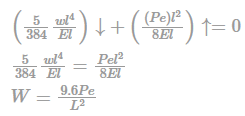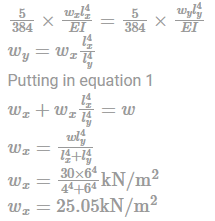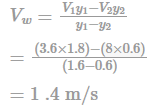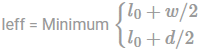Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 13 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Practice Test: Civil Engineering (CE)- 13
A monkey is trying to reach the top of a tree. He climbs 3 feet in a minute but slides down by 1.5 feet after each climb. If he reaches the top of the tree in 58 minutes, then the maximum possible height of the tree is ________ feets.
In the following question, a sentence has been given in Direct/Indirect Speech. Out of the four alternatives suggested, select the one which best expresses the same sentence in Indirect/Direct Speech.
My husband said to me, “Wait for me outside."
What of the following function(s) in an accurate description of the graph for the range(s) indicated?
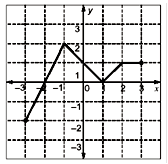
A. y = 2x + 4 for -3 ≤ x ≤ -1
B. y = |x-1| for -1 ≤ x ≤ 2
C. y = ||x|-1| for -1 ≤ x ≤ 2
D. y = 1 for 2 ≤ x ≤ 3

A rectangular room having dimensions 3.74 m x 5.78 m is required to be tiled using a minimum number of identical square tiles. The number of such tiles and area of each tile (in cm2) is given by
In the following question, out of the four alternatives, select the alternative which best expresses the meaning of the Idiom/Phrase.
To take into account
In an examination, a candidate attempts all the questions since there is no negative marking and all the questions carry equal marks. Out of the first 30 questions that he attempts, he has marked correct options for 20 questions whereas out of the remaining questions, he is able to mark only one third question with correct option. His overall score in the examination is 50%.
The total number of questions in the paper are;
Amol, Brijendra, Chander and Dron are sitting around a roundtable. One of them is an electronics engineer (ECE) who is sitting to the left of the Mechanical Engineer (ME). Amol is sitting opposite a Computer Science Engineer (CSE). It is also known that Dron likes to play computer games and Brijendra is sitting to the right of Civil Engineer (CE). Identify the correct match from the given choices.
In five cities A is more populated than B which is less populated then E. D is more populated than E but not as populated as A. C is less populated than B. Which city has the highest population?
One-third of Ramesh’s marks in Arithmetic is equal to half his marks in English. If he gets 150 marks in the two subjects to gather, how many marks has he got in English?
In a test given by Prof Virus during the minors, Raju gets 32% marks and fails by 20 marks whereas Chatur gets 30 marks more than passing marks while scoring 42% marks. The marks required to get twice the passing marks are _______.
During the subsurface investigations for design of foundations, a standard penetration test was conducted at 4.5m below the ground surface. The record of number of blows is given below.
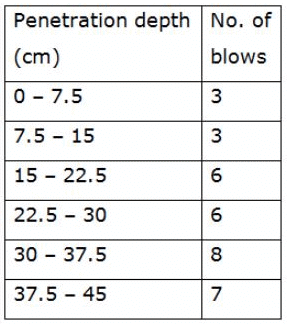
Q. Assuming the water table at ground level, soil as fine sand and correction factor for overburden as 1.0, the corrected ‘N’ value for the soil would be
A beam-column having overall depth and width is 550 mm and 250 mm. If torsional moment for this beam is 30 kN.m then twisting moment will be-
An isolated ‘T’ beam is used on the walkway. The beam is simply supported with an effective span of 6 m. Effective width of flange for shown figure is :
What is the maximum possible eccentricity in a prestressed concrete beam of circular cross-section? Diameter of the section is d. Tension is not allowed anywhere and any time in the cross-section. Neglect dead load (self-weight).
Deposit with flocculated structure is formed when
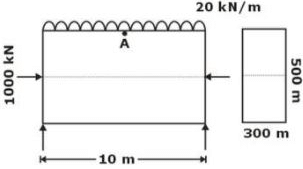
A simply supported prestressed beam of 300 × 500 mm in c/s is subjected to a superimposed load of 20 kN/m over a span of 10m. If a prestressing force of 1000 kN is applied through a straight tendon located along centroidal axis then what is the extreme top fiber stress at the mid section:
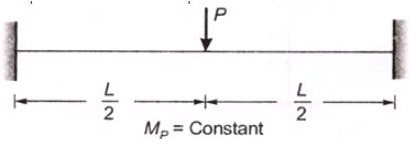
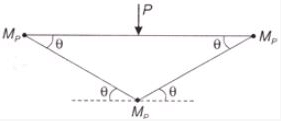
What will be the maximum possible uniformly distributed load (inclusive of self-weight) over the entire span of a simply supported beam of span ‘L’ such that the deflection at midspan at service condition is zero? The cross-section is rectangular. The prestressing force ‘P’ is applied with uniform eccentricity ‘e’. Assume no losses.
If Qs4 and Qs6 are the equilibrium discharges of S- curve for the catchment obtained by 4 hour UH summation and 6 hour UH summation, respectively, then Qs4/Qs6 is __________. (Up to 2 decimal places)
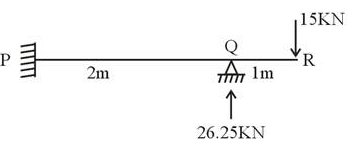
The beam PQR shown in the given figure is horizontal. The distance to the point of contraflexure from the fixed end P is _____m. (up to two decimal place)
30 KN/m2 load acting on a 4m × 6m 2-way slab. Effective Load acting in a shorter direction is_____ KN/m2.
A stream function is given by:
Ψ = 3xy2 + (x2+2)y
The flow rate across a line joining points A(0,5) and B(1,2) is
Before passage of a surge, the depth and velocity of flow at a section are 1.8 m and 3.6 m/s. After the surge passage, they are 0.6 m and 8 m/s respectively. The speed of the surge is?
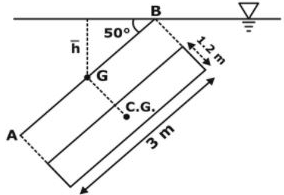
A rectangular plate 1.2 x 3 m is immersed in a liquid of relative density 0.85 with its 1.2 m side horizontal and just at the water surface. If the plane of plate makes an angle of 50o with the horizontal, the pressure force on one side of the plate is
A beam with both continuous ends has a clear span of 6m and supports 600 mm wide. The effective depth of the beam is 550 mm. As per IS 456-2000, the effective span of the beam (in m) is____________
A turbine develops 2516 kW at 240 rpm. The torque in the shaft is approximately:
A Kaplan turbine has a runner of diameter 4.0 m. The diameter of the hub is 1.6 m. If the velocity of flow and the swirl velocity at the inlet side of the blade at the hub are 6.0 m/s and 10.0 m/s, respectively, the flow and swirl velocities at the inlet side of the tip are, respectively:
A pipe of 30 cm diameter conveying 300 l/s of water has a right-angled bend in a horizontal plane. The resultant force exerted on the bend if pressure at inlet and outlet of the bend are 24.525N/cm2 and 23.544N/cm2 is ___ N.
A sample of saturated cohesionless soil tested in a drained triaxial compression test showed an angle of internal friction of 30°. The deviator stress at failure for the sample at a confining pressure of 200kPa is equal to
The daily cover of MSW landfills consists of which one of the following?