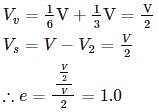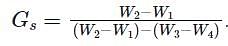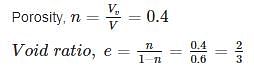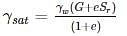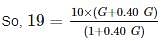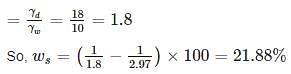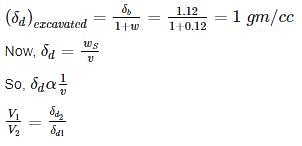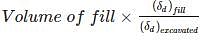Test: Soil Mechanics- 1 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Soil Mechanics- 1
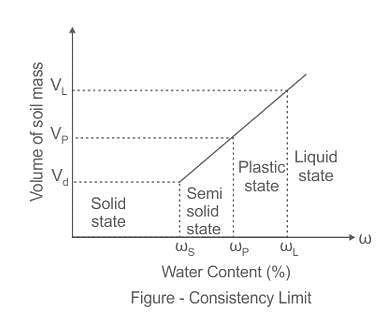
If the plasticity index of a soil is 45%, then the soil will be:
Consider the following statements. The incorrect statement is:
The term ‘Loess’ indicates those soils which are
1. Uniformly graded
2. Poorly graded
3. Made up of more than 50% sand size particles
4. Made up of more than 50% of silt particles
5. These are transported by winds
Which of the above statements are correct:
Match List – I (Type of soil) with List-II (Mode of transportation and deposition) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

In wet soil mass, air occupies 1/6 of its volume and water occupies 1/3 of its volume. The void ratio of the soil is
The given figure indicate the weights of different pycnometers:
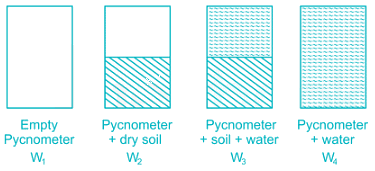
The specific gravity of the solids is given by
The following data are given for soil:
• Porosity: n = 0.4
• The specific gravity of the soil solids: Gs = 2.68
• Moisture content: w = 12%
Determine the mass of water in kg to be added to 10 m3 of soil for full saturation.
The water content of a soil sample is found to be 35%. If the percentage of air voids present in the soil sample is 5%. Then compute dry unit weight and air content of the soil sample when the void ratio of the soil sample is 0.65.
Take specific gravity of soil solids and unit weight of water to be 2.70 and 10 kN/m3.
A fully saturated clay has a water content of 40% and unit weight 19 kN/m3. After oven drying the dry density of the soil becomes 18 kN/m3. The shrinkage limit for the soil sample is ______%. (Take γw=γw=10 kN/m3)
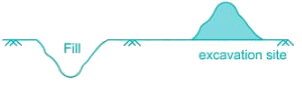
The soil has to be excavated from a borrow-pit which has a density of 1.12 gm/cc with a water content of 12% to fill a land. The soil is compacted to a density of 1.32 gm/cc with water content 20%. Find the volume of soil to be excavated in m3 for 1000 m3 volume of the fill?
|
31 docs|280 tests
|