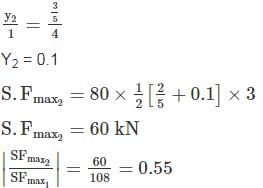Test: Structural Analysis- 2 - Civil Engineering (CE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Mock Test Series - Test: Structural Analysis- 2
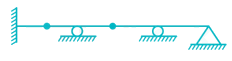
Which one of the following structures is statically determinate and stable?
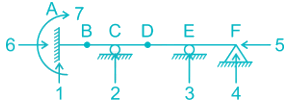
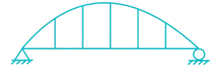
Determine the kinematic indeterminacy of the beam shown below:

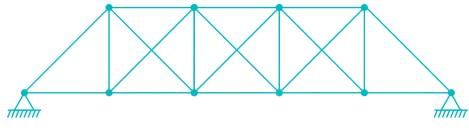
The total degree of indeterminacy (external + internal) for the bridge truss is :

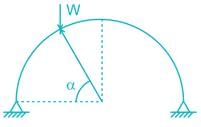
A two hinged semi-circular arch of radius R carries a concentrated load W at the crown. The horizontal thrust is
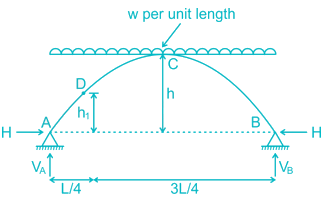
A three – hinged parabolic arch rid of span L and crown rise ‘h’ carries a uniformly distributed superimposed load of intensity ‘w’ per unit length. The hinges are located on two abutments at the same level and the third hinge at a quarter span location from the left-hand abutment. The horizontal trust on the abutment is:
In a two-hinged parabolic arch (consider arch to be initially unloaded) an increase in temperature induces -
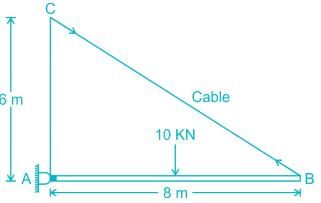
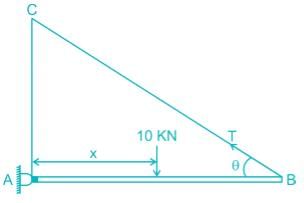
Find the maximum tension in the cable in KN if a unit load of 10 KN can move in either direction in the beam AB?
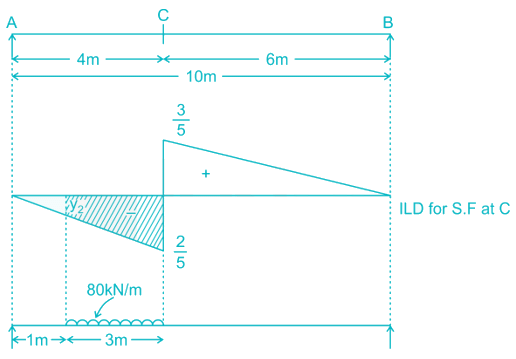
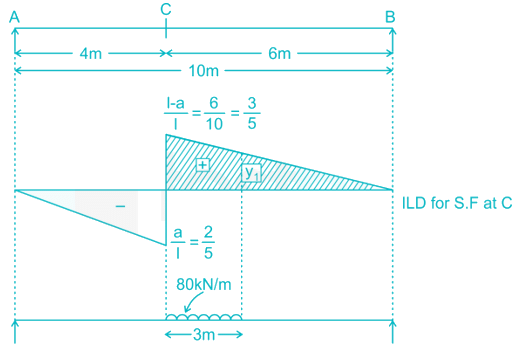
A uniformly distributed load of 80 kN per meter run of length 3 m moves on a simply support girder of span 10 m. The magnitude of the ratio of Maximum negative shear force to the maximum positive shear force at 4 m from the left end will be _______ (up to two decimal places).
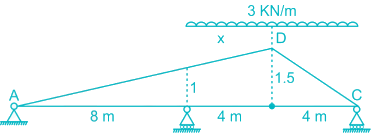
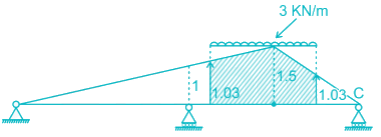
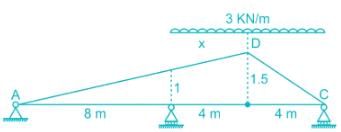
Find the maximum reaction developed at B when a udl of 3KN/m of span 5m is moving towards right in the beam shown below:-
|
31 docs|280 tests
|



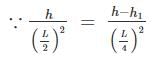
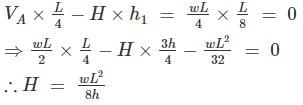
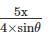
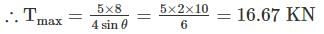
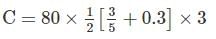 (S.F)max1 =108kN
(S.F)max1 =108kN