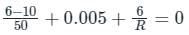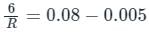Test: Zener Diodes - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test GATE ECE (Electronics) Mock Test Series 2026 - Test: Zener Diodes
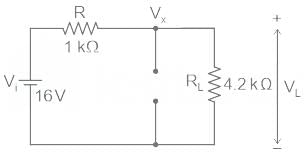
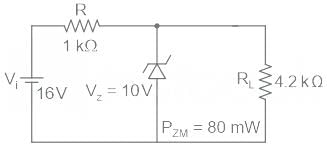
For the Zener diode network shown in figure, determine the value of VL?

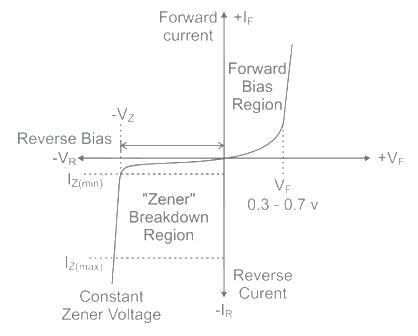
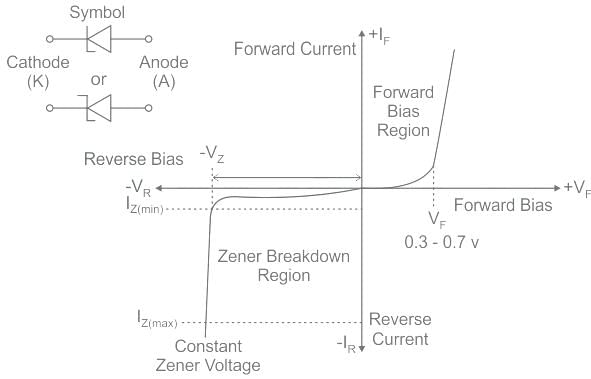
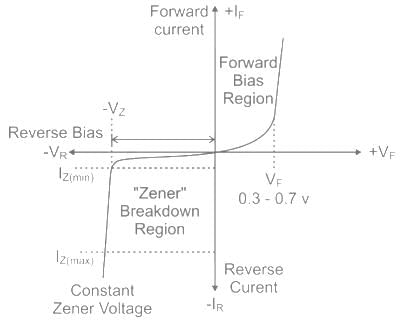
Zener breakdown occurs when reverse bias of voltage is approximately
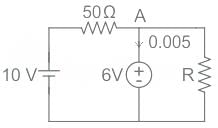
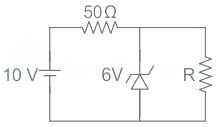
The 6 V zener diode shown in the figure has zero zener resistance and a knee current of 5 mA. The minimum value of R, so that the voltage across it does not fall below 6 V, is

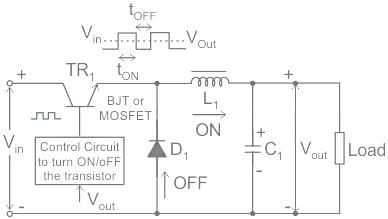
Zener diode is used as the main component in dc power supply for
Find the output voltage of the given network if Ein = 6 V and the Zener breakdown voltage of the Zener diode is 10 V.
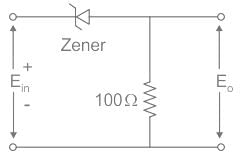
Which of the following devices is used in voltage regulators and voltage limiters as a fixed reference voltage in the network?
The 6 V Zener diode shown in the figure has zero Zener resistance and a knee current of 5 mA. The minimum value of R so that the voltage across it does not fall below 6 V is
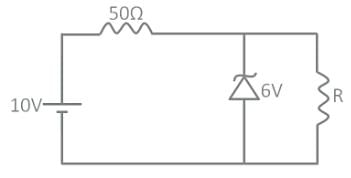
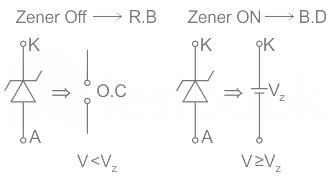
Zener diode works under which region of V - I characteristics of the semiconductor diode?
Which among the following act as a switch in switching regulator?
|
26 docs|263 tests
|