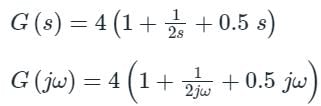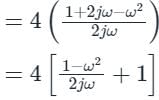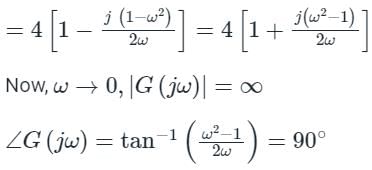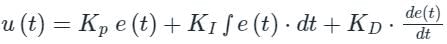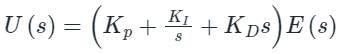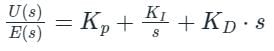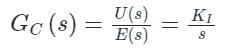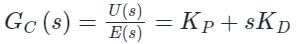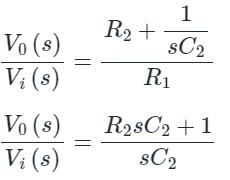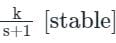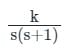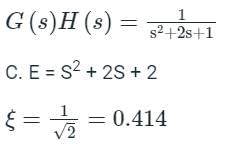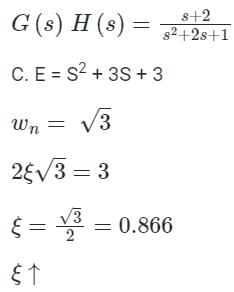Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam > Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Tests > Test: PID Controllers - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test: PID Controllers - Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) MCQ
Test Description
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: PID Controllers
Test: PID Controllers for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 is part of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation. The Test: PID Controllers questions and answers have been prepared
according to the Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) exam syllabus.The Test: PID Controllers MCQs are made for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) 2025 Exam.
Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: PID Controllers below.
Solutions of Test: PID Controllers questions in English are available as part of our course for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) & Test: PID Controllers solutions in
Hindi for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) course.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam by signing up for free. Attempt Test: PID Controllers | 15 questions in 45 minutes | Mock test for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) preparation | Free important questions MCQ to study for Electronics and Communication Engineering (ECE) Exam | Download free PDF with solutions
Test: PID Controllers - Question 1
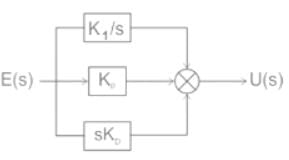
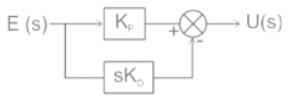
The transfer function of a PID controller is given by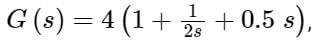 as ω tends to zero
as ω tends to zero
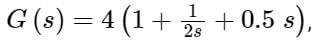 as ω tends to zero
as ω tends to zero
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 1
Test: PID Controllers - Question 2
PID controllers are tuned on the frequency response of the closed-loop system by
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 2
Test: PID Controllers - Question 3
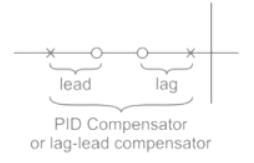
The magnitude plot of a rational transfer function G(s) with real coefficients is shown below. Which of the following compensators has such a magnitude plot?
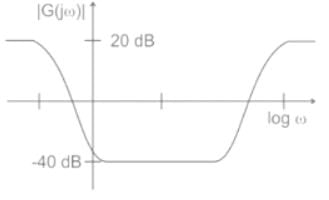

Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 3
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 4
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 5
Test: PID Controllers - Question 6
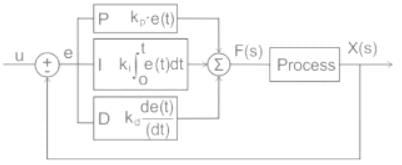
Consider the following statements regarding a control system:
(a) Addition of pole to left half of s-plane reduce the relative stability
(b) Addition of zero to left half of s-plane increase the damping factor
(c) Integral controller reduces the steady state error
(d) Derivate controller cannot be used in isolation
Which of the above statements are true?
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 6
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 7
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 8
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 9
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 10
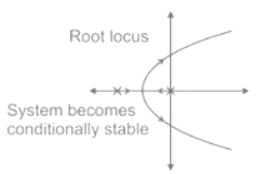
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 11
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 12
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 13
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 14
Detailed Solution for Test: PID Controllers - Question 15
Information about Test: PID Controllers Page
In this test you can find the Exam questions for Test: PID Controllers solved & explained in the simplest way possible.
Besides giving Questions and answers for Test: PID Controllers, EduRev gives you an ample number of Online tests for practice
Download as PDF