Test: Chemical Equilibrium (13 July) - JEE MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Daily Test for JEE Preparation - Test: Chemical Equilibrium (13 July)
If the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2SO2 + O2 ⇋ 2SO3 is 64 at 500 K, then the equilibrium constant for the reaction  at the same temperature is
at the same temperature is
 at the same temperature is
at the same temperature isSolubility of a substance which dissolves with a decrease in volume and absorption of heat will be favoured by:
At constant pressure, the presence of inert gases:
The degree of dissociation of an electrolyte depends on:
In the equilibrium reaction, N2 + 3H2 ⇔ 2NH3 , the sign of Δ H accompanying the reaction is;
In a reversible reaction H2 + I2 ⇋ 2HI, if the concentration of H2 and I2 are increased, the value of Kc:
For an exothermic reaction, the equilibrium constant :
An increase in pressure would favor the following reaction:
Assertion A: A catalyst has no effect on the state of equilibrium
Reason R: A catalyst influences the rates of both forward and backward reactions to the same extent.
Which of the following is not affected by change in pressure?
|
360 tests
|


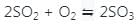
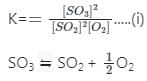
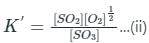
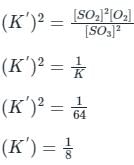
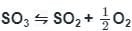 at the same temperature is 1/8
at the same temperature is 1/8

















