Test: General Methods of Isolation and Purification - 2 - Chemistry MCQ
18 Questions MCQ Test - Test: General Methods of Isolation and Purification - 2
In the commercial electrochemical process for aluminium extraction, the electrolyte used as:
Electrolytic reduction of alumina to aluminium by Hall Heroult process is carried out:
Which of the following processes is used in extractive metallurgy of magnesium?
Which ore contains both iron and copper ?
Native silver metal forms a water soluble complex with a dilute aqueous solution of NaCN in the presence of
Extraction of metal from the ore cassiterite involves is a
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4.5H2O), atacamite (Cu2CI(OH3)), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However, 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalopyrite involved partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. Partial roasting of chalcopyrite produces
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4.5H2O), atacamite (Cu2CI(OH3)), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However, 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalopyrite involved partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. In self-reduction, the reducing species is
Froth floatation method is mostly used for the concentration of _____________
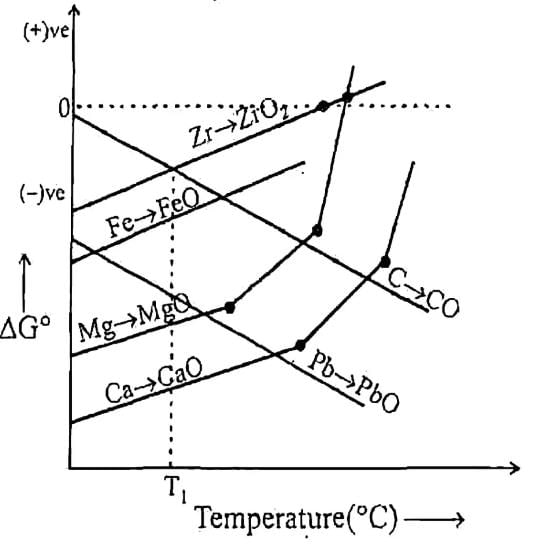
Q. Which of the above metal oxide is having minimum thermal decomposition temperature.

Q. Which of above curve is wrongly presented.

Q. Which of the following metal’s oxide can reduced by Fe as reducing agent at temperature T,
The chemical process in the production of steel from haematite ore involve:
The chemical composition of “slag” formed during the smelting process in the extraction of copper is:
The methods chiefly used for the extraction of lead and tin from their ores are respectively:
Extraction for zinc from zinc blende is achieved by:
Oxidation states of the metal in the minerals haematite and magnetite, respectively, are
How many number of water molecule (s) directly bonded to the metal centre in CuSO4.5H2O is



















