Test: Periodic Properties- 2 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Periodic Properties- 2
Among NaF , NaCl , NaBr and Nal , the NaF has highest melting point because
Consider the following changes:
M (s) → M (g) ........(1)
M (s) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(2)
M (g) → M+ (g) + 2e- .......(3)
M+ (g) → M2+ (g) + e- .......(4)
M (g) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(5)
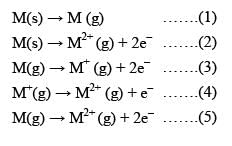
The second ionization energy of M could be calculated from the energy values associated with:
M (s) → M (g) ........(1)
M (s) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(2)
M (g) → M+ (g) + 2e- .......(3)
M+ (g) → M2+ (g) + e- .......(4)
M (g) → M2+ (g) + 2e- .......(5)
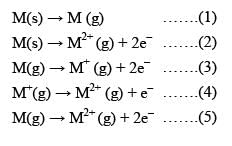
The correct order of second I. E. of C, N, O and F are in the order:
The correct values of ionization enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of Si, P, Cl and S respectively are:
Consider the following changes
A → A+ + e- : E1
and A+ → A2+ + e- ; E2
The energy required to pull out the two electrons are E1 and E2 respectively. The correct relationship between two energies would be...
First the ionization energies (in kJ/mol) of three representative elements are given below:
Then incorrect option is:
Which of the following statement is correct regarding following process:
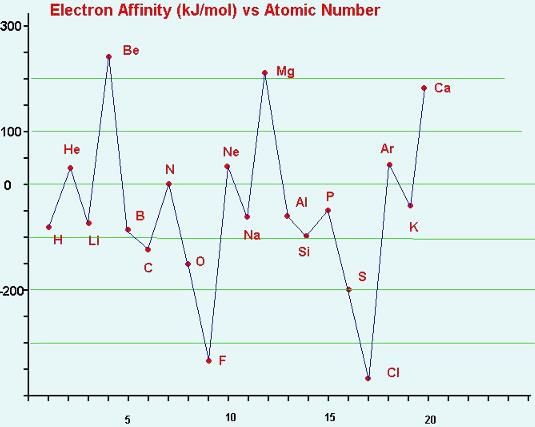
The correct order of increasing electron affinity of the following elements is:
The second electron gain enthalpies (in kJ mol–1) of oxygen and sulphur respectively are:
The formation of the oxide ion O2–(g) requires first an exothermic and then an endothermic step as shown below:
This is because:
Identify the wrong sequence of the elements in a group
The electron affinity of the following elements can be arranged:
In which of the following arrangements, the order is not correct according to the property indicated against it:
Consider the following conversions:
That according to given informat ion the incorrect statement is:
The incorrect statement regarding given information is
In the compound M—O—H, the M—O bond will be broken if:
An element has an atomic number of 15 with which of the following elements will it show similar chemical properties.
If the ionization and electron gain enthalpy of an element are 275 and 86 Kcalmol−1 respectively, then the electronegativity of the element on the Mulliken scale is:
Consider the following statements: (I) The radius of an anion is larger than that of the parent atom. (II) The ionization energy generally increases with increasing atomic number in a period (III) The electronegativity of an element is the tendency of an isolated atom to attract an electron.Which of the above statements is/are correct:
Which of the following order is correct for the property ment ioned in brackets: