Test: Structural and stereoisomerism in Coordination Complexes - Chemistry MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Structural and stereoisomerism in Coordination Complexes
The optical isomer that rotates the plane of polarised in the clockwise direction is called ______
Which of the following compounds has a meridional isomer?
Which of the following do not show geometrical isomerism? (Assume all ligands are unidentate)
How many geometrical isomers are possible in a complex of type [MA2(D)2], where A is unidentate and D is didentate?
A tetrahedral compound of type [MP2Q2] has two geometrical isomers.
A coordination complex [MX2L2], has a CN=4 and two unidentate ligands X and L. When the two L ligands are arranged opposite to each other in its geometry, it is called _______ isomer.
Which of the following is not a subdivision of structural isomerism?
Two or more compounds that have the same chemical formula, but different arrangement of atoms are called _______
Optical isomers are also known as __________
In the coordination entity [Co(NH3)3(NO2)3], if all three N atoms of the amine ligands occupy adjacent positions at the corners of an octahedral face, the geometrical isomer formed is known as _______ isomer.
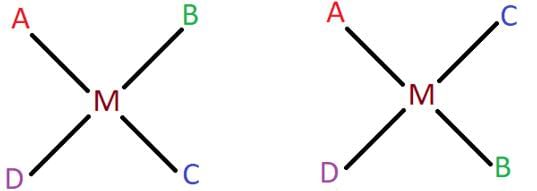
The square planar complex [MABCD] is known to form three isomers, two cis and one trans. Shown below are the two cis isomers of the complex. Identify the third trans isomer.
Identify the trans isomer of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2] from the following.
How many geometrical isomers are possible in [Al(C2o4)3]3-?
Geometrical isomerism can be observed in some homoleptic complexes.
Which type of isomerism exhibits compounds with same chemical formula and bonds but different spatial arrangement?



















