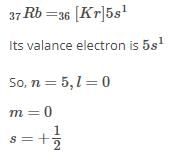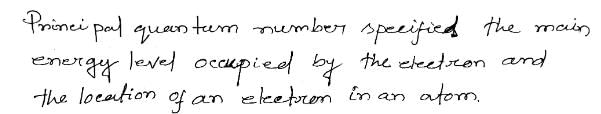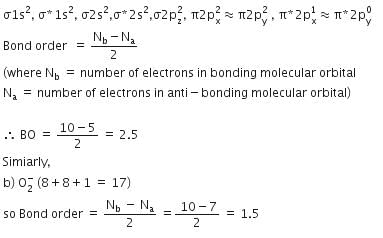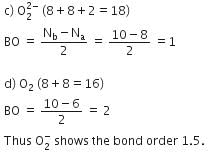Test: Quantum Numbers & Electronic Configuration - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Quantum Numbers & Electronic Configuration
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Which is a possible set of quantum numbers for a valence unpaired electrons in ground state atom of phosphorus (Z = 15)?
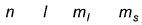
For a multi-electron atom, set of quantum numbers is given as
2,0,0,1/2 ; 2,0,0,-1/2
Q. Thus, the next higher allowed set of n and / quantum numbers for this atom in its ground state is
Magnetic moments of the following isoelectronic species (24 electrons) are in order
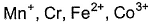
The orbital angular momentum for a d-orbital electron is given by
The number of radial nodes in 3s and 2p respectively are
A hydrogen like species in fourth orbit has radius 1.5 times that of Bohr's orbit. In neutral state, its valence electron is in
Following suborbits with values of n and l are given
Q. Increasing order of energy of these suborbits is
The correct set of four quantum numbers for the valence electron of rubidium atom (Z = 37) is
[JEE Main 2013]
For Cr(24), (EC) : [Ar] 4s1 3d5 The number of electrons with l = 1 to l = 2 are respectively
Last filling electron in lanthanides find place in 4f-orbital. Which of the following sets of quantum number is correct for an electron in 4f orbital?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-15) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Quantum numbers have been matched with their characteristics. Select correct matching(s).
In the following pair, each has two orbitals I and II. Select the ones in which II experiences larger effective nuclear charge than l
In a multi-electron atom, which of the following orbitals described by the three quantum numbers will have the same energy in the absence of magnetic and electric fields?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
The quantum number which specifies the location of an electron as well as energy is
Quantum Numbers are solutions of _____________
Which quantum numbers gives the shell to which the electron belongs?
Direction (Q. Nos. 18) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Match the entries in Column I with correctly related quantum number(s) in Column II
Direction (Q. Nos. 19 and 20) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Q. Bond order of 1.5 is shown by
The maximum number of electrons that can have principal quantum number, n = 3 and spin quantum number,