Test: Beginning of European Commerce- 2 - UPSC MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test History for UPSC CSE - Test: Beginning of European Commerce- 2
Like the Dutch the English had come to the east for the spice trade. But soon they were forced to concentrate on India. Why did his happen?
The Dutch position in India was undermined in the second half of the eighteenth century because
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? Download the App |
In 1658, who conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese?
Between 1654 and 1667, which two powers fought in India?
Initially, the Mughals tried to develop friendly relations with the English. Why?
I. They could use the English to counter the Portuguese on the sea.
II. They could use the English to help them in opening trading posts in the Spice Islands.
III. Indian merchants would certainly benefit by competition among their foreign buyers.
The Dutch and the English entered the East as friend against the common enemy, the Portuguese. However, their commercial rivalry led to the massacre of the Englishman by the Dutch at
The English set up their first factory on Indian soil in 1612 at
The English opened their first factory in south India in 1611 at
Fort St. David was chief centre of the Coromandal trade. It later developed into
Who gave Bombay to Charles II of England as a dowry gift for his marriage with Catherine of Braganza?
The Battle of Bedara in 1759 was fought between the English and an European power whose influence in India came to an end. Identify it.
With the decline of Portuguese power a number of its settlements were lost. Who captured Hormuz in Persian Gulf from the Portuguese in 1622 A.D.?
Which is/are incorrect regarding the lease of Madras to the English by the local Raja in 1639?
In 1608, Captain William Hawkins approached the Mughal court for permission to erect a factory at
The linkage with European trade had negative factors. Which was not one of them?
Which Englishman remarked, “I know these people are best treated with the sword in one hand and the caducean (a rod carried by a messenger) in the other?
An item was developed by the European powers which supplemented the European sources for gunpowder and which was also used as a ballast for ships going to Europe. What was it?
Name the English merchant who attempt to obtain from Akbar afarman for trade in Gujarat?
Who wrote “The discovery of America and the cape route to India were the two greatest and most important events recorded in the history of mankind?
In 1612 the English East India Company opened its first factories in
Who wrote that “the time now requires you to manage general commerce with the sword in your hands”?
In 1686 a war broke out in Bengal between Aurangzeb and the English East India Company. What was its outcome?
In 1691 the East India Company was granted exemption from the payment of custom duties in return for Rs. 3,000 a year in
From whom did the East India Company secure a farman confirming the privileges granted in 1681 and extending them to Gujarat and the Deccan?
The East India Company was granted undisputed right to free trade in Bengal, Bihar and Orissa by
The East India Company secured Diwani or right to collect revenue, in Bengal, Bihar and Orissa from
The East India Company opened its first factory in south at
By the middle of the 18th century, the population of three major cities had increased tremendously. Keeping this in mind, match the following.
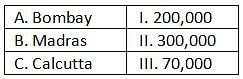
|
121 videos|490 docs|176 tests
|












