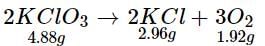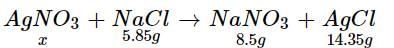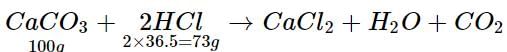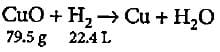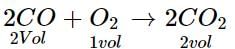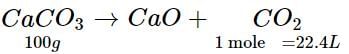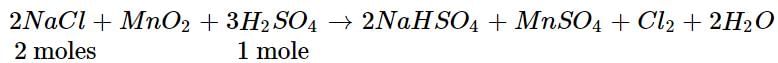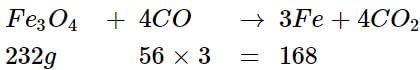RC Mukherjee Test: Laws of Chemical Combinations - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - RC Mukherjee Test: Laws of Chemical Combinations
4.88 g of KCIO3 when heated produced 1.92 g of O2 and 2.96 g of KCl. Which of the following statements regarding the experiment is correct?
How much mass of silver nitrates will react with 5.85 g of sodium chloride to produce 14.35 g of silver chloride and 8.5 g of sodium nitrates if law of conservation of mass is followed?
What mass of hydrochloric acid is needed to decompose 50 g of limestone?
What mass of sodium chloride would be decomposed by 9.8 g of sulphuric acid if 12 g of sodium bisulphate and 2.75 g of hydrogen chloride were produced in a reaction?
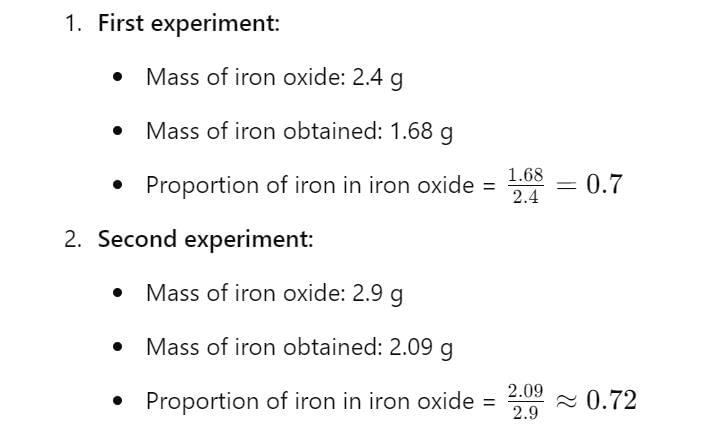
In an experiment, 2.4g of iron oxide on reduction with hydrogen gave 1.68 g of iron. In another experiment, 2.9 g of iron oxide gave 2.09 g of iron on reduction.Which law is illustrated from the above data?
The following data are obtained when dinitrogen and dioxygen react together to form different compounds:
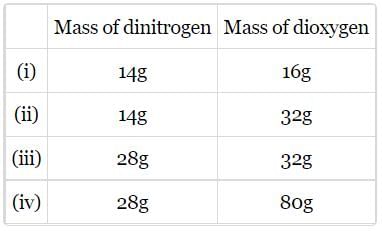
Which law of chemical combination is obeyed by the above experimental data?
Which of the following statements illustrates the law of multiple proportions?
Which of the following pairs illustrates the law of multiple proportions?
Given below are few statements. Mark the statement which is not correct.
What quantity of copper oxide will react with 2.80 L of hydrogen at NTP?
At NTP, 1L of O2 reacts with 3 L of carbon monoxide. What will be the volume of CO and CO2 after the reaction?
Calcium carbonate decomposes on heating to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. How much volume of CO2 will be obtained by thermal decomposition of 50 g of CaCO3?
Chlorine gas is prepared by reaction of H2SO4 with MnO2 and NaCl. What volume of CI2 will be produced at STP if 50 g of NaCl is taken in the reaction?
HCl is produced in the stomach which can be neutralised by Mg(OH)2 in the form of milk of magnesia. How much Mg(OH)2 is required to neutralise one mole of stomach acid?
Iron can be obtained by reduction, of iron oxide (FC3O4) with CO according to the reaction:
Fe3O4 + 4CO → 3Fe + 4CO2
How many kg of Fe3O4 should be heated with CO to get 3 kg of iron?