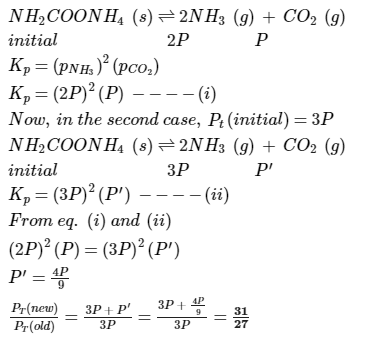Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Heterogeneous Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
22 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Chemical Equilibrium: Heterogeneous Equilibrium
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-10) This section contains 10 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Vapour pressure of NH4HS (s)is 20 mm at 25°C, for
NH4HS (s)⇌ NH3(g) + NH3(g) + H2S(g)
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
Total pressure when NH4HS (s) dissociates at 25°Cin a vessel which already contains H2S (g)at a pressure of 15 mm, is
Once the equilibrium is reached under given condition:
Ca(HCO3)2 is strongly heated and after equilibrium is attained, temperature changed to 25° C.
Ca(HCO3)2(s)⇌CaO(s) + 2CO2 (g) + H2O(g)
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
Kp = 36 (pressure taken in atm)
Thus, pressure set up due to CO2 is
Na2SO4.10H2O dehydrates according to the equation,
Na2SO4· 10H2O (s)⇌ Na2sO4(s) + 10 H2O(g)
; Kp = 2.56 x 10-20
What is the pressure of water vapor at equilibrium with a mixture of Na2SO4· 10H2O and Na2sO4
Ca(HCO3)2 decomposes as,
Ca (HCO3)2(s) ⇌ CaCO3(s) + H2O(g) + CO2(g)
Equilibrium pressure is found to be 0.12 bar. What is pco2 if the reaction mixture also contains H2O(g)at 0.20 bar?
For the following equilibrium,
Assume following equilibria when total pressure set up in each are equal to 1 atm, and equilibrium constant (Kp) as K1; K2 and K3
Thus,
For the equilibrium,
at 1000 K. If at equilibrium pCO = 10 then total pressure at equilibrium is
Ammonium carbamate dissociates as,
In a closed vessel containing ammonium carbamate in equilibrium with its vapour, ammonia is added such that partial pressure of NH3 now equals the original total pressure. Thus, ratio of the total pressure to the original pressure is
Kc forthe decomposition of NH4HS(s) is 1.8x 10-4 at 25°C.
If the system already contains [NH3] = 0.020 M, then when equilibrium is reached, molar concentration are
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d)
Passage I
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Partial pressure of NH3(g) or HCI (g) at equilibrium is
Passage I
Solid ammonium chloride is in equilibrium with ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases
0.980 g of solid NH4CI is taken in a closed vessel of 1 L capacity and heated to 275° C.
Q. Percentage decomposition of the original sample is
Passage lI
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. Under the given partial pressure, reaction is
Passage lI
One of the reactions that takes place in producing steel from iron ore is the reduction of iron (II) oxide by carbon monoxide to give iron metal and carbon dioxide.
Initial partial pressure
CO(g) = 1.40 atm
CO2(g) = 0.80 atm
Q. When equilibrium is attained,
Direction (Q. Nos. 15 and 16) This section contains 2 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive)
Hot copper tunnings can be used as an “oxygen getter" for inert gas supplies by slowly passing the gas over the copper tunnings at 650 K.
Q. How many molecules of O2 are left in 1 L of a gas supply after equilibrium has been reached?
At 1000 K, pressure of CO2 in equilibrium with CaCO3 and CaO is equal to 2.105 atm. The equilibrium constant for the reaction,
is 1.9 at the same temperature when pressure are in atm. Solid C, CaO, and CaCO3 are mixed and allowed to come to equilibrium at 1000 K in a closed vessel.
Q. What is the pressure of CO (g)at equilibrium (in atm)?
Direction (Q. Nos. 17) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Given at 298 K
Solid ammonium carbonate (NH2CO2NH4) dissociates completely into ammonia and carbon dioxide when it evaporates :
At 298 K, the total pressure of the gases in equilibrium with the solid is 0.116 atm. Derive the value of equilibrium constant Kp.
At 90° C , the following equilibrium is established :
If 0.20 mole of hydrogen and 1.0 mole of sulphur are heated to 90°C in a 1.0 dm3 flask, what will be the partial pressure of H2S gas at equilibrium?
Graphite is added to a vessel that contains CO2(g) at a pressure of 0.830 atm at a certain high temperature. The pressure rises due to a reaction that produces CO (g). The total pressure reaches an equilibrium value of 1.366 atm. Calculate the equilibrium constant of the following reaction.
For the equilibrium,
Kp = 0.166 at 1000 K. Exactly 10.0 g of CaCO3 is placed in a 10.0 L flask at 1000 K. After equilibrium is reached, what mass of CaCO3 remains?
Equilibrium constant for the reaction PCL5⇋PCL3+CL2 is 0.0205 at 230°C and 1 atmospheric pressure if at equilibrium concentration of PCL5 is 0.235 moles liter−1liter-1and that of CL2= 0.028 moleslit−1lit-1 then conc. of PCL3 at equilibrium is
|
127 videos|245 docs|87 tests
|