Test: Critical Phenomenon (Old NCERT) - NEET MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test NCERT Based Tests for NEET - Test: Critical Phenomenon (Old NCERT)
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-3) This section contains 3 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. The critical tem perature of water is higher than that of O2 because the H2O molecules have
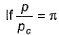 (reduced pressure),
(reduced pressure), 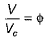 (reduced volume) and
(reduced volume) and 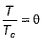 (reduced temperature), then,
(reduced temperature), then,
Direction (Q. Nos. 4) Choice the correct combination of elements and column I and coloumn II are given as option (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE option is correct.
Q. Values of different types of temperatures have been given in Column II. Match these values with the correct definition of temperatures in Column I and mark the correct answer from codes :
Direction (Q. Nos. 5-6) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Based on the following isotherms, select correct statements.
Direction (Q. Nos. 7-10) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I : Gases do not liquefy above th e ir Tc (critical temperature), even on applying high pressure.
Statement Il : Above Tc , m olecular speed is high and interm olecular attractions cannot hold the molecules together, because they escape due to high speed.
Statement I : At Tc , liquid passes into gaseous state im perceptibly and continuously.
Statement II : At Tc, density of liquid and gaseous phase is equal.
Statement I : At Tc, there is no distinction between the gaseous state and liquid state and no second phase is formed irrespective of the pressure of the system.
Statement II : At the critical point, densities of a substance in gaseous and liquid states are equal.
Statement I : Reduced equation of state in terms of reduced temperature θ reduced volume and reduced pressure π can be applied to solid, gases and liquid.
Statement II: Equation is independent of p, V and T as well as independent of van der Waais’ constant a and b.
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-16) This section contains 3 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage I
Densities of O2(g) and O2(/) and also their average values are plotted against temperatures.
Q. The point of intersection is Tc. Based on above graph, critical volume of O2 is
Passage I
Densities of O2(g) and O2(/) and also their average values are plotted against temperatures.
Q. Van der Waais’ constant ‘b' of O2 gas is thus,
Passage II
When interm olecular forces in a real gas are taken zero, variation of pV with pressure p at a given temperature Is shown by following isotherm.
Q. Thus, critical volume Vc is
Passage II
When interm olecular forces in a real gas are taken zero, variation of pV with pressure p at a given temperature Is shown by following isotherm.
Q. If Tc = 100 K fo r this gas then, pc is
Passage III
Isotherms of carbon dioxide , I (at T1), II (at T2),
III (at T3) and IV (at T4) are given. Also, T1 < T2 < T3 < T4 .
Q. Consider the following facts.
I. On increasing volume at T1 or T2 there is sharp decrease in pressure indicating liquefaction.
II. At T3, there is no horizontal curve indicating no liquefaction. Thus, T3 is critical temperature.
III. Along CB or GF, there is liquefaction thus liquid and gaseous phases are present.
Select the correct facts.
Passage III
Isotherms of carbon dioxide , I (at T1), II (at T2),
III (at T3) and IV (at T4) are given. Also, T1 < T2 < T3 < T4 .
Q. Complete liquefaction at T1, and T2 takes place respectively at points.
|
748 tests
|




















