Test: Alkenes - NEET MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 11 - Test: Alkenes
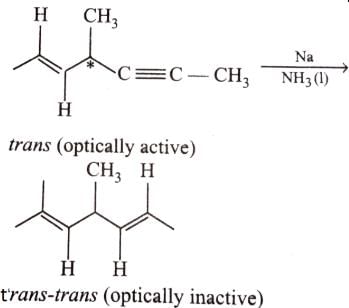
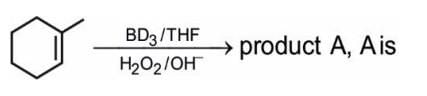
Which of the following compounds will lose optical activity after the reaction ?
Direction (Q, Nos. 13 - 16) This section is based on Statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Q.
Statement I : 2-butyne on reduction with Pd/CaCO3 gives c/s-2-butene.
Statement II : Hydrogenation proceed through adsorption mechanism.
Statement II : Hydrogenation proceed through adsorption mechanism.
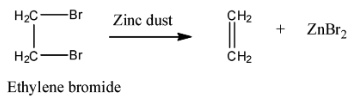
Statement I : 2, 3-dibromo butane with Zn-dust gives frans-2-butene as major product.
Statement II : frans-2-butene is more stable than c/s-2-butene.
Ethylene on reaction with bromine forms which among the following product?
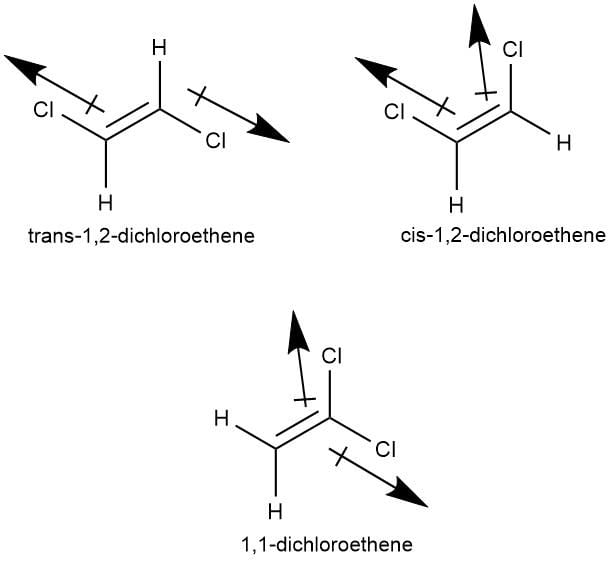
Out of the following compounds , which will be have a zero dipole moment.
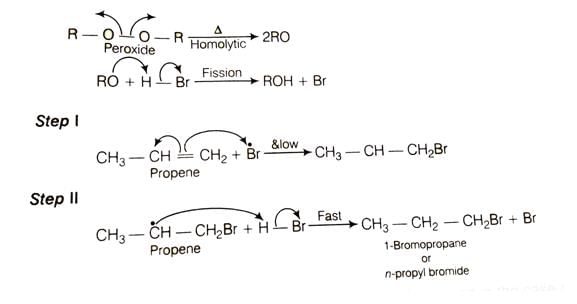
When propene reacts with HBr in the presence of peroxide, it gives rise to
C2H5Br + alc. KOH → _______ + KBr +H2O
Complete the above reaction by filling in the blank using the correct option given below.
Which one of the following compounds will burn with a yellow flame emitting a lot of black smoke?
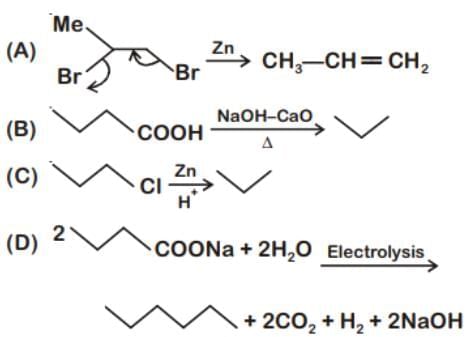
Which of the following reaction produce propane as a major product?
|
119 videos|338 docs|74 tests
|