Assertion & Reason Test: Equilibrium - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test - Assertion & Reason Test: Equilibrium
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): Increasing order of acidity of hydrogen halides is HF < HCI < HBr < HI
Reason (R): While comparing acids formed by the elements belonging to the same group of periodic table. H-A bond strength is a more important factor in determining acidity of an acid than the polar nature of the bond.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): The ionization of hydrogen sulphide in water is low in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R): Hydrogen sulphide is a weak acid.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Aqueous solution of ammonium carbonate is basic.
Reason (R) : Acidic/basic nature of a salt solution of a salt of weak acid and weak base depends on Ka and Kb value of the acid and the base forming it.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : In the dissociation of PCl5 at constant pressure and temperature, addition of helium at equilibrium increases the dissociation of PCl5.
Reason (R) : Helium removes Cl2 from the field of action.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): A solution containing a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate maintains a constant value of pH on addition of small amounts of acid or alkali.
Reason (R) : A solution containing a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts as a buffer solution around pH 4.75.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
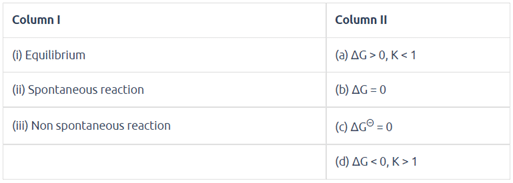
Assertion (A) : For any chemical reaction at a particular temperature, the equilibrium constant is fixed and is a characteristic property.
Reason (R) : Equilibrium constant is independent of temperature.
In the following question, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A): An aqueous solution of ammonium acetate can act as a buffer.
Reason (R) : Acetic acid is a weak acid and NH4OH is a weak base.
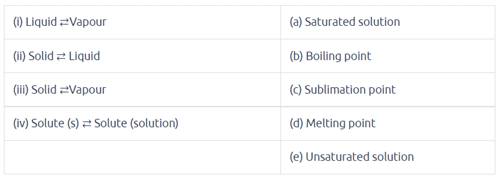
Match the following equilibria with the corresponding condition:
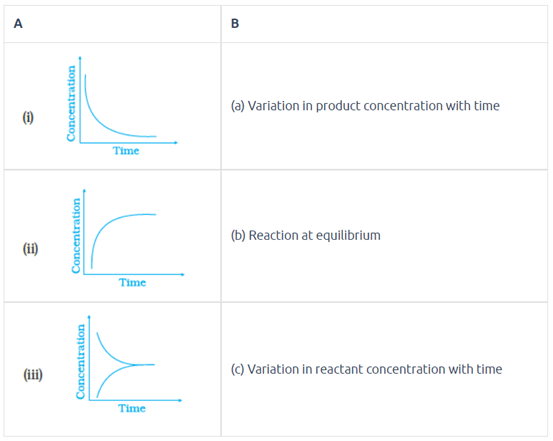
Match the following graphical variation with their description.