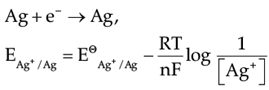Assertion & Reason Test: Electrochemistry - NEET MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Assertion & Reason Test: Electrochemistry
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Conductivity of an electrolyte increases with decrease in concentration.
Reason (R): Number of ions per unit volume decreases on dilution.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Λm for weak electrolytes shows a sharp increase when the electrolytic solution is diluted.
Reason (R): For weak electrolytes degree of dissociation increases with dilution of solution.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Electrolytic conduction increases with increase in temperature.
Reason (R): Increase in temperature cause the electronic movement more rapid
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Molar Conductivity of an ionic solution depends on temperature.
Reason (R): Molar Conductivity of an ionic solution depends on the concentration of electrolytes in the solution.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Ecell should have a positive value for the cell to function.
Reason (R): Ecathode < Eanode.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Cu is less reactive than hydrogen.
Reason (R): Eo Cu2+ / Cu is negative.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Copper sulphate can be stored in a zinc vessel.
Reason (R): Zinc is more reactive than copper.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): EAg+/Ag increases with increase in concentration of Ag+ ions.
Reason (R): EAg+/Ag has a positive value.
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as.
Assertion (A): Electrolysis of NaCl solution gives chlorine at anode instead of O2.
Reason (R): Formation of oxygen at anode requires over voltage.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion: The resistivity for a substance is its resistance when it is one meter long and its area of cross section is one square meter.
Reason: The SI units of resistivity is ohm metre (m).
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : On increasing dilution, the specific conductance keeps on increasing.
Reason : On increasing dilution, degree of ionisation of weak electrolyte increases and molality of ions also increases.
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Assertion : Galvanised iron does not rust.
Reason : Zinc has a more negative electrode potential than iron.
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|