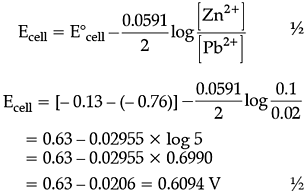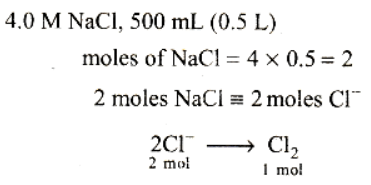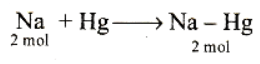Case Based Questions Test: Electrochemistry - NEET MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET - Case Based Questions Test: Electrochemistry
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. What is the conductivity of 0.02 M KCl solution?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The cell constant of a conductivity cell ________.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. What will happen to the conductivity of the cell with the dilution?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The cell constant is usually determined by measuring the resistance of the cell containing a solution whose conductivity is already known. For this purpose, we generally use KCl solutions whose conductivity is known accurately at various concentrations and at different temperatures. Consider the resistance of a conductivity cell filled with 0.1 M KCl solution is 200 Ohm. If the resistance of the same cell when filled with 0.02 M KCl solution is 420 Ohm. (Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl solution is 1.29 S m–1.)
The following questions are Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. SI unit for conductivity of a solution is
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A galvanic cell consists of a metallic zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M Zn(NO3)2 solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M Pb(NO3)2 solution.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. How will the cell be represented ?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:

Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A galvanic cell consists of a metallic zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M Zn(NO3)2 solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M Pb(NO3)2 solution.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. What product is obtained at cathode?
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
A galvanic cell consists of a metallic zinc plate immersed in 0.1 M Zn(NO3)2 solution and metallic plate of lead in 0.02 M Pb(NO3)2 solution.
The following questions are multiple choice questions.
Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. Which of the following statements is not correct about an inert electrode in a cell ?
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells.
In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): The mass of copper and silver, deposited on the cathode be same.
Reason (R): Copper and silver have different equivalent masses.
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells.
In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): At equilibrium condition Ecell = 0 or ΔrG = 0.
Reason (R): Ecell is zero when both electrodes of the cell are of the same metal.
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): In a galvanic cell, chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
Reason (R): Redox reactions provide the chemical energy to the cell.
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. Aqueous copper sulphate solution and aqueous silver nitrate solution are electrolysed by 1 ampere current for 10 minutes in separate electrolytic cells. In these questions, a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion (A): The negative sign in the expression EZn2+/Zn = – 0.76V means Zn2+ cannot be oxidised to Zn.
Reason (R): Zn is more reactive than hydrogen & Zn will oxidised, & H+ will get reduced.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. The total number of moles of chlorine gas evolved is
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few gram of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. If cathode is a Hg electrode, then the maximum weight of amalgam formed from this solution is
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
All chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/molecules are present in a few grams of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/molecular masses. To handle such large numbers conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCl is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer:
Q. In electrolysis of NaCl when Pt electrode is taken then H2 is liberated at cathode while with Hg cathode it forms sodium amalgam :-
|
9 docs|1259 tests
|