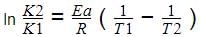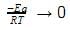Test: Temperature Dependence of a Reaction - NEET MCQ
10 Questions MCQ Test Chemistry Class 12 - Test: Temperature Dependence of a Reaction
How many times the rate of reaction increases at 200C for a reaction having the activation energies in the presence and absence of catalyst as 50 kJ/mol and 75 kJ/mol?
If Ef and Eb are the activation energies of the forward and reverse reactions and the reaction is known to be exothermic, then:
The ratio of the rate constant of a reaction at two temperatures differing by __________0C is called temperature coefficient of reaction.
The effect of temperature on reaction rate is given by
The activation energies of two reactions are given as Ea1= 40 J and Ea2= 80 J, then the relation between their rate constants can be written as:
The activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by
The rate constant, activation energy and Arrhenius parameter of a chemical reaction at 25°C are 3.0 x 10-4 s-1, 104.4 kJ mol-1 and 6.0 x 1014 s-1 respectively. The value of the rate constant at infinite temperature is is
The plot of ln k vs 1/T is a straight line. The slope of the graph is:
For a chemical reaction the rate constant is nearly doubled with the rise in temperature by
The reactions with low activation energy are
|
108 videos|286 docs|123 tests
|